Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The shared epitope (SE) is an amino acid sequence motif coded by several HLA-DRB1 alleles that are overrepresented among people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). SE-positivity is associated with the production of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA), RA risk, and possibly a more severe disease course. Recent studies showed ACPA positivity to be associated with a significantly greater response to abatacept treatment. Given these prior observations, the purpose of this study was to determine if there is an association between SE status, ACPA status, and the effectiveness of drugs used to treat RA in a real-world setting.
Methods: Data were provided by participants with RA in FORWARD, The National Databank for Rheumatic Diseases, that had known SE and ACPA status. FORWARD participants complete comprehensive questionnaires every six months that include information on medication use and health status. Inclusion criteria required initiation of a TNFi, abatacept, or JAKi during the study period. These individuals had a baseline observation (prior to medication start) and a follow up observation (after medication start) approximately six months later. Descriptive statistics were calculated by drug exposure group for each SE/ACPA cohort. Change in patient activity scale II (PAS-II; a composite index composed of HAQ-II and visual analog scales for pain and patient global) scores between baseline and follow up was calculated and classified as improved (≥1 point improvement), no change (within 1 point), or worsened (≥1 point worsening). Adjusted linear regression models were generated for each medication group to determine the relationship between SE/ACPA group and change in PAS-II, using the SE–/ACPA– group as the reference. For models with a significant relationship between SE/ACPA group and change in PAS-II, an additional model was created using the SE+/ACPA+ group as reference.
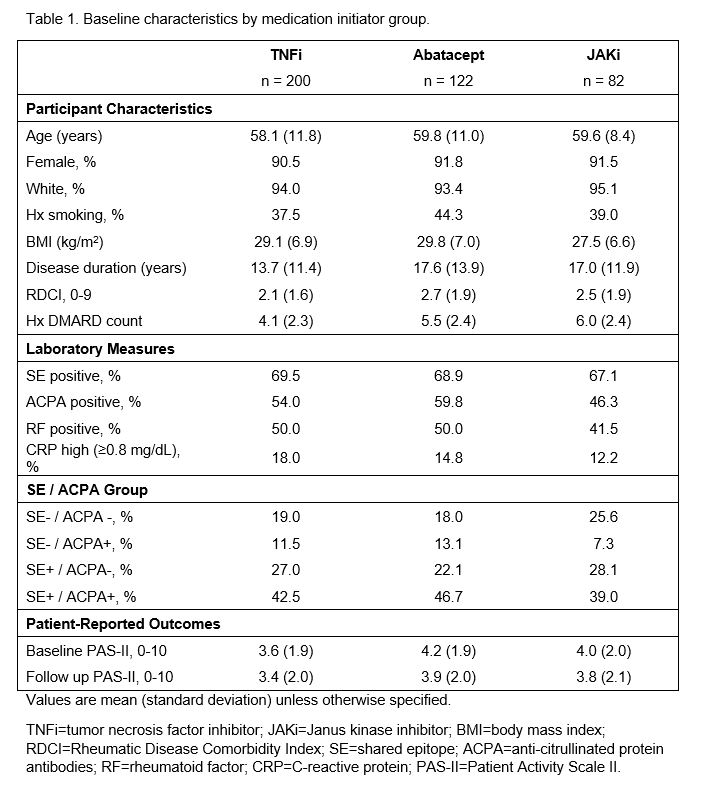
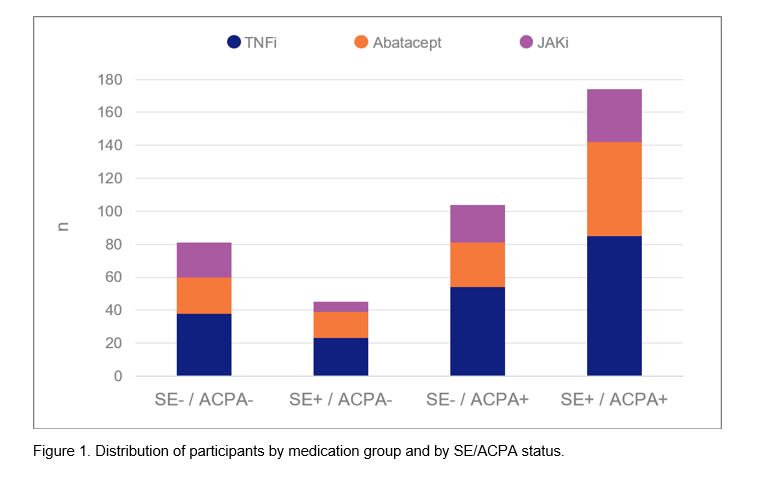
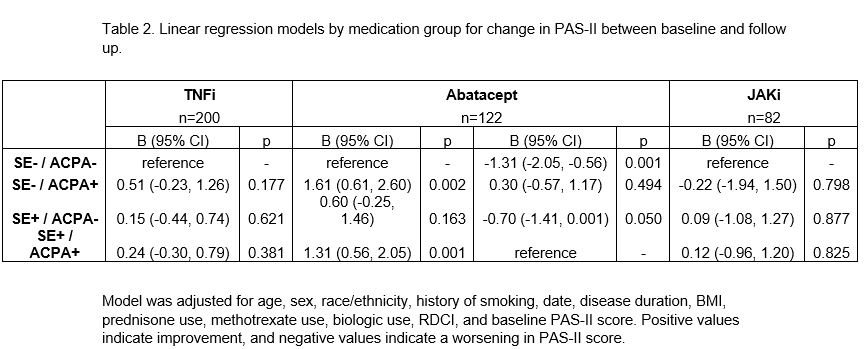
Results: Baseline characteristics of the 404 included participants are presented in Table 1 (200 TNFi, 122 abatacept, and 82 JAKi initiators) and the distribution of participants by medication group and by SE/ACPA status is presented in Figure 1. In models for TNFi and JAKi, there was no significant relationship between SE/ACPA status and change in PAS-II (Table 2). Among abatacept initiators, the two ACPA+ groups were more likely to experience an improved PAS-II score compared to the SE–/ACPA– group (B [95% CI] for SE–/ACPA+ : 1.6 (0.6, 2.6), p=0.002; for SE+/ACPA+: 1.3 [0.6, 2.1], p=0.001) and the two ACPA– groups were more likely to experience a worsened PAS-II score compared to the SE+/ACPA+ group (for SE–/ACPA–: -1.3 [-2.1, -0.6], p=0.001; for SE+/ACPA–: -0.7 [-1.4, 0], p=0.050). Change in PAS-II did not vary significantly by SE status.
Conclusion: Using a US-wide, real-world registry, we observed a greater improvement in patient reported RA disease activity after initiation of abatacept in ACPA+ individuals. Neither SE status nor ACPA status predict response to TNF or JAKi, suggesting that the predictive value of ACPA is more specific to abatacept users. This provides early evidence that ACPA status, rather than correlative SE status, may be the stronger predictor of abatacept response among individuals with RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wipfler K, Baker J, Sayles H, Han X, Park S, Wittstock K, Mikuls T, Michaud K. Examining the Relationship Between Shared Epitope, ACPA Seropositivity, and Real-World Drug Effectiveness in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/examining-the-relationship-between-shared-epitope-acpa-seropositivity-and-real-world-drug-effectiveness-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/examining-the-relationship-between-shared-epitope-acpa-seropositivity-and-real-world-drug-effectiveness-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/