Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: Comparative Effectiveness, Biosimilars, Adherence & the Real World
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Data on biological survival, stratified for discontinuation reasons, and predictors that influence survival time have not been explored extensively. Therefore, we aim to explore real-world first and second-line biological survival and determine its influenceability in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients.
Methods: Data from the local pharmacy database and patient records of a university hospital in the Netherlands were used. RA patients who started a biological between 2000-2020 were included. Data on age, anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor (RF)-status, presence of erosions, gender, body mass index, time to first biological, biological survival time, use of csDMARDs and discontinuation reasons were collected.
Results: Of the included 318 patients, 39 (12%) started their first biological within 6 months after diagnosis. Median time between diagnosis and first biological prescription was 3.6 years (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.0-7.2). 50% of patients started their first biological after 2013. Median survival time of the first- and second-line biological was respectively 1.7 years (95%CI 1.3-2.2) and 0.8 years (95%CI 0.5-1.0)(p=0.0001)(figure 1A). Discontinuation reasons for the first-line biological were ineffectiveness (47%), adverse events (17%), remission (16%), pregnancy (30%), or patient preference (10%)(table 1). Multivariable Cox regression analyses, performed on the population that discontinued due to inefficacy or adverse events, showed that use of csDMARDs (HR=1.32, p< 0.001) positively influenced biological survival (figure 1B) RF positivity on the other hand (HR=0.82, p=0.03) negatively influenced biological survival. Biological survival in ACPA positive patients was longer