Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Exhaustion can occur after prolonged activation of T cells limiting their immunosurveillance function leading to cancer emergence. Among the exhaustion markers expressed on T cells are PD-1 and TIGIT. While exhaustion has been extensively studied in cancer where it is the target of immune checkpoint inhibitors it is less investigated in the field of Immune mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs). In an era where PD-1 agonists like peresolimab are trialed in rheumatoid arthritis, better understanding of the role of exhaustion in IMIDs is crucial. This work aims to assess the level of circulating exhausted CD4 and CD8 T cells in patients with IMID and prospectively assess how these cell subsets at baseline might impact response to anti-TNF.
Methods: We have included 25 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 22 patients with spondyloarthritis (SPA) and 20 patients with Sjogren disease (SjD). T-cell exhaustion has been assessed by flow-cytometry on fresh whole blood. Exhausted T cells were defined as double positive PD-1+ TIGIT+ among circulating CD8 and CD4 T cells. Patients with RA and SA were evaluated at baseline and 3 months after anti-TNF initiation. IFNα2a, IFN-β, IFNγ, IFNλ1, and IP-10 were measured in sera in all the patients at baseline using MSD technology. Response to anti-TNF treatment was defined by treatment maintenance on drug at 12 months post initiation. Patients who switched treatment for side effects were excluded. Associations between exhausted T-cells and categorical or continuous variables were performed by logistic regression/Fisher exact test or Mann–Whitney test, respectively.
Results: The median level of exhausted CD4 T cells (T4ex) was higher in SjD (15,4%) compared to RA (11,5%), SPA (9,26%) and to healthy volunteers. Median CD8+ exhausted T cells (T8ex) were higher in SjD patients (23.20%) and RA patients (24.00%) compared to HV (18%) and SPA patients (16,2%). There was no association between T4ex or T8ex and disease activity scores or demographic variables. Interestingly, in SjD, T4ex were positively associated to serum IgG levels (r=0.698, p< 0.001), IFN-γ levels (R=0.635, p=0.017) and IP-10 levels (R=0.612, p=0.005).
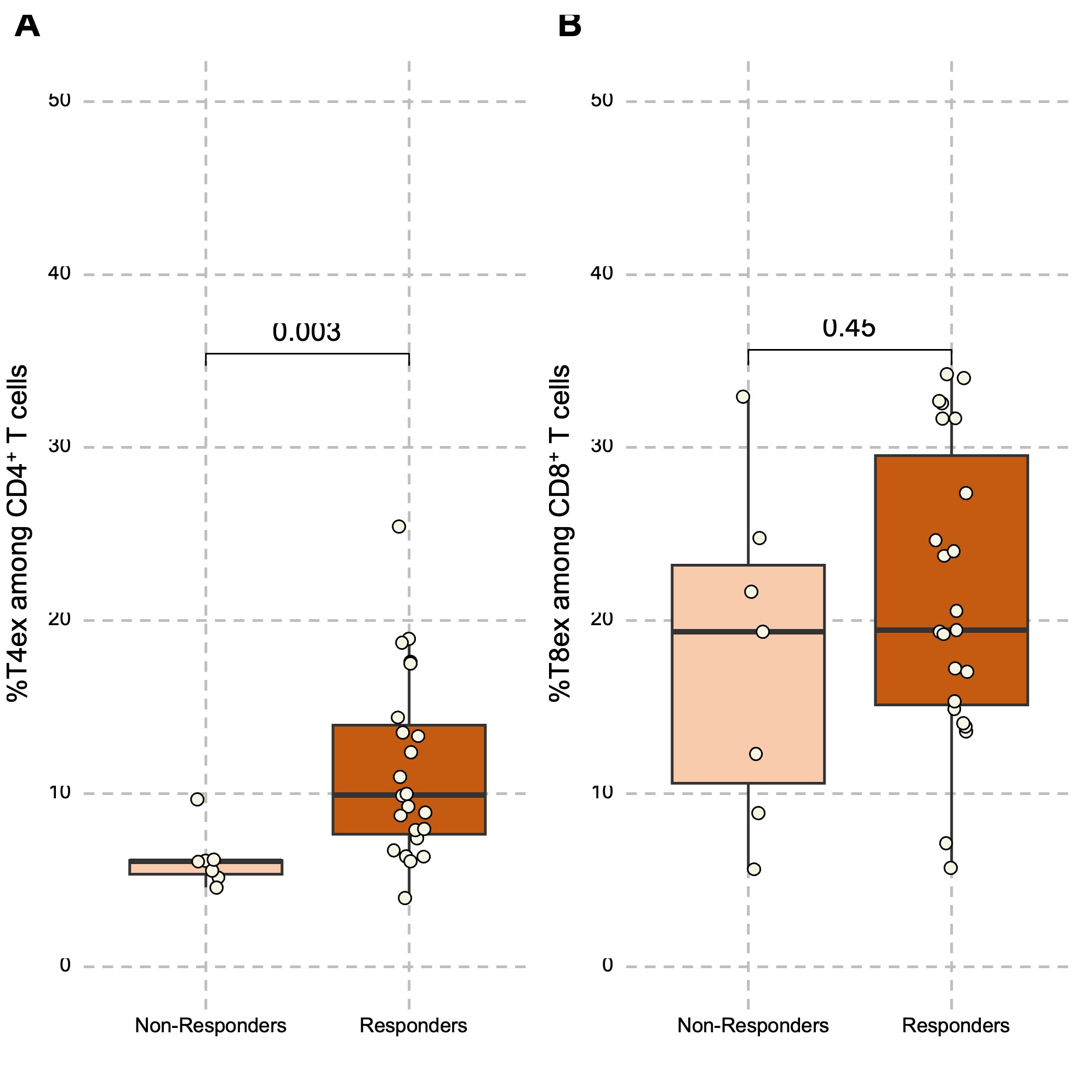
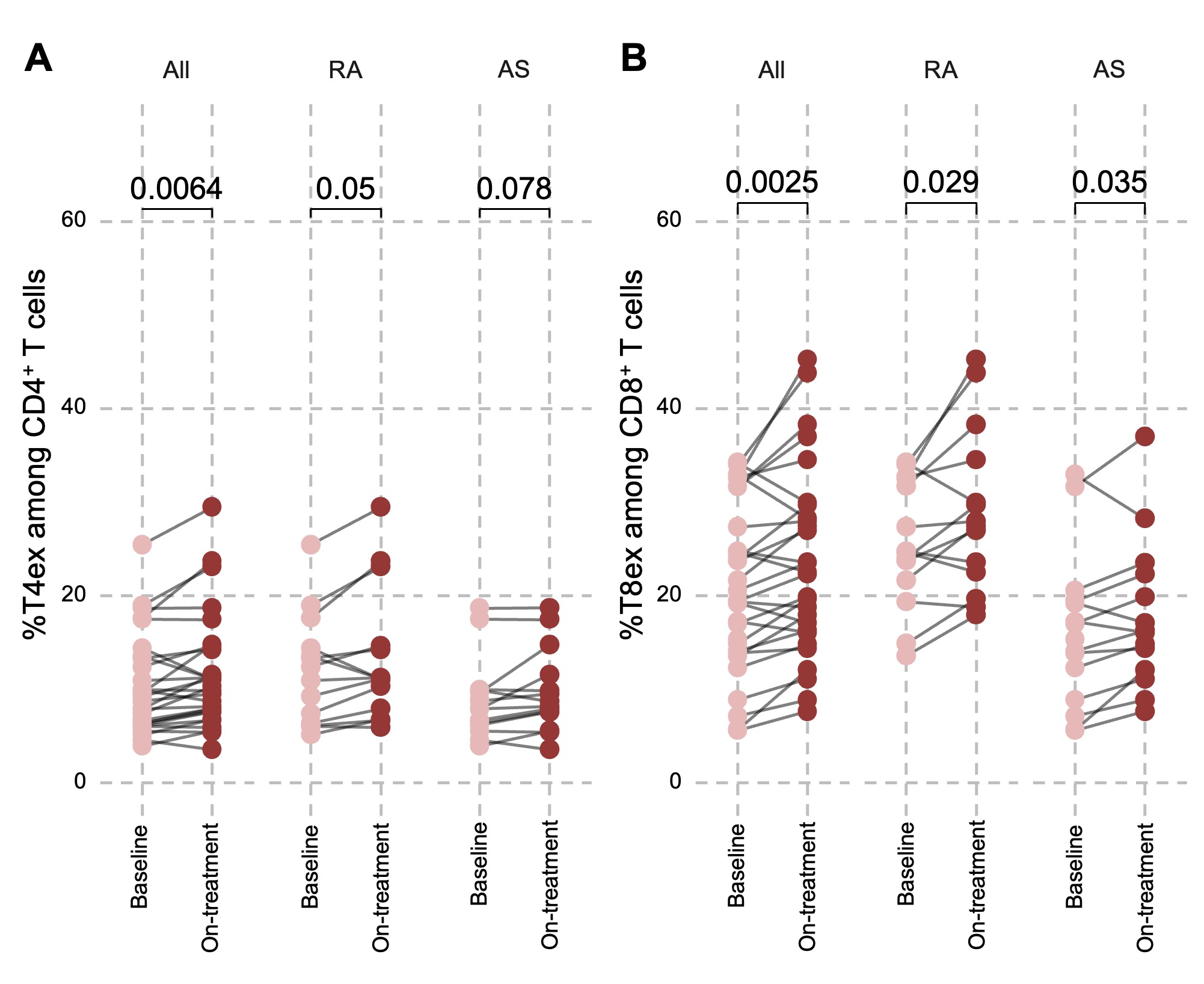
At baseline before treatment, T4ex among CD4+ T cells were significantly higher in anti-TNF-α responders vs non responders (median: 9.89% [7.64;13.95] vs. 6.07% [5.34;6.14] respectively, p=0.003) (Figure 1). Finally, we observed a significant increase of exhausted CD8+ and CD4+ T cells 3 months after anti-TNF treatment in RA and SPA treatment compared to baseline (figure 2). This increase was not significantly different between anti-TNF responders and non-responders.
