Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is an inflammatory immune-mediated musculoskeletal skin disease that affects approximately 25% of psoriasis patients causing progressive disability. As a heterogeneous disease, with sometimes subtle manifestation, accurate assessment of PsA is difficult. As such, there is a need for early detection diagnostic tests for PsA. A liquid chromatography – high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) general untargeted metabolomics analysis following solid phase microextraction (SPME) was applied to serum samples collected from patients with PsA and psoriasis without PsA (PsC), to perform discovery analysis to investigate potential diagnostic markers of PsA.
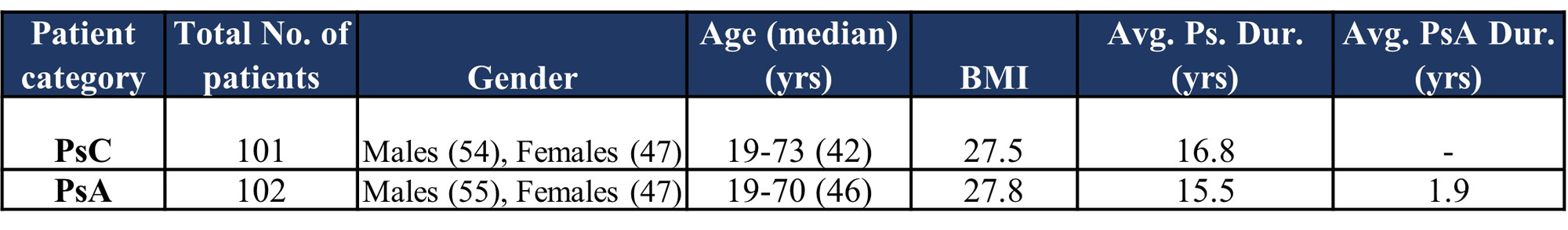
Methods: Serum samples were obtained from a biobank of carefully phenotyped PsC (n=100) and PsA (n = 101) patients who had no history of cancer, had no active infection nor received previous treatment with biologics. Novel high throughput technique – SPME – was used to prepare all samples simultaneously followed by LC-HRMS analysis.
Data (pre)processing and feature identification was performed using 2 workflows – Compound Discoverer 3.3 and an independent Rscript. Supervised multivariate analysis and various Machine Learning (ML) algorithms including logitboost, adaptive boosting, support vector machine (SVM), logistic regression, and random forest (RF), were used for predictive feature analysis. Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic (AUROC) was then used to evaluate the performance of these features. Only features in models with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.85 or greater were considered as candidate biomarkers.
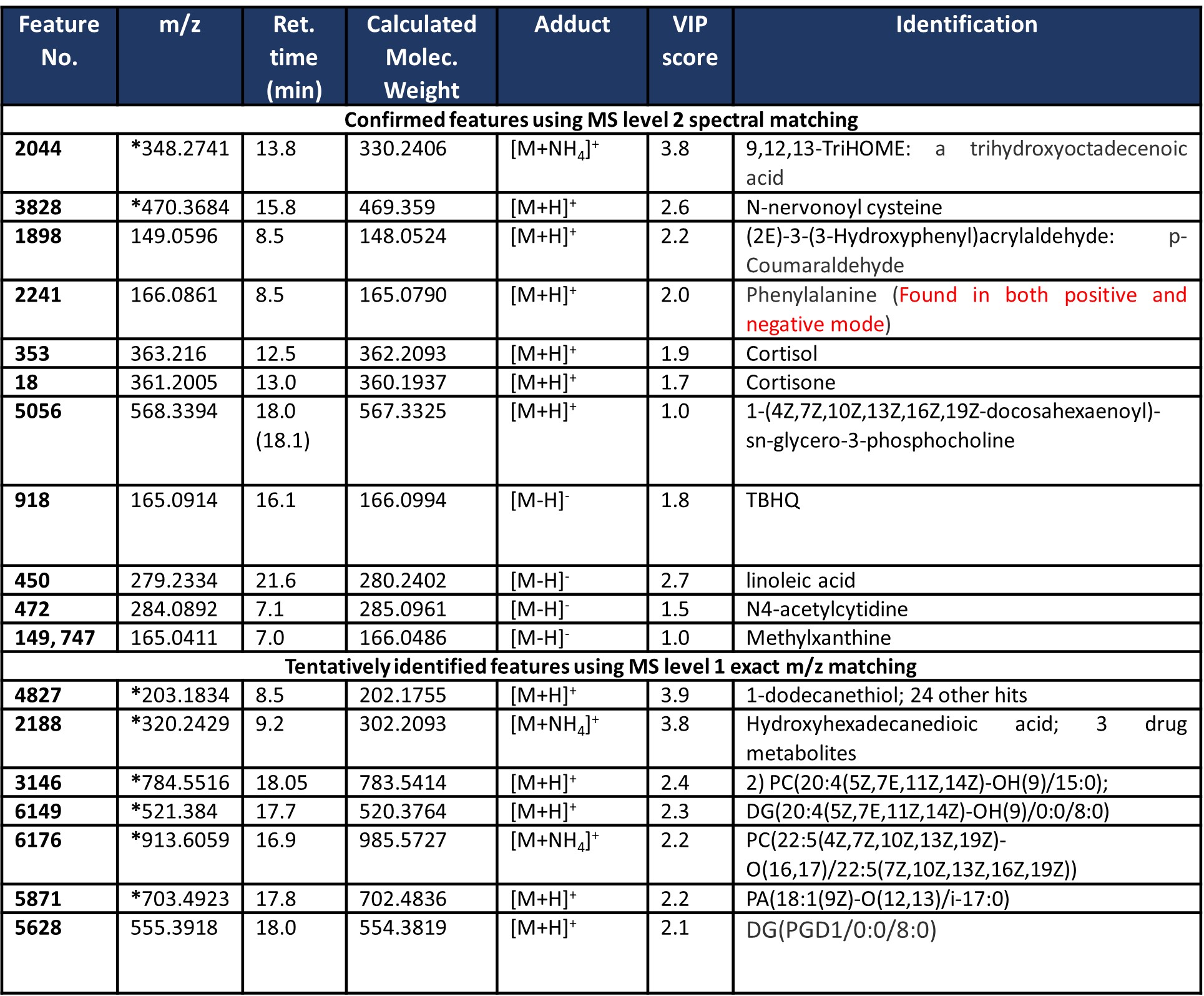
