Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1945–1972) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are characterized by muscle weakness and inflammation. There is an increased risk of developing cancer in patients (pts) with IIM compared to the general population. While most cancers are detected within the 1st year of IIM diagnosis, ongoing monitoring is recommended for 3-5 years post-diagnosis.
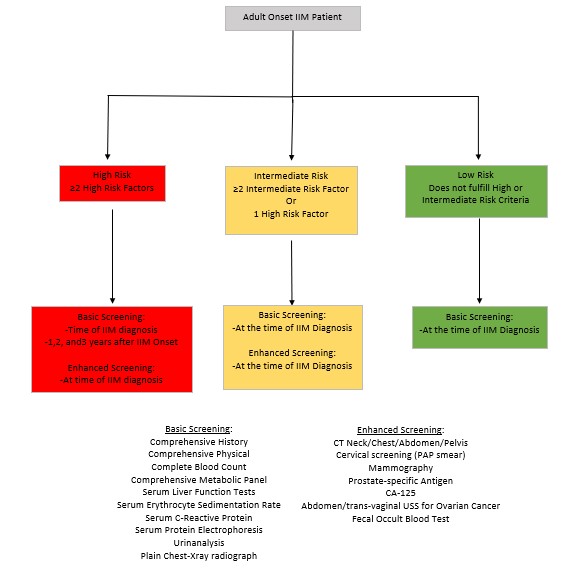
In November 2021, a systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted to inform cancer screening guidelines in IIM. The review aimed to evaluate the cancer screening investigations and develop evidence-based guidelines. These guidelines were subsequently developed in collaboration with experts from around the world, utilizing a Delphi process involving 75 participants from 22 countries. The manuscript detailing the proposed guidelines is forthcoming. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness/appropriateness of the screening methods employed at our institution and compare them with the proposed guidelines.
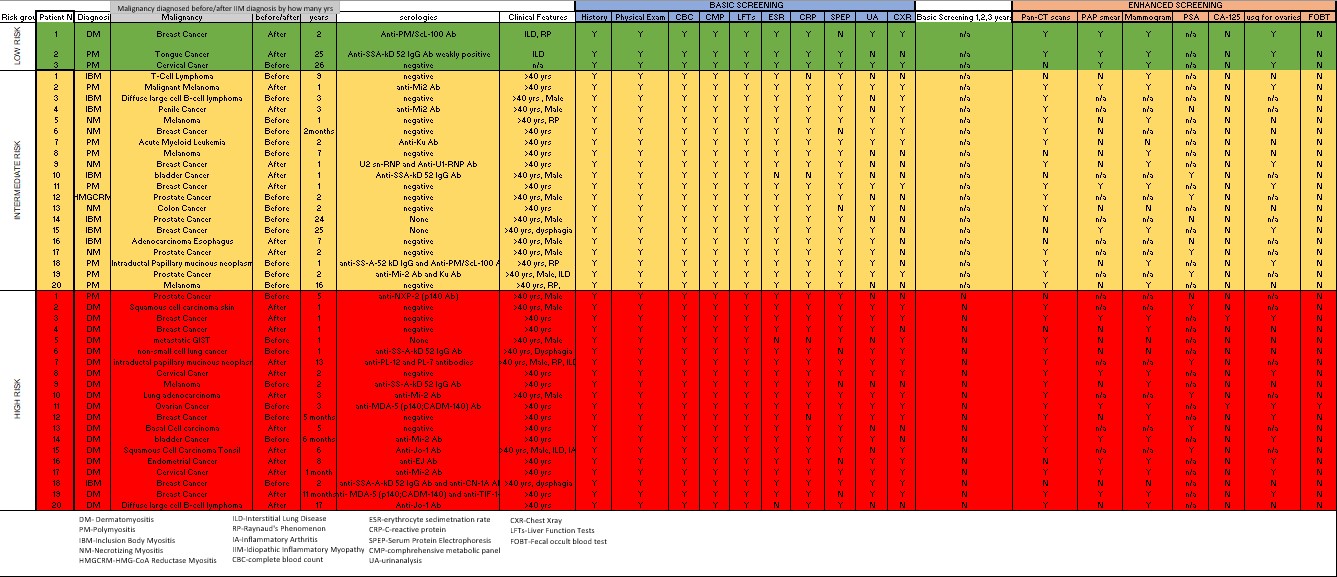
Methods: A retrospective chart review at our tertiary medical center using EMR-EPIC, Research Electronic Data Capture software, and Heron Research database, to identify pts being treated for IIM and diagnosed with malignancy between 1/2012 to 1/2022. We implemented risk stratification methods based on the proposed guidelines for malignancy screening in patients with IIM.