Conclusion: Exhausted T-cells are differentially enriched between IMIDs. Sjögren patients showed the most consistent increased in T4ex and T8ex,T4ex being associated with IgG levels, IFNg and IP-10. High baseline levels of T4ex are associated with better response to anti-TNF. After 3 months of anti-TNF treatment, all RA and SPA patients display an increase of T4ex and T8ex regardless their response to treatment. Further work is needed to evaluate if a high level of T4ex could be a biomarker predictive of response to agonists of TIGIT or of PD1 like peresolimab.
A) comparison of the baseline percentage of T4ex among CD4 Tcells between anti-TNF responders and non-responders at 3 months in RA and SPA patients
B) comparison of the baseline percentage of T8ex among CD8 Tcells between anti-TNF responders and non-responders at 3 months in RA and SPA patients
T4ex : Exhausted CD4+ T cells (PD_1+ TIGIT+). T8ex : Exhausted CD8+ T cells (PD_1+ TIGIT+).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bitoun S, Naigeon M, Roulleaux- Dugage M, De Oliveira C, Berthot C, Mariette X, Nocturne G, Chaput-Gras N. Exhausted T-cells Are Increased in Autoimmune Diseases and Predict Response to Anti-TNF in RA and SPA Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exhausted-t-cells-are-increased-in-autoimmune-diseases-and-predict-response-to-anti-tnf-in-ra-and-spa-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exhausted-t-cells-are-increased-in-autoimmune-diseases-and-predict-response-to-anti-tnf-in-ra-and-spa-patients/