Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: We recently described that methotrexate (MTX) could exert its immunomodulatory effect through the induction of A20 expression , a protein that negatively regulates NFkB signalling induced by TLR ligands or TNF stimulation. On the other hand, different single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in TNFAIP3, the gene that codes the A20 protein, have been associated with an increased risk to develop rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It is likely that these variants could be associated with lower expression and activity of A20.This study aims to determine whether those SNPs in TNFAIP3, associated with increased risk of RA, are useful for predicting MTX response.
Methods: We analysed data from PEARL study (Princesa Early Arthritis Register Longitudinal study; CEIC approval registry no 518; March 2011) in which sociodemographic, clinical, analytical, therapeutic variables and biological samples are collect by protocol in 5 structured visits.
We assessed clinical response (no, moderate and good) at six months in those patients who started MTX at the baseline and maintained this drug in monotherapy, by using the EULAR and HUPI response criteria. The following SNPs in TNFAIP3, rs600144, rs11970361, rs582757, rs11970411, and rs17780429, were genotyped using TaqMan probes (ThermoFisher Scientific; part number:C_7701163_10, C_238210_20, C_8300291_10, C_32241642_10, C_34723620_10, respectively).
To determine whether there was an association between the response to MTX and the SNPs, an order logistic regression model was performed using the ologit command of Stata 14.1. The model was adjusted for age, sex, MTX dose (median 15 mg; interquartile range 12.5 – 20) and disease activity at baseline.
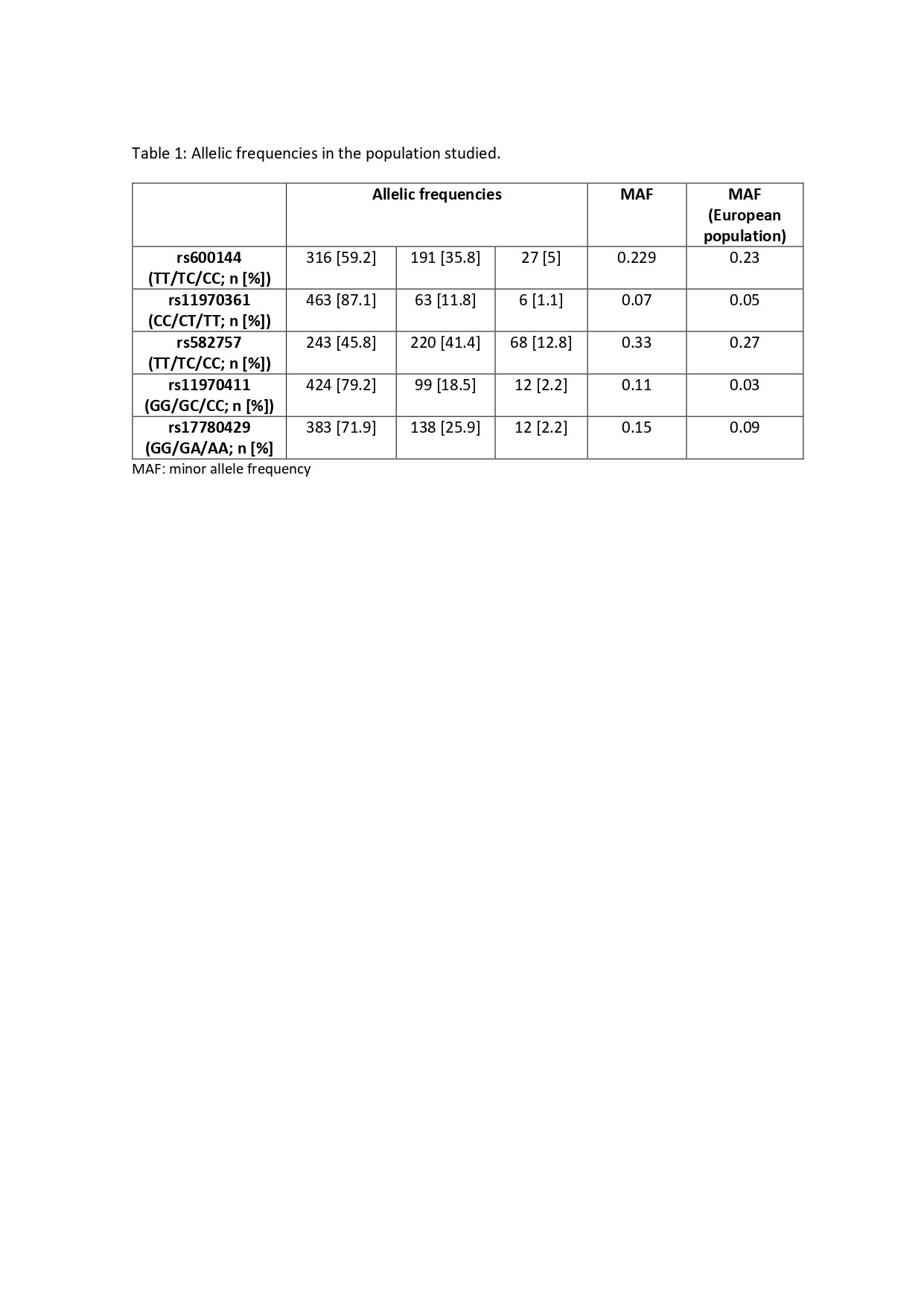
Results: The whole population studied comprised 539 patients (79% female, mean age at disease onset 55 years; RA and UA) whose allelic frequencies of the SNPs in TNFAIP3 are shown in Table 1. The minor allele (A) frequency (MAF) of rs17780429 was significantly lower in RA than in UA (13.4% vs 42.1%; p=0.018). In addition, the MAF (C) of rs600144 was lower in ACPA+ than in negatives patients (19.9% vs 38.6%; p=0.017). In the 235 patients who fulfilled the study criteria for response to MTX, it was observed that the presence of the T allele of rs11970361 showed a trend to lower response, assessed either with the EULAR or HUPI criteria, although statistical significance was not achieved, likely due to the low frequency of this allele. By contrast, carriers of the G allele of rs582757 were associated with lower HUPI response in an additive manner, reaching statistical significance for homozygous GG cases (OR 0.39 [0.16 to 0.91]; p=0.029).
Conclusion: Genetic variants of TNFAIP3 could explain phenotypic differences in early arthritis patients and might help to predict response to MTX. The low variability in the population of some of these SNPs would make difficult their implementation in clinical practice.
This study has been possible thanks to ISCIII grants PI18/00371 and PI21/0526, and unrestricted grant from Gebro Pharma.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Triguero A, BALDIVIESO ACHA J, Roy Vallejo E, Quiroga-Colina P, Llorente Cubas I, Garcia-Vicuña R, Puig kröger a, Gonzalez I. Exploratory Study of the Usefulness of TNFAIP3 Genetic Variants in Predicting Response to Methotrexate in Early Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploratory-study-of-the-usefulness-of-tnfaip3-genetic-variants-in-predicting-response-to-methotrexate-in-early-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploratory-study-of-the-usefulness-of-tnfaip3-genetic-variants-in-predicting-response-to-methotrexate-in-early-arthritis-patients/