Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1306–1346) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The objective of this study was to identify clusters of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in clinical practice, according to evolution of disease activity over time (“trajectories”), when focusing on active RA at inclusion.
Methods: Monocentric study including all RA patients seen from January 2021 to December 2022 in day hospitalization in Cochin Hospital, with active disease at screening (DAS28CRP or ESR ≥ 3.2), and with at least one follow-up visit. DAS28CRP trajectories were identified using k-means clustering. Characteristics at baseline and last-follow up visit according to trajectory were described, then analyzed with logistic regression to estimate associations between baseline characteristics and trajectories. Secondary analyses evaluated impact of difficult-to-treat (D2T) status at baseline, and was defined as failure of at least 2 biological (b) or targeted synthetic (ts) DMARDs with different mechanisms of action according to EULAR definition of D2T RA.
Results: Among the 362 patients screened, 260 had at least 2 visits with DAS28CRP values and were included, with a mean follow-up of 24 months (standard deviation, SD 9). Patients were mostly women (87%) of 59 yo, 16 years of disease duration, 81% positive ACPA and 60% erosive status. At baseline, patients had active disease with mean DAS28CRP of 4.1 (SD 1), 4 swollen joints, 6 tender joints, and mean level of CRP of 8 mg/L. They had received a mean of 2 different b/tsDMARDs and 47 (18%) were D2T RA. Two trajectories of DAS28CRP were identified: trajectory A (tA, n=158) with improvement in disease activity over the follow-up period, and trajectory B (tB, n=102) with little change in disease activity (Figure 1). At baseline, patients in tB had higher DAS28CRP (4.6 vs 3.7 in tA), more current smokers (23 vs 12%), more D2T status (27 vs 12%), and more treatment with corticosteroids (61 vs 46%) and Janus Kinase inhibitors (JAKi) (9.8 vs 3.2%). Multivariate analysis showed association of trajectories with Body Mass Index (BMI), smoking status, DAS28CRP at baseline and JAKi treatment. At the last visit, patients in tB remained more active than tA with DAS28CRP of 3.9 (vs 2.07) and had received more b/tsDMARDs (3.1 vs 2.3). Finally, 174/260 (67%) had DAS28CRP < 3.2 at the end of follow-up, 149 (94%) in tA and 25 (25%) in tB. There was no difference in trajectories when comparing D2T patients and no-D2T patients (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This study revealed two trajectories of RA patients with active disease after a 2-year follow-up, one with achieved remission (tA) and the other with persistent high disease activity (tB). Current smoking and high BMI were the main drivers of tB, these comorbidities are known to be associated with poorer outcomes. Level of DAS28CRP at baseline and use of JAKi were also factors independently associated with trajectories, suggesting higher severity of the disease in these patients. Finally, D2T status had no impact on trajectories. Despite the implementation of a treat-to-target strategy, 75% of patients following tB did not achieve low disease activity at the end of the follow-up period, highlighting the need for early identification of such patients to ensure timely and optimized management.
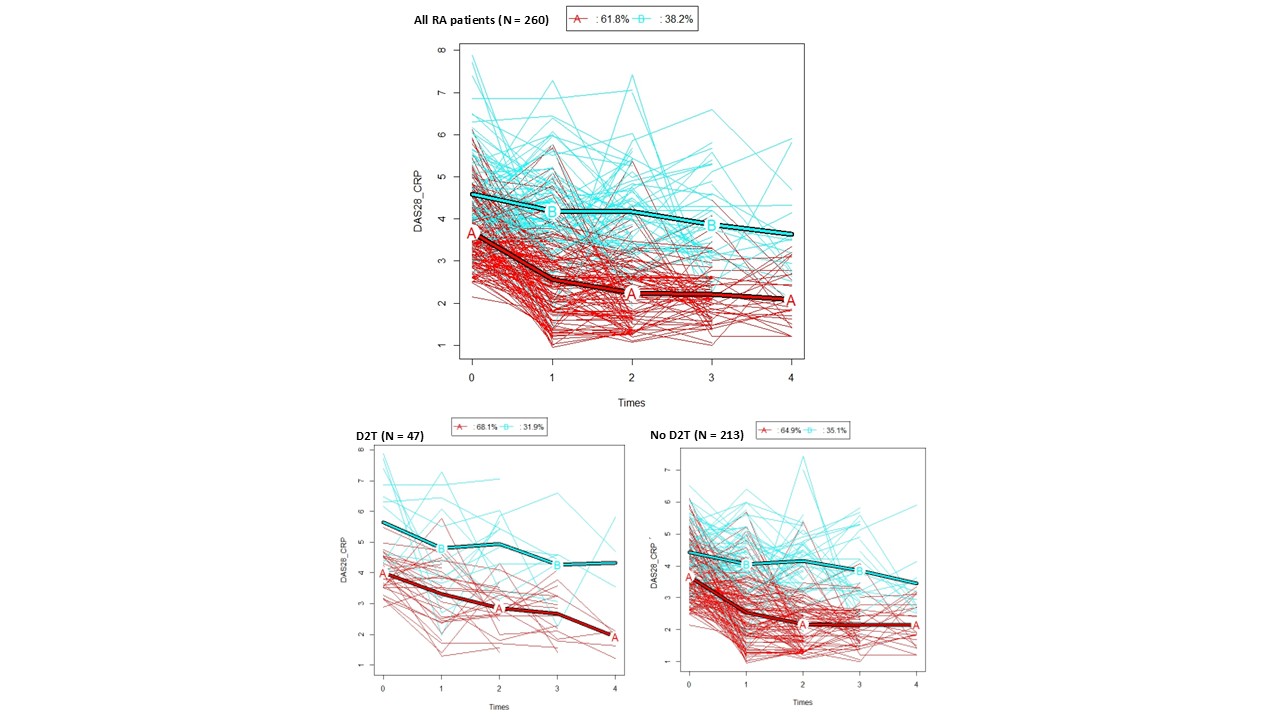 Trajectories of DAS28CRP during follow-up in all RA population, then according to D2T status.
Trajectories of DAS28CRP during follow-up in all RA population, then according to D2T status.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Portier E, Fogel O, Medkour T, Hecquet S, AVOUAC J. Evolution of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: analysis of disease activity trajectories in a tertiary‑care rheumatology department [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evolution-of-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-analysis-of-disease-activity-trajectories-in-a-tertiary%e2%80%91care-rheumatology-department/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evolution-of-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-analysis-of-disease-activity-trajectories-in-a-tertiary%e2%80%91care-rheumatology-department/
