Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease resulting in increased mortality. manifestations. involvement. The National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) in Taiwan provided nationwide, population-based claim data that can be linked to death registry to assess risk factors and cause of death in patients with RA.
The aim of the study was to investigate factors associated with 5-year mortality in patients with RA starting their first biological or target synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs).
Methods: Using the 2000–2020 NHIRD, we identified 12,612 RA patients who initiated their first b/tsDMARDs, including tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi), tocilizumab, abatacept, rituximab and tsDMARD. A multivariable Cox regression model was used to estimate the adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) with 95% confidence interval (CIs) for the association of the risk of 5-year mortality with the use of 5 categories of b/tsDMARDs (TNFi as a reference) after adjustment of potential confounders including age, sex, urbanization level of residence, income, comorbidities and medications.
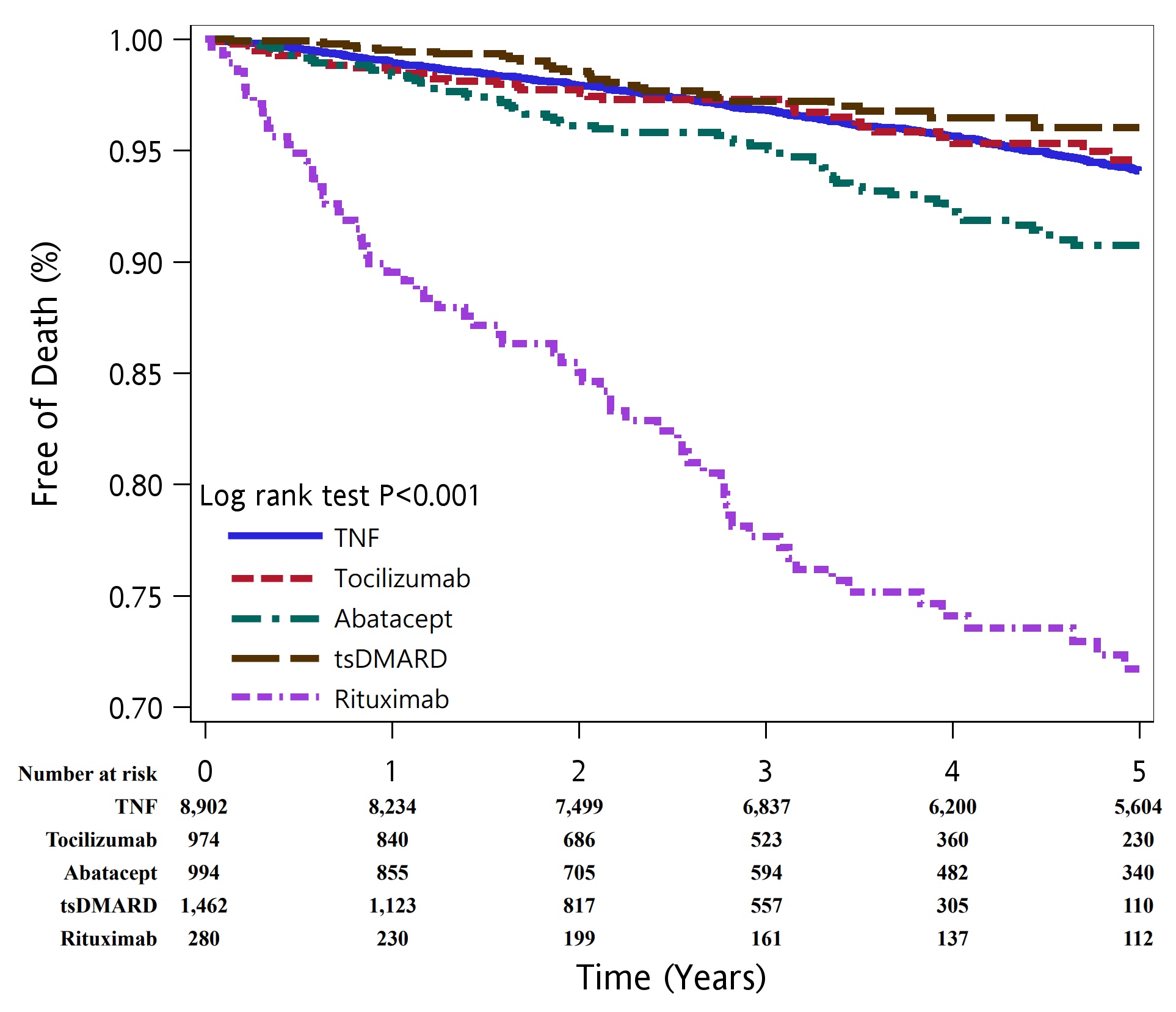
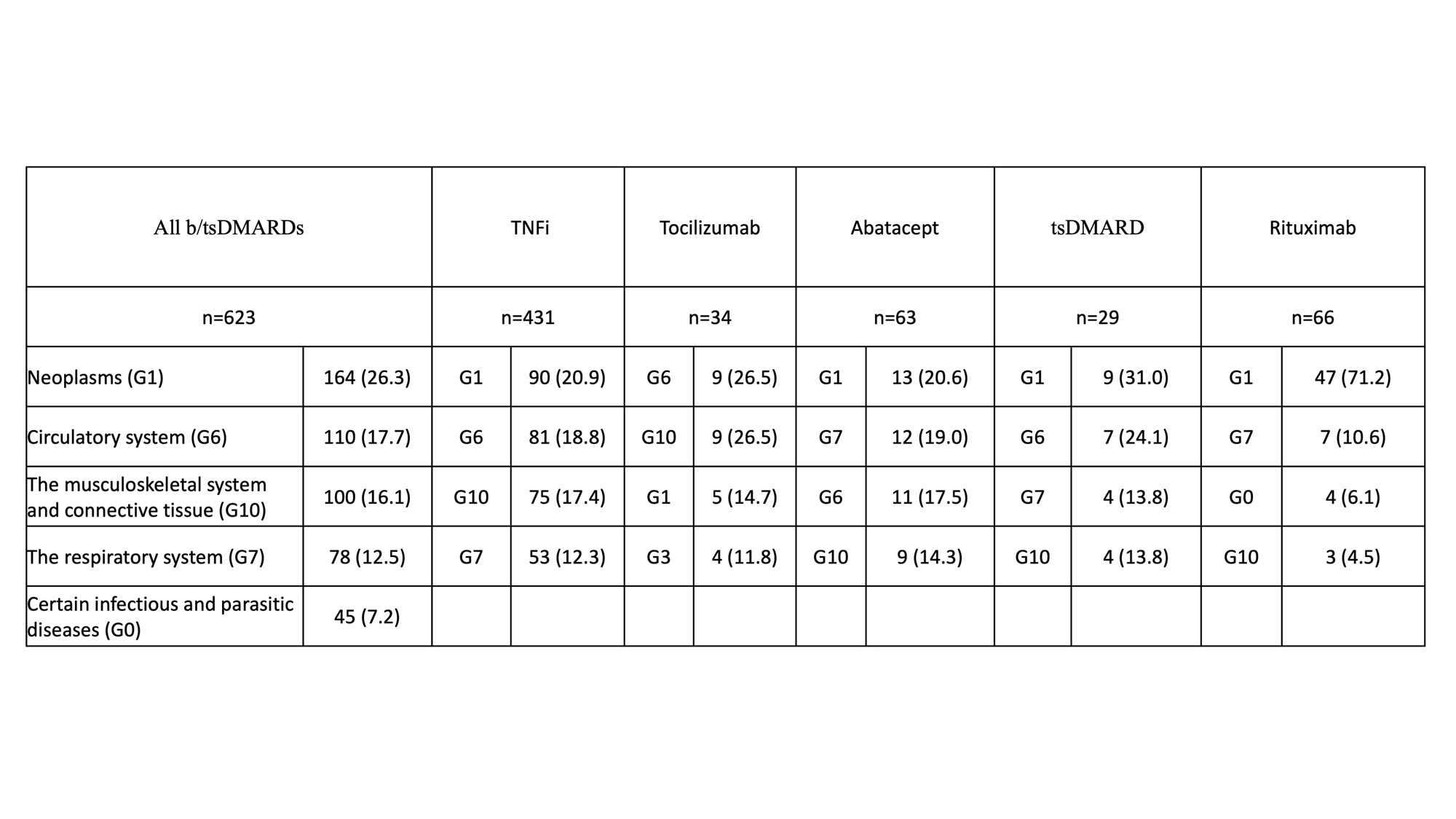
Results: We included 8,902 TNFi-treated patients, 974 tocilizumab-treated patients, 994 abatacept-treated patients, 1,462 tsDMARD-treated patients and 280 rituximab-treated patients. Figure 1 showed the 5-year survival curve in patients treated with b/tsDMARDs categorized into 5 groups based on mechanism of actions. Compared with TNFi-treated patients, multivariable Cox-regression analyses showed that 5-year mortality risk was higher in rituximab-treated patients (aHR, 3.47; 95% CI, 2.48–4.85) and lower in JAKi-treated patients (aHR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.44–0.96). Other significant predictors for 5-year mortality