Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: B cell depletion in the form of rituximab (RTX) is an established treatment modality for idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM). Treatment response is now assessed in myositis clinical trials using the internationally accepted Total Improvement Score (TIS). Data using TIS regarding RTX response in IIM remains lacking.
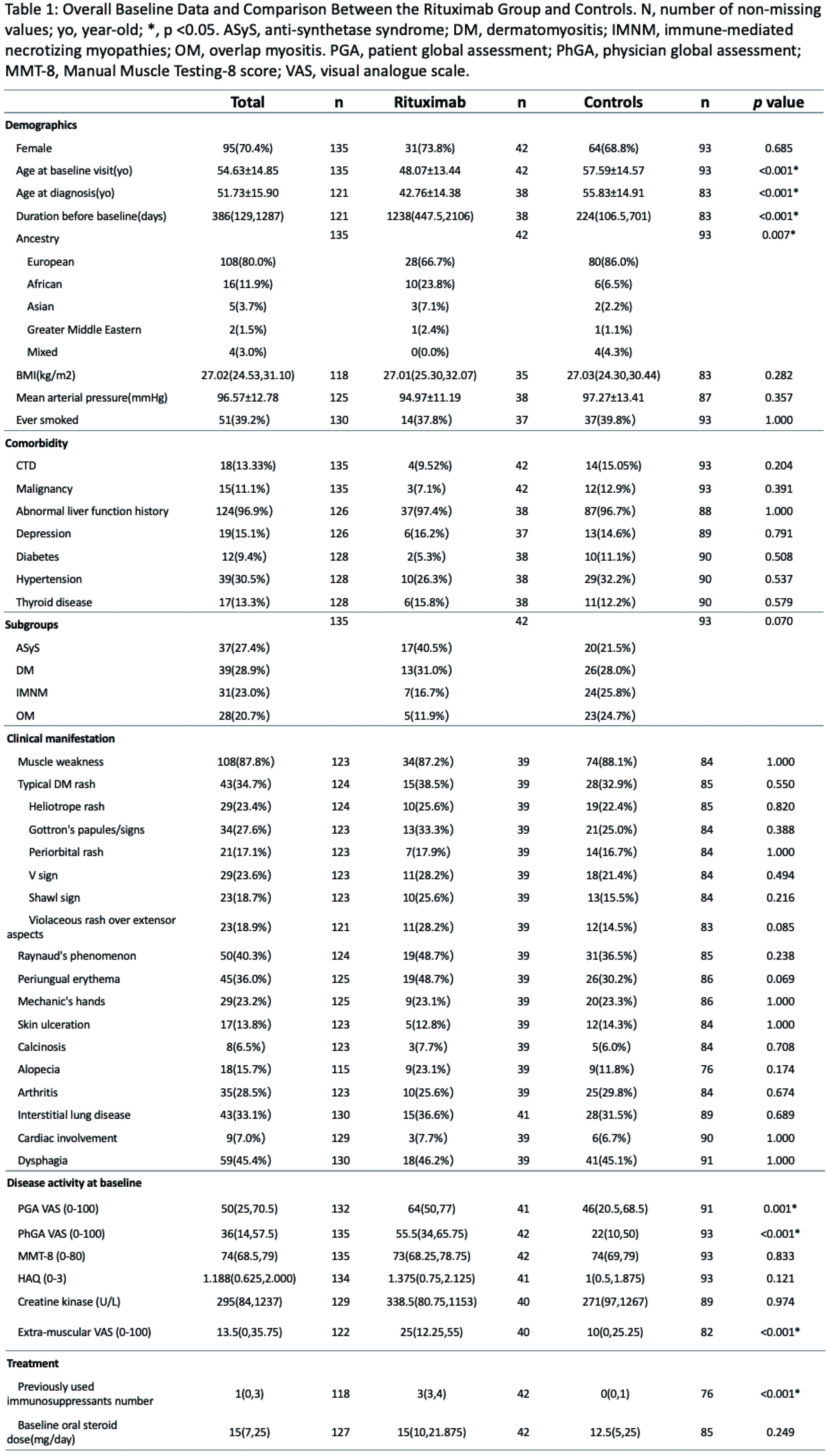
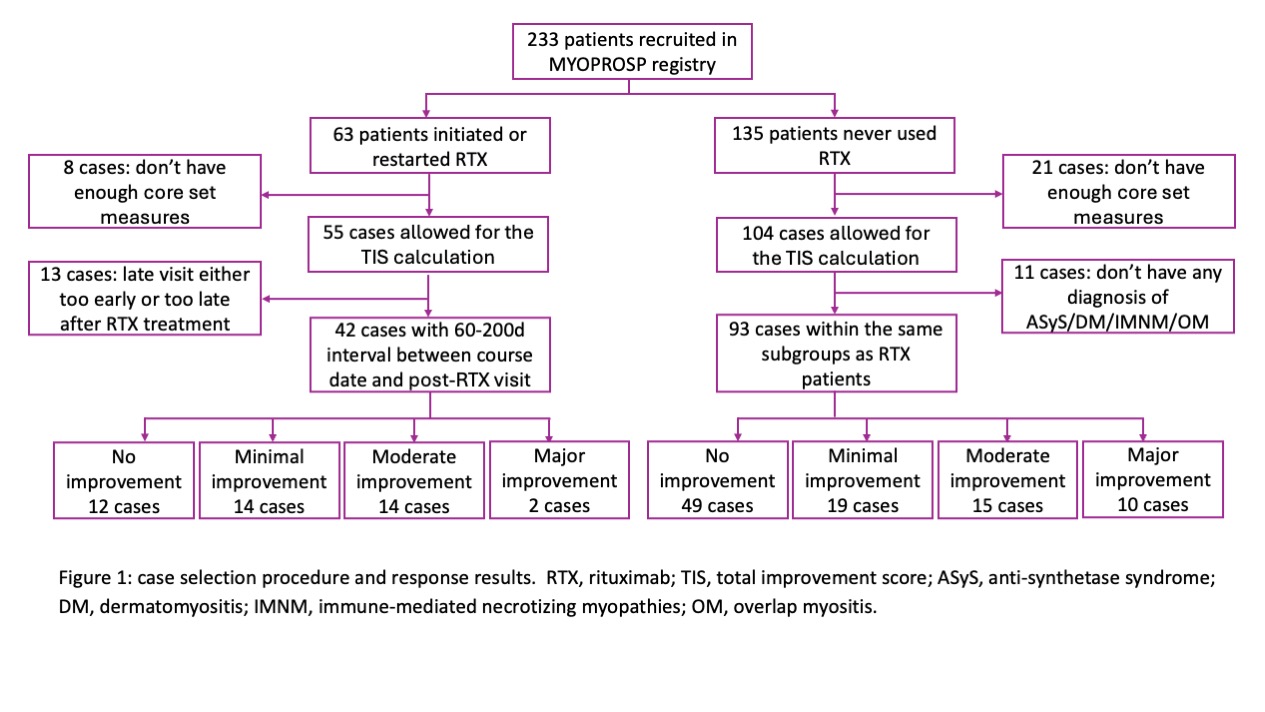
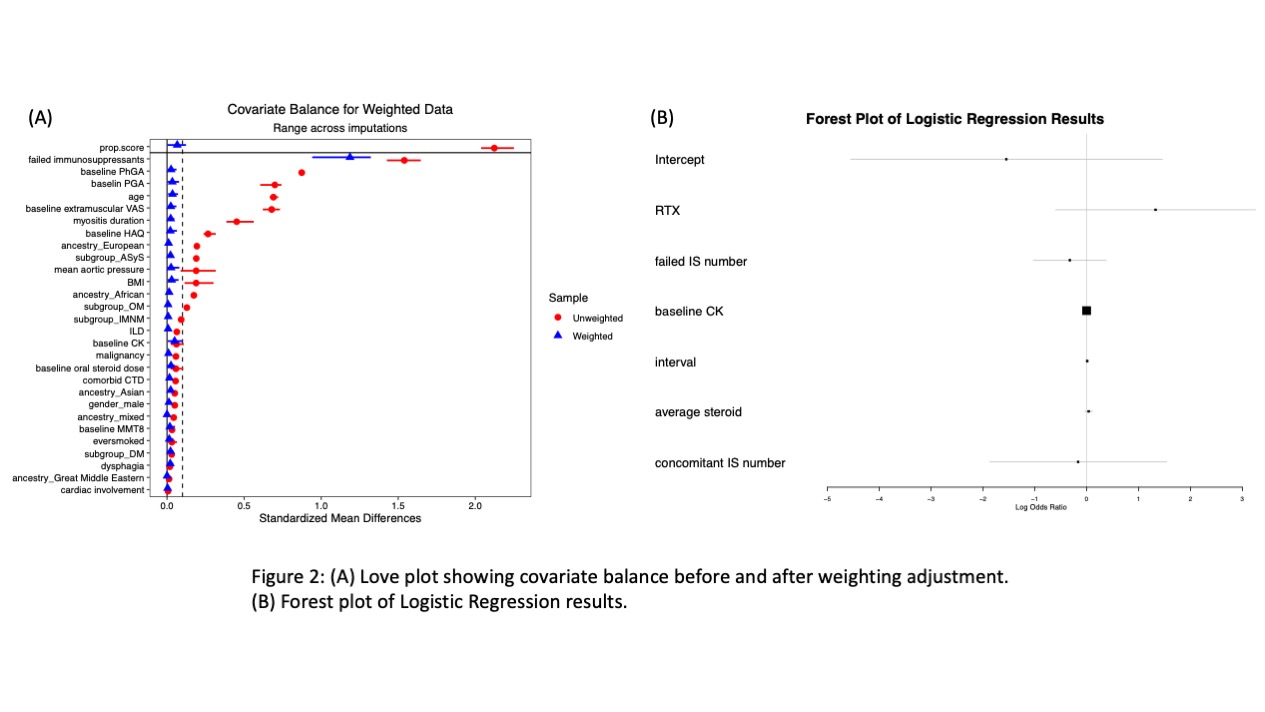
Methods: The MYOPROSP is a prospective observational cohort study that enrolled adult IIM cases from 23 centres in the UK during 2016-2020. We reviewed the registry to identify cases where RTX was initially administered or restarted. We also identified control cases who entered the registry during the same period but never received RTX matched by their myositis subgroups. The International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) core set measures were collected to generate TIS. The interval for the RTX group was limited to 60-200 days. Baseline characteristics were compared using t-test or Fisher’s exact test. Univariate logistic regression was first applied to compare response rate. Baseline covariates were balanced following the multiple imputations and inverse probability of treatment weighting (Figure 2A). Data were adjusted for concomitant drug number, average steroid dose, and follow-up interval using multivariate logistic regression.
