Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The use of biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDS) is the current standard of care for severe diseases like psoriatic arthritis (PsA) which affects approximately 25% of psoriasis patients. However, randomized controlled trials demonstrate a difference in the ACR20 response rate of only 20-30% in patients receiving treatment vs placebo. Thus, choosing the appropriate type of bDMARDS to administer targeted therapy of PsA remains challenging. Predictive biomarkers may help facilitate precision medicine. The objective of this study was to apply a global metabolomics approach to identify small molecules associated with treatment efficacy in PsA patients treated with either tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) or Interleukin 17A inhibitors (IL-17Ai).
Methods: Serum samples were obtained from PsA patients satisfying the CASPAR criteria. Patients were treated with either TNFi (n = 20; infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, certolizumab or golimumab) or IL-17Ai (n = 20; secukinumab or ixekizumab). Patients were evaluated at baseline and 3 months post-therapy and determined as responders or non-responders based on the Disease Activity Index for PsA (DAPSA) wherein responders had DAPSA < 14. Solid phase microextraction (SPME), a novel high throughput technique was used to prepare all samples simultaneously followed by liquid chromatography – high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) analysis. Data processing and feature identification was performed using 2 platforms – Metaboanalyst R and Compound Discoverer 3.3 respectively. Various Machine Learning (ML) algorithms including Naïve-Bayes (NB), logit boost, adaptive boosting, linear regression, support vector machine (SVM), linear discriminant analysis (LDA), and random forest (RF), was used for predictive feature analysis. Only features in models with an area under the curve of 0.7 or greater were considered as candidate metabolite markers.
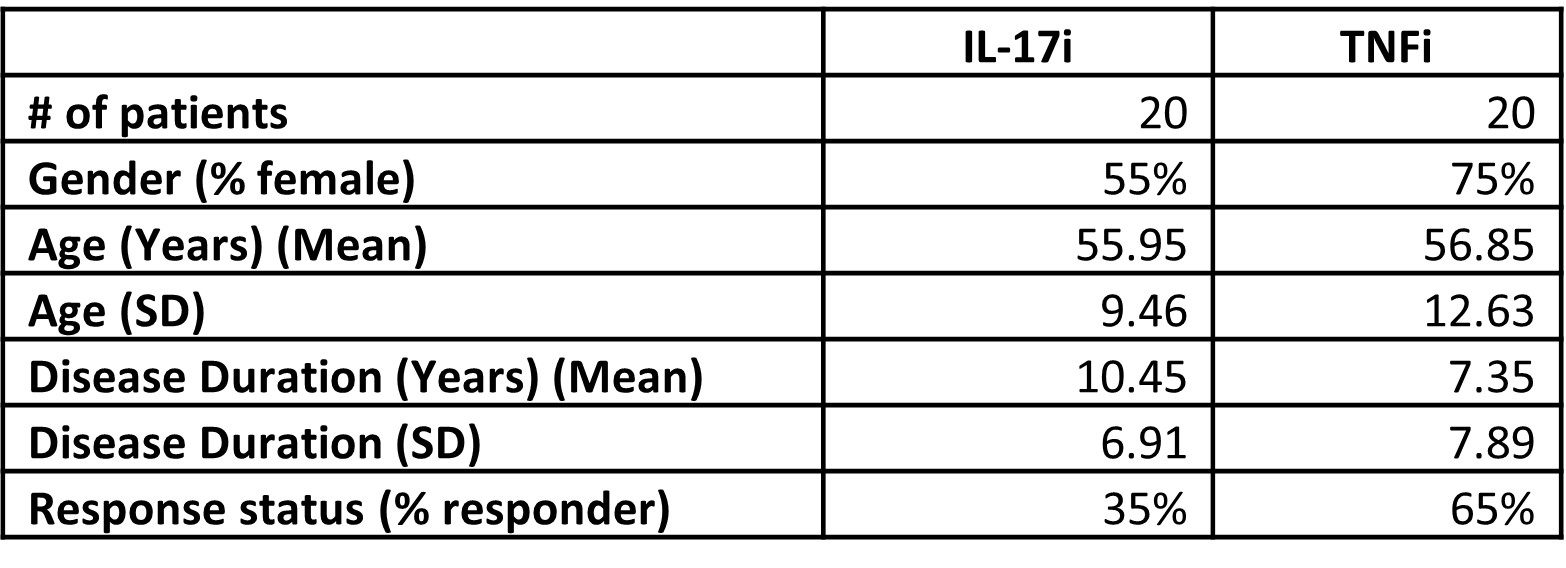
Results: Table 1 provides the demographic and disease characteristics of the patients at baseline. 7/20 (35%) of patients treated with TNFi and 13/20 (65%) of patients treated with IL17Ai were responders. As little as 5 features from an SVM model produced an AUROC value of 0.732, while as many as 20 features using NB produced a value of 0.812 between responders and non-responders for both treatments combined at baseline. When considering a single treatment option (TNFi or IL-17Ai only), less than 5 features were required to produce AUROC scores of > 0.9 in both positive and negative mode data. Several exposome-related metabolites were identified via MS level 2 spectral matching including cotinine, adipic acid, toluic acid, monobutylphthalate and tridecylic acid. Glycochenodeoxycholic acid, an endogenous metabolite was also identified.
Conclusion: The identification of cotinine – a metabolite found in tobacco, could indicate that a risk behaviour such as smoking, or an exposure to second hand smoke as well as glycochenodeoxycholic acid – a metabolite that stimulates the mitochondrial pathway to cell death, may indicate that multiple mechanisms of action affects response to treatment. Validation of these results is required.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koussiouris J, Looby N, Kotlyar M, Kulasingam V, Jurisica I, Mathew A, Rahman P, Chandran V. Exploring Metabolite Markers Associated with Treatment Response of Biologic Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-metabolite-markers-associated-with-treatment-response-of-biologic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-metabolite-markers-associated-with-treatment-response-of-biologic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/