Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to treat inflammatory back pain in patients (pts) with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). However, an increased risk of side effects associated with NSAIDs and their dosage has been reported1. Therefore, lower doses and a dose reduction is desirable. The objective of this study is to evaluate the short-term NSAID sparing effect of secukinumab (SEC) in AS pts with NSAID intake.
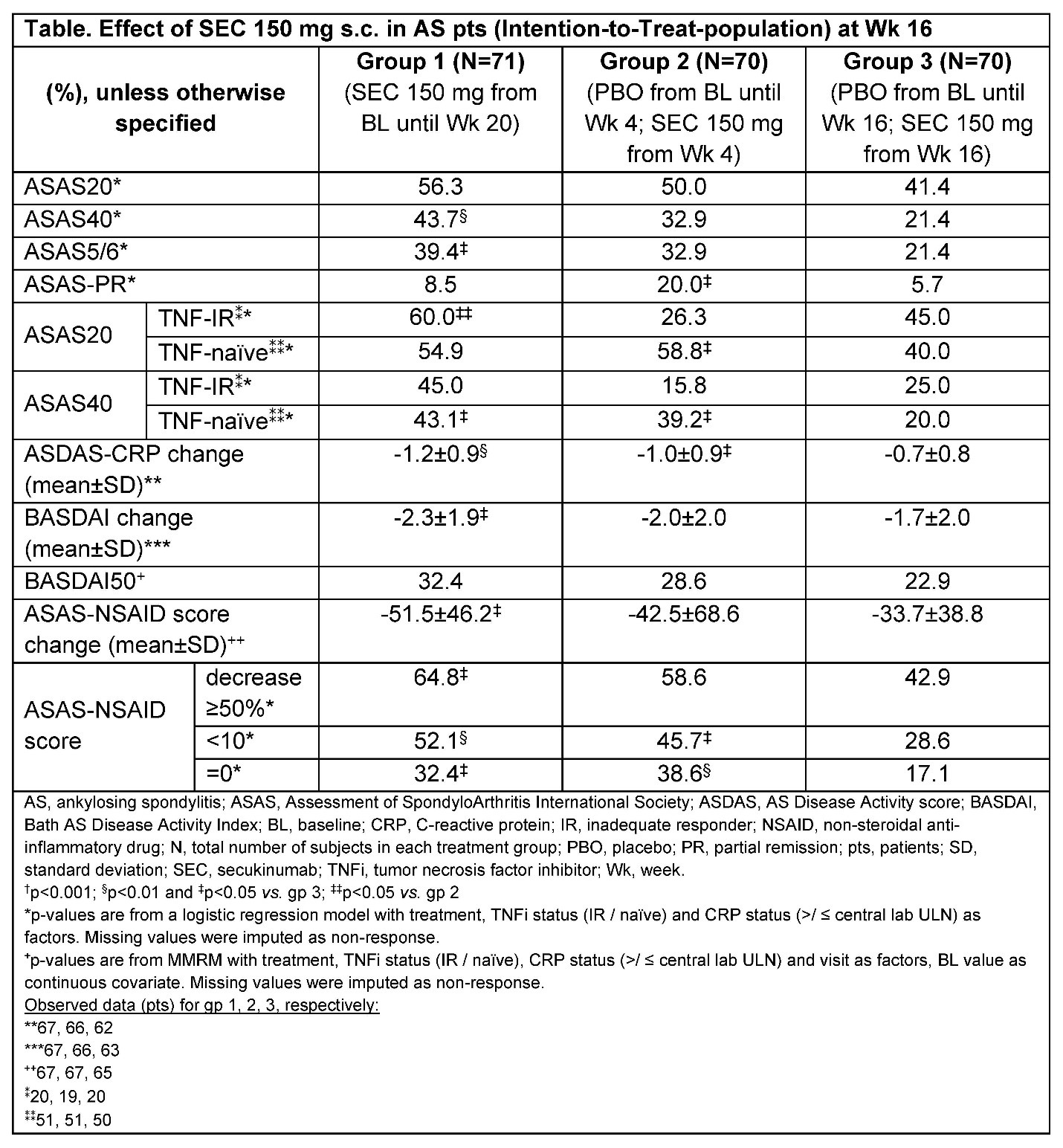
Methods: In a prospective controlled trial, 211 adult pts with active AS Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI ≥4) and an inadequate response (IR) to at least 2 NSAIDs at the highest recommended/tolerated dose and pts with an IR, or those who were naïve/intolerant to a maximum of 2 tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) were enrolled. NSAID intake was evaluated using the Assessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis (ASAS)-NSAID score. To be eligible, pts had to take at least 50% of the highest recommended/tolerated NSAID dose regularly. Pts were randomised (1:1:1) to receive SEC 150 mg s.c. from Week (Wk) 0 (group [gp] 1), Wk 4 (gp 2) and Wk 16 (gp 3). All groups received SEC 150 mg from Wk 16. NSAID tapering was allowed in all groups from Wk 4 onwards. The primary endpoint (PE) was an ASAS20 response of pooled gp 1 and gp 2 vs. gp 3 at Wk 12.
