Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: EULAR guidelines recommend a treat-to-target approach focusing on reducing inflammation to prevent joint damage, physical disability, and mortality.1 However, patients consider reduction in pain and fatigue, along with maintenance of physical function, and improvement in health-related quality of life (HRQoL) important areas for improvement with RA treatment.2 In the FINCH 2 study, filgotinib (FIL)—a potent, selective, oral small molecule Janus kinase 1 inhibitor—in combination with conventional synthetic (cs)DMARD therapy significantly improved the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients with an inadequate response to a biologic (b)DMARD compared with placebo (PBO).3 In addition, patients experienced significant improvements in HAQ-DI at week (W)12 and W24 with FIL 100 mg (p < 0.001, p = 0.003) or 200 mg (p < 0.001 for both) compared with PBO.3 The rate and magnitude of change in patient-reported outcomes (PROs) from FINCH 2 assessing pain, HRQoL and fatigue were evaluated.
Methods: Patients in this double-blind, randomized study (NCT02873936) received FIL 200 mg, FIL 100 mg, or PBO while continuing csDMARD therapy. PROs were collected prospectively on day 1 and at the W2, W4, W8, W12, W14, W16, W20, and W24 visits for assessment of pain (VAS pain scale]) and on day 1 and at W4, W12, and W24 for assessment of fatigue (FACIT-Fatigue) and HRQoL (SF-36). Changes from baseline for each PRO at each time point up to W24 were analyzed longitudinally using a mixed-effects model for repeated measures. P values for the difference between each FIL arm and PBO at each time point were calculated.
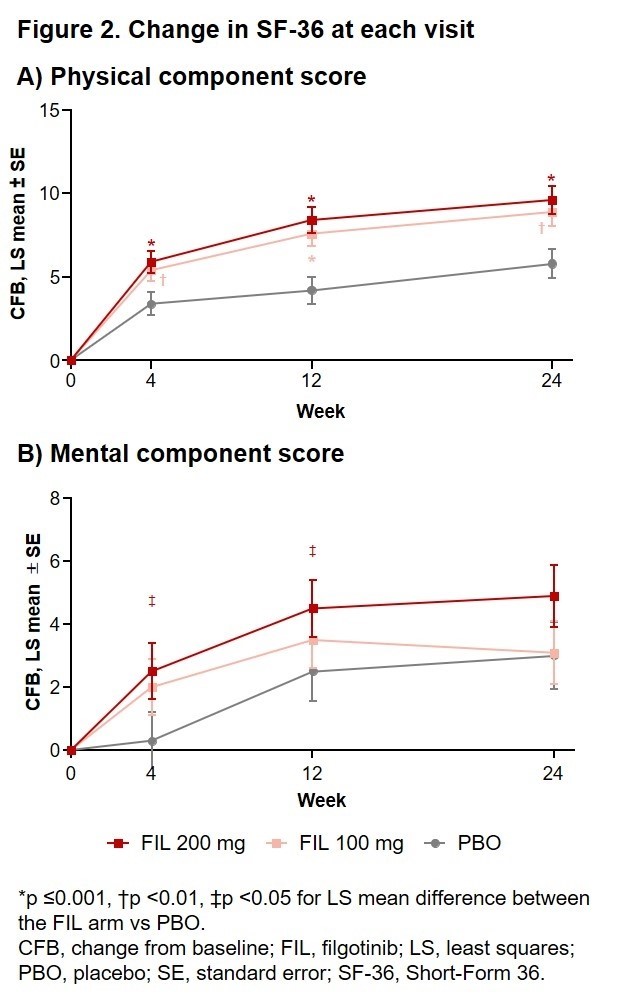
Results: Among the 448 patients randomized and treated (FIL 200 mg, n = 147; FIL 100 mg, n = 153; PBO, n = 148) 381 (85.0%) completed the study. Baseline mean (SD) VAS pain scale was 67 (21.0), SF-36 physical component summary (PCS) was 31.1 (7.89), SF-36 mental component summary (MCS) was 44.3 (11.6), and FACIT-Fatigue score was 24.4 (11.6); baseline values did not vary between treatment groups. Significantly greater improvements in VAS pain scores began at W2 and were maintained through W24 for patients who received either dose of FIL vs PBO (Fig 1A). FIL also significantly improved patients’ fatigue at W4, W12, and W24 compared with PBO for those receiving 200 mg doses, and at W4 and W12 for those receiving 100 mg doses (Fig 1B). HRQoL related to physical functioning (SF-36 PCS) was significantly enhanced at W4, W12, and W24 with both doses of FIL as compared with PBO (Fig 2A). Improvements to mental-health-related QoL (SF-36 MCS) were reported for FIL as early as W4 and maintained through W24, with statistically significant improvements at W4 and W12 for FIL 200 mg vs PBO (Fig 2B).
Conclusion: In a patient population with refractory disease that had inadequate response to prior bDMARDs and had significant disease at baseline, FIL treatment—coadministered with csDMARD therapy—was able to provide rapid and sustained improvements in key measures of pain, HRQoL, and fatigue as reported by patients.
References:
1) Smolen, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:960–77.
2) Fautrel, et al. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38:935–47.
3) Genovese, et al. JAMA. 2019;322(4):315–25.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Walker D, Takeuchi T, Bartok B, Rao S, Lee I, Besuyen R, Gottenberg J, Genovese M. Filgotinib Provided Rapid and Sustained Relief of Pain and Fatigue and Improved Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response to Biologic DMARDs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/filgotinib-provided-rapid-and-sustained-relief-of-pain-and-fatigue-and-improved-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-biologic-dmards/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/filgotinib-provided-rapid-and-sustained-relief-of-pain-and-fatigue-and-improved-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-biologic-dmards/