Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: 4M114 ACR/ARHP Abstract: Orthopedics, Low Back Pain & Rehabilitation (1952–1957)
Session Type: ACR/ARHP Combined Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Tendinopathy is an inflammatory and degenerative disorder caused by injuries and overuse. The Wnt pathway is upregulated in chronic tendinopathy and involved in inflammation, tenocyte differentiation, and fibrosis. SM04755, a novel, topical, small molecule Wnt pathway inhibitor, has previously been shown to inhibit inflammation, reduce fibrosis, and increase tenocyte differentiation (Deshmukh et al., Arthritis Rheumatol, 2016). Two further experiments are presented: 1. SM04755 treatment in an acute dose-response tendinopathy model and 2. SM04755 treatment in a repeat injury/delayed treatment (RIDT) tendinopathy model. These models simulate acute and acute-on-chronic clinical tendinopathy, respectively.
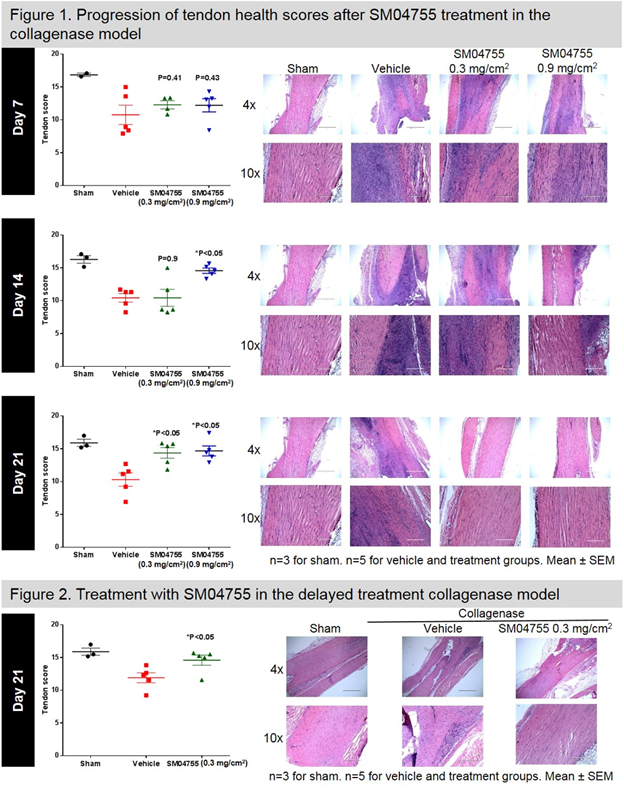
Methods: SM04755 was assessed in rodent Achilles tendinopathy models, induced by intra-tendon collagenase injection (500 µg). In the acute dose response model, a single injection of collagenase or sham per animal on Day -4 was followed on Day 0 by daily topical vehicle, or 0.3 mg/cm2 or 0.9 mg/cm2 SM04755. Achilles tendons were harvested on Days 7, 14, and 21. In the RIDT model, collagenase injections were given at Days -28 and -14, followed on Day 0 with daily topical vehicle or 0.3 mg/cm2 SM04755. Achilles tendons were harvested on Days 7, 14, 21, and 28. Blinded histology analyses scored tendon health based on linearity, tendon cell shape, tendon cell density, inflammation, and hemorrhage (range 5-20). Statistical analyses: one-way ANOVA for multiple group comparisons, t-tests for two group comparisons.
Results: In the acute dose-response model, SM04755 improved tendon health from baseline compared to vehicle as assessed by tendon histology scores. Vehicle scores were 10.77 [±1.46] at Day 7, 10.44 [±0.66] at Day 14, and 10.31 [±1.02] at Day 21. SM04755 (0.3 mg/cm2) scores were 12.30 [±0.62] at Day 7 (NS), 10.45 [±1.29] at Day 14 (NS), and 14.37 [±0.82] at Day 21 (P<0.05). SM04755 (0.9 mg/cm2) scores were 12.22 [±1.02] at Day 7 (NS), 14.57 [±0.41] at Day 14 (P<0.05), and 14.67 [±0.76] at Day 21 (P<0.05) (Fig. 1). In the RIDT model, vehicle scores were 12.35 [±0.30] at Day 7, 10.09 [±0.76] at Day 14, 11.92 [±0.77] at Day 21, and 13.72 [±0.35] at Day 28. SM04755 (0.3 mg/cm2) scores were 11.86 [±2.13] at Day 7 (NS), 9.44 [±0.48] at Day 14 (NS), 14.61 [±0.77] at Day 21 (P<0.05), and 14.93 [±0.46] at Day 28 (NS) (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: In the acute dose-response model, SM04755 (0.3 mg/cm2) showed statistically significant improvements in tendon scores compared to vehicle at Day 21. The 0.9 mg/cm2 dose achieved significance at Days 14 and 21, indicating faster response at higher SM04755 dose. In the RIDT model, SM04755 0.3 mg/cm2 dose promoted accelerated tendon healing compared to vehicle. Therefore, SM04755 demonstrated accelerated improvement of tendon histology in acute and RIDT models compared to vehicle and has potential as a tendinopathy therapy. Clinical studies are planned.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deshmukh V, Seo T, Yazici Y. Experimental Tendinopathy Treatment with SM04755, a Topical Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/experimental-tendinopathy-treatment-with-sm04755-a-topical-small-molecule-inhibitor-of-the-wnt-pathway/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/experimental-tendinopathy-treatment-with-sm04755-a-topical-small-molecule-inhibitor-of-the-wnt-pathway/