compared to ACPA negative patients taking in to account discontinuation due to remission (HR=1.43, p=0.023). This indicates that ACPA positive patients were less likely to discontinue their biological due to remission. Second-line TNF-inhibitor survival did not differ between patients with a primary, < 6 months, and secondary, ≥6 months, non-response on the first-line TNF-inhibitor (HR=1.28, p=0.34).
Conclusion: Biological survival diminishes with the number of biologicals used. Biological survival is prolonged if patients use concomitant csDMARDs, and is shortened when patients are RF positive. ACPA positivity lowers the chance to discontinue biologicals due to remission.
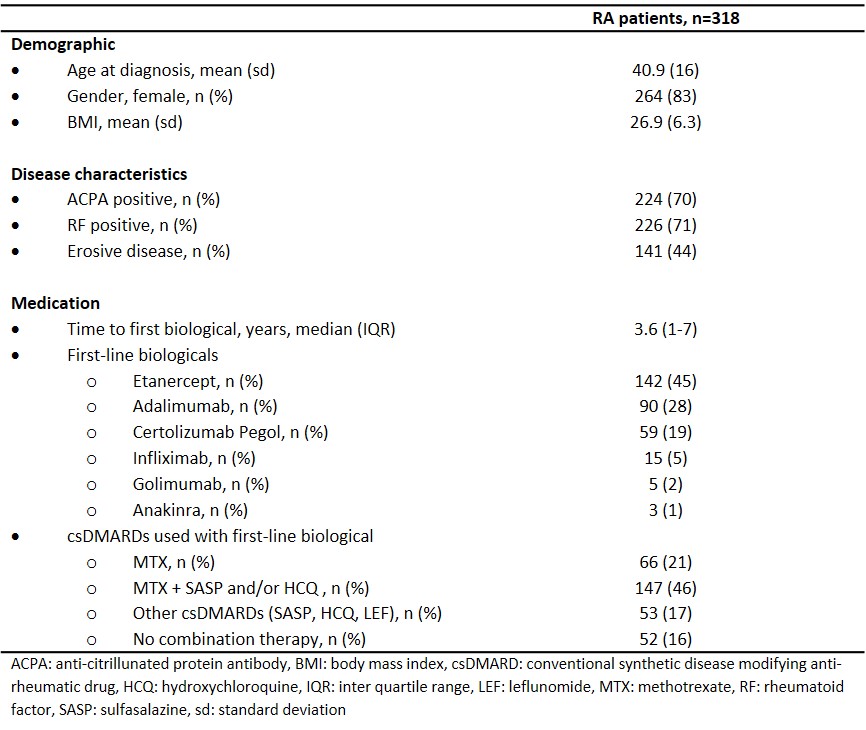 Table 1 Characteristics of patient population
Table 1 Characteristics of patient population
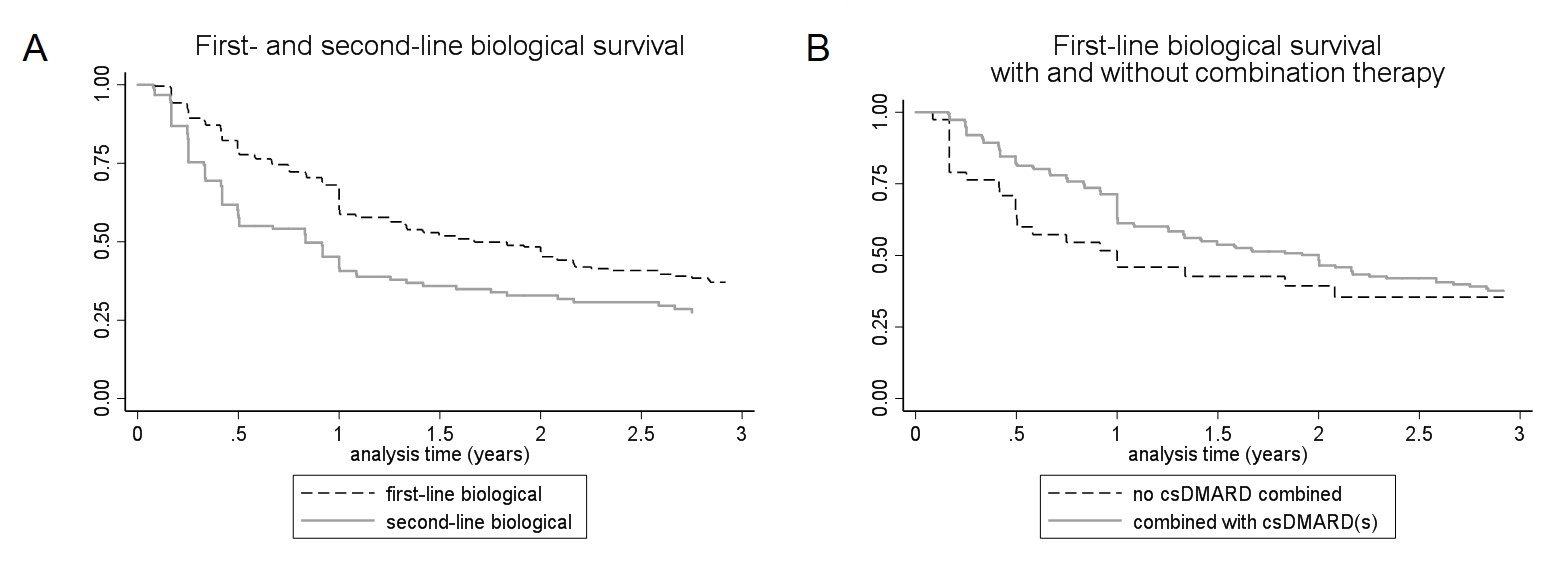 Figure 1 Kaplan Meier curves for biological survival. (A) Biological survival of first- and second-line biological in rheumatoid arthritis patients. (B) Biological survival with and without combination therapy with a csDMARD.
Figure 1 Kaplan Meier curves for biological survival. (A) Biological survival of first- and second-line biological in rheumatoid arthritis patients. (B) Biological survival with and without combination therapy with a csDMARD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Mulligen E, Ahmed S, Weel A, Hazes M, van der Helm - van Mil A, de Jong P. Factors That Influence Biological Survival in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results of a Real-world Cohort from the Netherlands [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-that-influence-biological-survival-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-of-a-real-world-cohort-from-the-netherlands/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-that-influence-biological-survival-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-of-a-real-world-cohort-from-the-netherlands/