included male gender (aHR, 1.90; 95% CI, 1.61–2.24), age (aHR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.07–1.09), low income (aHR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.21–1.78), comorbidities within one year before the index date (heart failure: aHR, 1.72; 95% CI, 1.14–2.59; diabetes mellitus: aHR, 1.50; 95% CI, 1.22–1.84; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: aHR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.02–1.63; renal disease: aHR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.02–1.85), a history of sepsis within prior one year (aHR, 2.61; 95% CI, 1.73–3.92), and use of medications within prior one year (methotrexate: aHR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.51–0.83; prednisolone dose > 5mg/day: aHR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.33–2.70). Table 1 showed the top 4 causes of death in all and each group of b/tsDMARD-treated patients.
Conclusion: This study showed that among patients with RA initiating b/tsDMARDs, the 5-year mortality risk was higher in rituximab-treated patients and lower in tsDMARD-treated patients compared with TNFi-treated patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen H. Factors Associated with 5-year Mortality in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Initiating Their First Biological or Target Synthetic DMARDs: A Nationwide, Population-based Cohort Study of 12,612 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-5-year-mortality-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-initiating-their-first-biological-or-target-synthetic-dmards-a-nationwide-population-based-cohort-study-of-12612-patie/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-5-year-mortality-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-initiating-their-first-biological-or-target-synthetic-dmards-a-nationwide-population-based-cohort-study-of-12612-patie/