Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Despite new therapeutic approaches in RA, the mortality gap between RA patients and the general population persists, and may even be increasing. Cardiovascular (CV) complications consist the leading cause of this increase in mortality. In this study, we tried to investigate the impact of biological agents (BA) on cardiovascular risk factors in RA patients.
Methods: Forty-nine, biologic-naïve RA patients, fulfilling the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria with no previous history of CV disease were recruited in the study. We compared total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c), triglycerides (TGs), Apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1), Apolipoprotein B (ApoB), Lipoprotein A (LpA), systolic blood pressure, inflammatory markers such as CRP and ESR between baseline and after 6 months of BA initiation. An ultrasonographic measurement of intima-media thickness (IMT) of carotids was performed by an experienced sonographer at baseline and after 6-month follow-up in order to determine the presence of subclinical atherosclerosis. The titer of autoantibodies against oxidised LDL (anti-oxLDL) was also estimated in a subgroup of 35 patients.
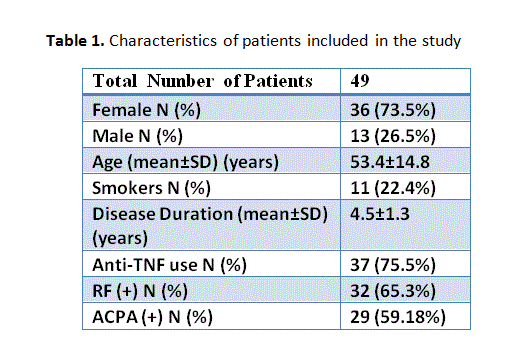
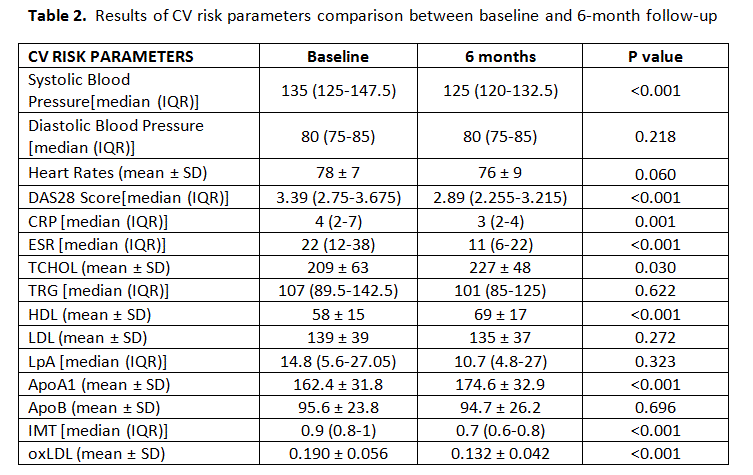
Results: As regards the characteristics of patients, the mean (SD) age was 53.4 (14.8) years, 73.5% were women and 22.4% were smokers (Table 1). BA were administered in all patients and anti-TNF use was the most common (75.5% of patients). Six months after treatment initiation, patients presented with a significant increase in mean (SD) HDL [69 (17) vs 58 (15)] and ApoA1 [174 (33) vs 162 (32)] levels (p< 0.001) with a simultaneous significant reduction of mean (SD) systolic blood pressure [125 (12.5) vs 135 (22.5)] and the titer of anti-oxLDL [0.132 (0.042) vs 0.190 (0.056)]. ΙΜΤ was also reduced after 6-month reassessment [0.7 (0.2)mm vs 0,9 (0.2)mm, (p< 0.001 for all comparisons)] (Table 2).
Conclusion: An improved lipid profile (increased HDL-c in combination with reduction of the anti-oxLDL titer) and a significant reduction of IMT were observed in a six-month period of BA administration. This study confirms that RA patients are prone to early atherosclerosis and BA initiation correlates strongly with more favorable values of CV risk parameters.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Papamichail G, Markatseli T, Georgiadis A, Xydis V, Milionis H, Drosos A, Voulgari P. Evaluation of Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, Treated with Biological Agents: 6-month Follow-up [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-cardiovascular-risk-factors-and-atherosclerosis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-biological-agents-6-month-follow-up/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-cardiovascular-risk-factors-and-atherosclerosis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-biological-agents-6-month-follow-up/