Results: Sixty-three patients in MYOPROSP initiated or restarted RTX; 42 with computable TIS met the interval requirement. 93 controls were identified, among which 51 had a change in therapy around baseline. The RTX group was significantly younger at diagnosis and enrollment and had a longer disease duration (Table 1). There were no significant differences in gender distribution, BMI, clinical manifestations, or baseline oral steroid doses. The RTX group failed more treatment compared to the controls. Baseline physician global activity, patient global activity, and extra-muscular activity were significantly higher in the RTX group. During a median 128-day follow-up, the rituximab group had a higher TIS (median 32.50 [interquartile range 17.5-46.9] RTX vs. 17.5[7.5-40.0] controls). 30/42 (71.4%) RTX patients vs. 44/93 (47.3%) controls (Odds Ratio (OR) 2.78, 95% Confidence Interval (CI) 1.27-6.09, p=0.01, univariate logistic regression) achieved at least minimal improvement (Figure 1). However, on applying multivariate analysis, the association no longer reached statistical significance (pooled OR 3.78, 95% CI 2.57-24.92, p=0.17) (Figure 2B).
Conclusion: Using TIS in an observational setting, we have demonstrated that patients receiving RTX are more likely to respond to treatment than patients receiving conventional immunosuppressants, despite them having longer disease duration and failing more therapies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lyu X, Gordon P, Gunawardena H, McHugh N, Tansley S, Prabu A, Lanyon P, Miller J, Ong V, Isaacs A, Yee C, Cotton C, Kiely P, Stathopoulou E, Taylor J, Jeffery R, Bharadwaj A, Lilleker J, Lamb J, Chinoy h. Evaluating the Efficacy of Rituximab in the Treatment of Refractory Adult Idiopathic Inflammatory Myositis Using Total Improvement Score: Data from a Real-World Multi-Centre Registry in the United Kingdom [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-the-efficacy-of-rituximab-in-the-treatment-of-refractory-adult-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis-using-total-improvement-score-data-from-a-real-world-multi-centre-registry-in-the-united-kin/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-the-efficacy-of-rituximab-in-the-treatment-of-refractory-adult-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis-using-total-improvement-score-data-from-a-real-world-multi-centre-registry-in-the-united-kin/