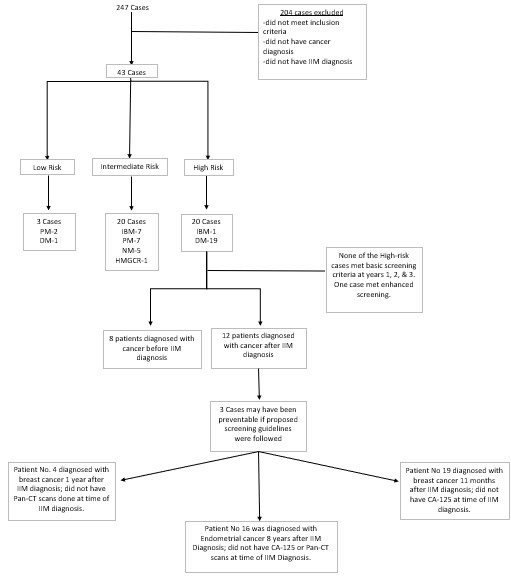
Results: Among the 20 high-risk cases identified, 12 pts were diagnosed with cancer after their IIM diagnosis, none met the basic screening recommendations for the first 3 years following IIM diagnosis. One patient met the criteria for enhanced screening. Among the 20 intermediate-risk cases, 7 were diagnosed with cancer after IIM diagnosis. 15 of 20 intermediate-risk cases did not undergo complete basic screening, and none met the criteria for enhanced screening. Among the 3 low-risk pts, 1 met the basic screening requirements. The most missed component of enhanced screening was fecal occult blood test, while the most frequently overlooked element of basic screening was chest x-ray. 3 high-risk pts may have had their cancers detected earlier if screening guidelines were followed.
9 of 15 female pts with gynecological and breast cancers were classified as high-risk. Among the 26 female intermediate/high-risk cases, 16 did not undergo PAP smears, 5 did not have mammograms, and 13 did not undergo abdominal/trans-vaginal ultrasounds. Additionally, there were 5 gastrointestinal malignancies, and 10 of 40 intermediate/high-risk pts did not have pan-CT scans.
Conclusion: We conclude the proposed guidelines, particularly for high-risk cases, play a vital role in detecting malignancies occurring after IIM diagnosis. Most high-risk cases were diagnosed with cancer within 1-5 years of initial IIM diagnosis. A significant proportion of malignancies observed were female-specific cancers (breast/gynecologic), many that occurred within 1-3 years of IIM diagnosis. This suggests the importance of enhanced screening up to 3-5 years beyond the initial diagnosis of IIM in high-risk pts. It is evident that our institution did not fully adhere to the proposed guidelines; however, these results could form a quality improvement project aimed at enhancing cancer screening for pts with IIM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Giri P, Bath A, Bhadbhade P. Evaluation of Cancer Screening Methods in Patients Diagnosed with Inflammatory Muscle Disease at Kansas University Medical Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-cancer-screening-methods-in-patients-diagnosed-with-inflammatory-muscle-disease-at-kansas-university-medical-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-cancer-screening-methods-in-patients-diagnosed-with-inflammatory-muscle-disease-at-kansas-university-medical-center/