Results: Table 1 provides the demographic and disease characteristics of the included subjects. Table 2 provides a summary of the results from predictive feature analyses. A minimum of ten features and a maximum of eighty features from the adaptive boost models produced an AUC of 0.896 and 0.921 respectively. All other models with feature numbers ranging between twenty to eighty produced AUC between 0.891 and 0.915. Several small molecules could be validated via MS Level 2 spectral database matching. Trihydroxyoctadecenoic acid and N-nervonoyl cysteine contributed significantly to the multivariate supervised analysis and performed well according to high AUROC scores. Interestingly, lipids such as docosahexanoyl-sn-gylcerophosphocholine were identified via MS level 2, but there were several other features that were found to be significant that could only be tentatively identified as glycero-lipids and fatty acids. Results from this metabolomics workflow were integrated with top-down multi-omics data for the same patients. Data integration revealed that confirmed and tentatively identified features like glycero- and phospholipids overlapped differentially expressed pathways from the transcriptome.
Conclusion: SPME-LC-HRMS based untargeted metabolomic analyses have identified small molecules (lipids) with excellent discriminative ability between PsA and PsC. Thus, the development of quantitative targeted assays for these metabolites and subsequent validation may provide diagnostic markers for PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Looby N, Kotlyar M, Pastrello C, Ganatra D, Kulasingam V, Jurisica I, Chandran V. Exploring the Serum Metabolome for Potential Diagnostic Markers of Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-serum-metabolome-for-potential-diagnostic-markers-of-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-serum-metabolome-for-potential-diagnostic-markers-of-psoriatic-arthritis/