Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There is a critical need for measures to evaluate structural progression in the pediatric sacroiliac joint. We aimed to evaluate the precision and construct validity of the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) sacroiliac joint structural score (SSS) in children with suspected or confirmed juvenile spondyloarthritis.
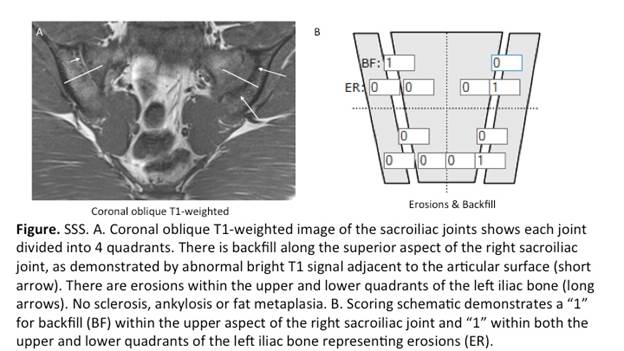
Methods: The SSS assesses a spectrum of structural lesions of the sacroiliac joint on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including fat metaplasia, erosion, backfill, and ankylosis on 5 consecutive slices through the cartilaginous part of the joint. These components are scored 0-20 (backfill and ankylosis) or 0-40 (fat metaplasia, erosion). We developed a pediatric training module that included a detailed description of each SSS component plus sclerosis (0-40), scoring methodology, and numerous examples (Figure). After reviewing the module, 5 readers (1 adult and 3 pediatric radiologists, 1 adult rheumatologist), blinded to clinical details except age, scored 30 studies that included semicoronal T1-weighted sequences. Inter-observer reliability was assessed using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). We assessed correlation (construct validity) between the mean SPARCC SSS developers’ scores and disease duration with Spearman correlation. Discrimination was tested by comparing the mean SPARCC SSS developers’ scores between children with and without limited mobility (retained lumbar lordosis, modified Schober <20 cm, or both).
Results: The SSS had face validity and was feasible to score in the 30 pediatric cases with suspected or confirmed spondyloarthritis. 21 (70%) were male and median age was 15.5 years (IQR 12.7-16.8). Median symptom duration was 30 months (IQR 2.3-74.7). The ICCs for the SSS components are shown in the Table. Erosion, backfill, and ankylosis had good reliability (>0.40) while reliability for fat metaplasia and sclerosis were low. 27 (18%), 106 (70%), 44 (29%), 83 (55%), and 13 (9%) of studies had a score>0 for fat metaplasia, erosion, backfill, sclerosis, and ankylosis, respectively. Correlations of symptom duration with each component of the SSS were low (r range -0.13-0.26). SSS components did not discriminate between children with and without limited back mobility.
Conclusion: The SSS was feasible to score and had acceptable reliability for pediatric sacroiliac joint MRI evaluation. Low ICC for fat metaplasia may reflect low frequency of this feature in pediatric SpA or difficulty in assessment since hematopoietic marrow can appear patchy. Low ICC for fat metaplasia and sclerosis highlight the need for additional calibration.
|
SSS Median (IQR), All readers |
All Readers
(N=5) ICC (95% CI) |
Pediatric Radiologists (N=3) ICC (95% CI) |
SPARCC developers (N=2) ICC (95% CI) |
|
| Fat metaplasia (0-40) |
0 (0-0) |
0.37 (0.21-0.56) |
0.46 (0.25, 0.67) |
0.89 (0.77-0.95) |
| Erosion (0-40) |
4 (0-10) |
0.47 (0.29-0.65) |
0.39 (0.15, 0.61) |
0.72 (0.48-0.86) |
| Backfill (0-20) |
0 (0-1) |
0.54 (0.38-0.71) |
0.36 (0.14, 0.58) |
0.82 (0.56-0.92) |
| Sclerosis (0-40) |
1 (0-5) |
0.39 (0.21-0.59) |
0.42 (0.17, 0.65) |
0.61 (0.08-0.83) |
| Ankylosis (0-20) |
0 (0-0) |
0.59 (0.43-0.74) |
0.46 (0.24, 0.66) |
0.72 (0.49-0.85) |
| Table. ICC for SSS components. ICC<0.40 is poor, 0.40≤ICC<0.75 is good and ICC≥0.75 is excellent. | ||||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chauvin NA, Maksymowych WP, Lambert RG, Jaremko J, Biko DM, Brandon TG, Paschke J, Weiss PF. Feasibility and Reliability of the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Sacroiliac Joint Structural Score for Children with Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/feasibility-and-reliability-of-the-spondyloarthritis-research-consortium-of-canada-sacroiliac-joint-structural-score-for-children-with-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/feasibility-and-reliability-of-the-spondyloarthritis-research-consortium-of-canada-sacroiliac-joint-structural-score-for-children-with-spondyloarthritis/