Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: B cell depleting therapy (rituximab) and Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell transplantation (AHSCT) result in impaired ability to mount a humoral immune response.
Evusheld (tixagevimab co-packaged with cilgavimab) is a passive vaccine against SARS-CoV-2.
The aim of our study was to evaluate prospectively the efficacy and safety of evusheld vaccine for preventing SARS-COV2 infection in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRD) treated with rituximab or AHSCT.
Methods: We compared rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis patients treated with rituximab or AHSCT, who agreed to receive evusheld, to patients who refused. The primary outcome was the risk of severe COVID19 infection (omicron variant) defined as pneumonia, hospitalization, or death. A secondary outcome was safety.
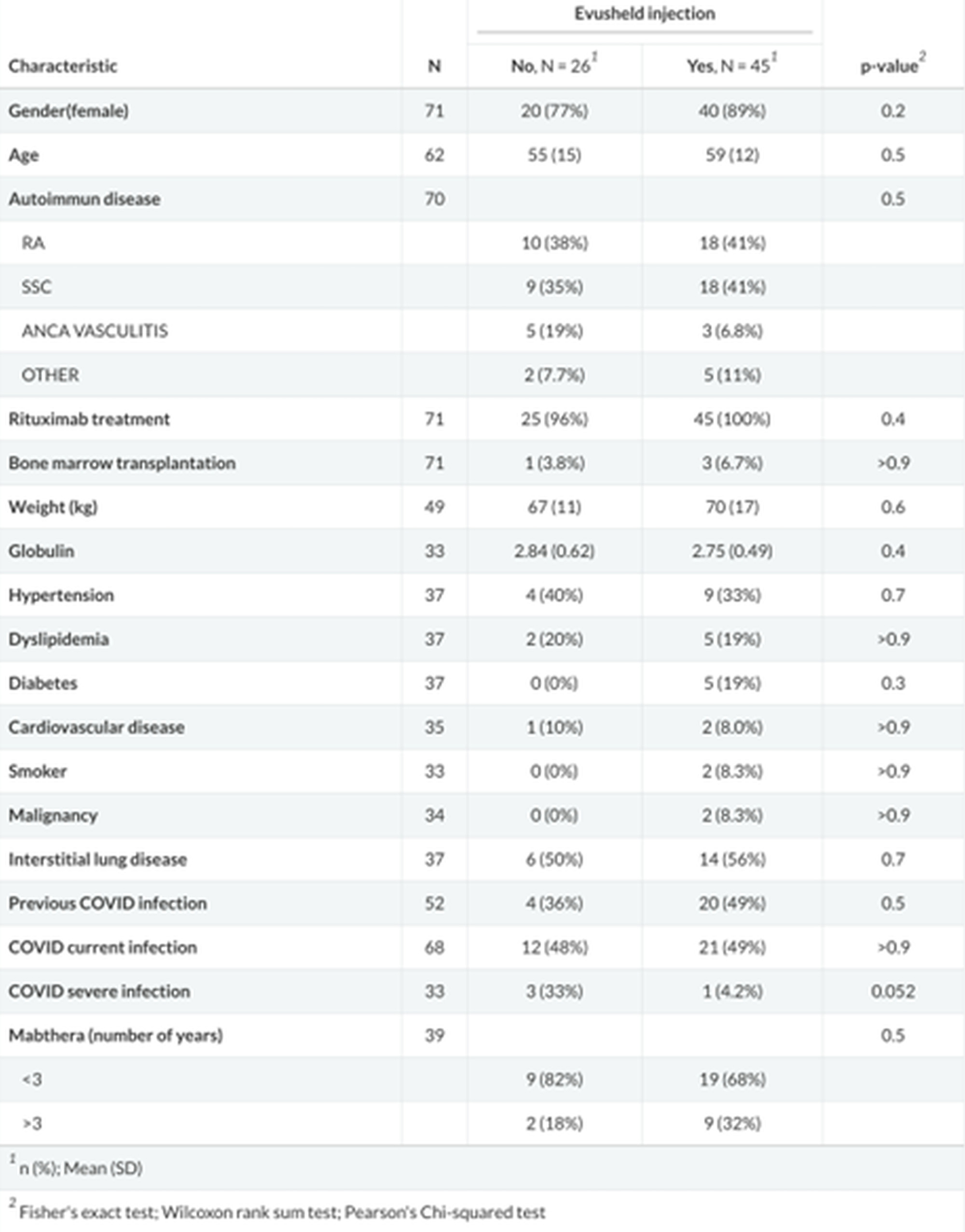
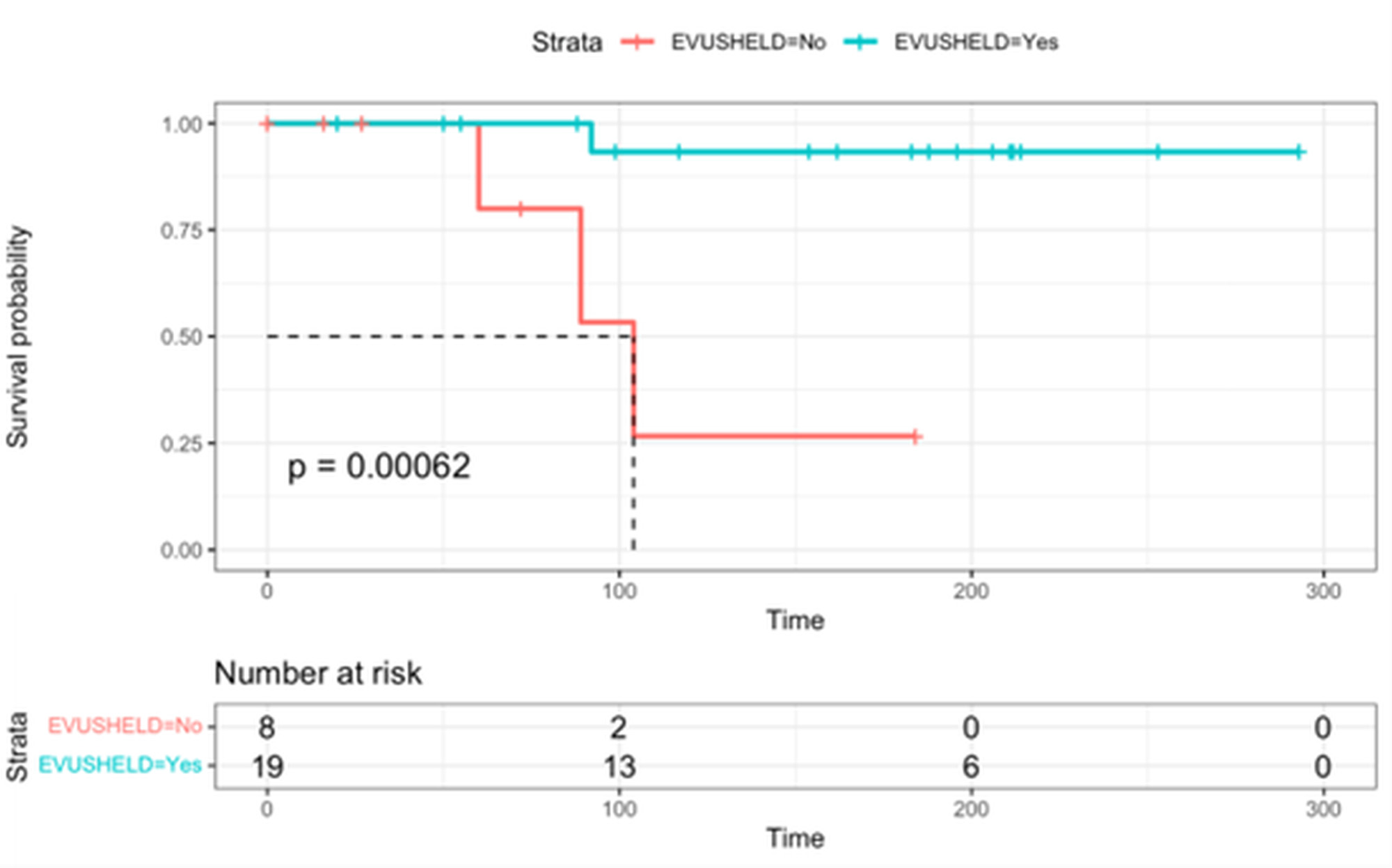
Results: A total of 45 AIRD patients (41 treated by rituximab and 4 systemic sclerosis patients who underwent AHSCT) in the intervention group and 26 in the control group, were recruited. There was no difference between the groups with regard to sex, age, years of rituximab treatment, previous mRNA vaccination and serum immunoglobulins level (table1). No difference in the infection rate was found between intervention group and control group (21 (49%) versus 12 (48%) respectively). Four patients had a severe infection, 3 in the control group and 1 in the intervention group. Evusheld reduced the risk for severe infection by 94% (HR 0.06, 95% CI 0.01-0.76, p-value 0.017) (figure 1). There were no adverse events related to evusheld injection.
Conclusion: Evusheld decreased the risk for severe COVID19 infection in patients with AIRD treated with B-cell depleting therapy or after AHSCT in a period in which Omicron BA.5, BQ1 and BQ.1.1 variants were prevalent in Israel, with a favorable safety profile.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kaly L, Volevich m, keret s, Awisat A, Shouval A, Rosner I, Rozenbaum M, Boulman N, Rimar D. Evusheld Efficacy and Safety in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases (AIRD) Treated by B Cell Depeting Therapy or Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation: A Prospective Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evusheld-efficacy-and-safety-in-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-aird-treated-by-b-cell-depeting-therapy-or-autologous-stem-cell-transplantation-a-prospective-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evusheld-efficacy-and-safety-in-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-aird-treated-by-b-cell-depeting-therapy-or-autologous-stem-cell-transplantation-a-prospective-observational-study/