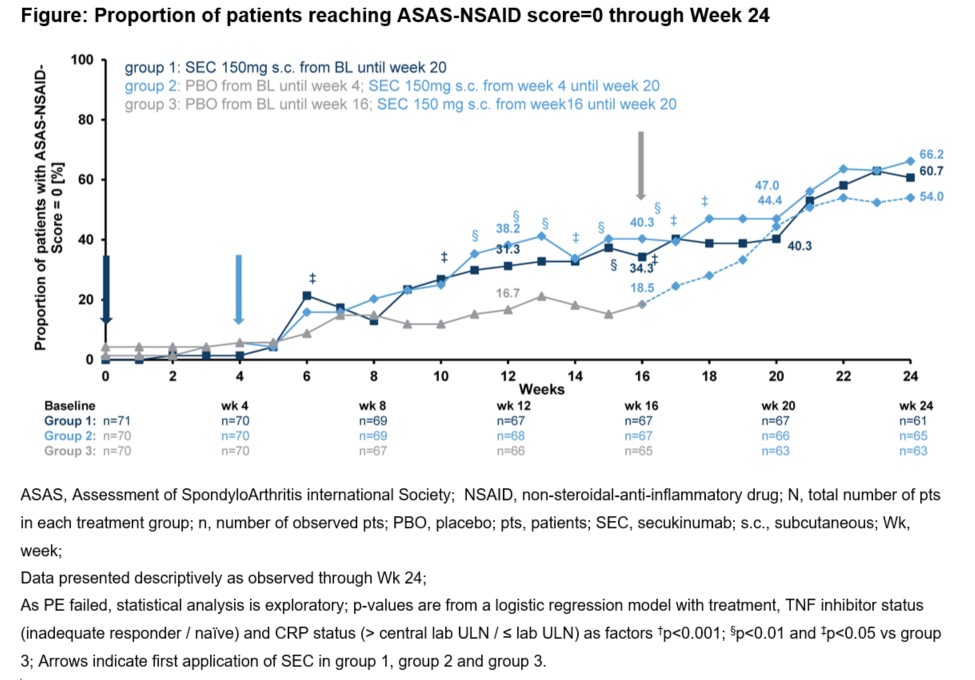
Results: There were 71 pts in gp 1, 70 in gp 2 and 70 in gp 3. Baseline (BL) characteristics were comparable across groups; mean age (SD) was 45.2 (12.3) years (yrs), time since diagnosis was 7.4 (9.8) yrs, 57.8% male, 79.0% human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-B27 positive 48.6% pts had an elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) 40.8% were current/ever smoker and 72.0% were TNFi-naïve. The ASAS-NSAID (SD) scores at BL were: gp 1 vs. gp 2 vs. gp 3: 82.9 (37.7) vs. 79.9 (45.3) vs.82.3 (39.1). BASDAI and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS)-CRP scores were similar between groups: 6.0 (1.4) vs. 6.2 (1.5) vs. 6.2 (1.3), and 3.4 (0.7) vs. 3.3 (0.8) vs. 3.4 (0.7), respectively. The ASAS20 response at Wk 12 of pooled gp 1 and 2 vs. gp 3 was 51.1% vs. 44.3% but the PE was not met (p=0.35). A higher proportion of pts in gp 1 and 2 achieved ASAS40 and BASDAI50 and other secondary outcomes at Wk 16 (Table). More pts in gp 1 and 2 reduced their NSAID intake from BL through Wk 16 vs. gp 3 (Table and Figure).
Conclusion: In this population of pts with AS, SEC provided clinical improvements in conventional clinical outcomes and a short-term NSAID sparing effect.
References:
1. Burmester G, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:818-822.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiltz U, Baraliakos X, Brandt-Jrgens J, Wagner U, Lieb S, Sieder C, Mann C, Braun J. Evaluation of the Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Sparing Effect of Secukinumab in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: Multicenter, Randomised, Double-blind, Phase IV Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-nonsteroidal-anti-inflammatory-drug-sparing-effect-of-secukinumab-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-multicenter-randomised-double-blind-phase-iv-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-nonsteroidal-anti-inflammatory-drug-sparing-effect-of-secukinumab-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-multicenter-randomised-double-blind-phase-iv-study/