Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) have increased cardiovascular (CV) risk due to accelerated atherosclerosis (ATS) caused by systemic inflammation, and vascular impairment. To date, there is no specific tool recommended for evaluation of CV risk in SSc. This study aimed to evaluate the CV risk in SSc compared to healthy controls (HC) and to explore the accuracy of SCORE and SCORE2 for general population, and its modifications.
Methods: 92 SSc patients (81 females; mean age 52; mean disease duration 6.8 years; dcSSc: n=28, lcSSc: n=64) and 197 HC (147 females, mean age 56.7) with no history of CV disease (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial events) were included. Disease activity and clinical features were evaluated in SSc. In all participants comorbidities and current medication was recorded, all underwent examinations of carotid artery disease (CARD), carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT), pulse wave velocity (PWV), ankle-brachial index (ABI), and body composition (by densitometry and bioelectrical impedance analysis). The risk of fatal CV events was evaluated by the Systematic COronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) and SCORE2, in SSc also by the modified (mSCORE) by coefficient 1.5 as recommended by EULAR for inflammatory arthritis, and 3.59 (SCOREx3.5; SCORE2x3.5) based on the estimated CV risk in SSc (1).
Results: SSc patients had a trend to more prevalent dyslipidemia (p=0.063) and significantly more often prediabetes (p< 0.001), but a comparable prevalence of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and current smoking to HC. Nevertheless, SSc used significantly more frequently antihypertensives than HC (p< 0.001), including vasoactive treatment by calcium channel blockers. SSc had significantly increased prevalence of CARD, unfavorable CIMT and ABI (p< 0.05 for all), and a trend to lower SCORE, but no significant difference in SCORE2 compared to HC. On the contrary, the overall CV risk based on US examination (CARD, CIMT) was significantly higher in SSc. In SSc, the CV risk and markers of subclinical ATS were associated especially with age, HbA1c, disease duration, and mean arterial pressure (p< 0.05 for all).
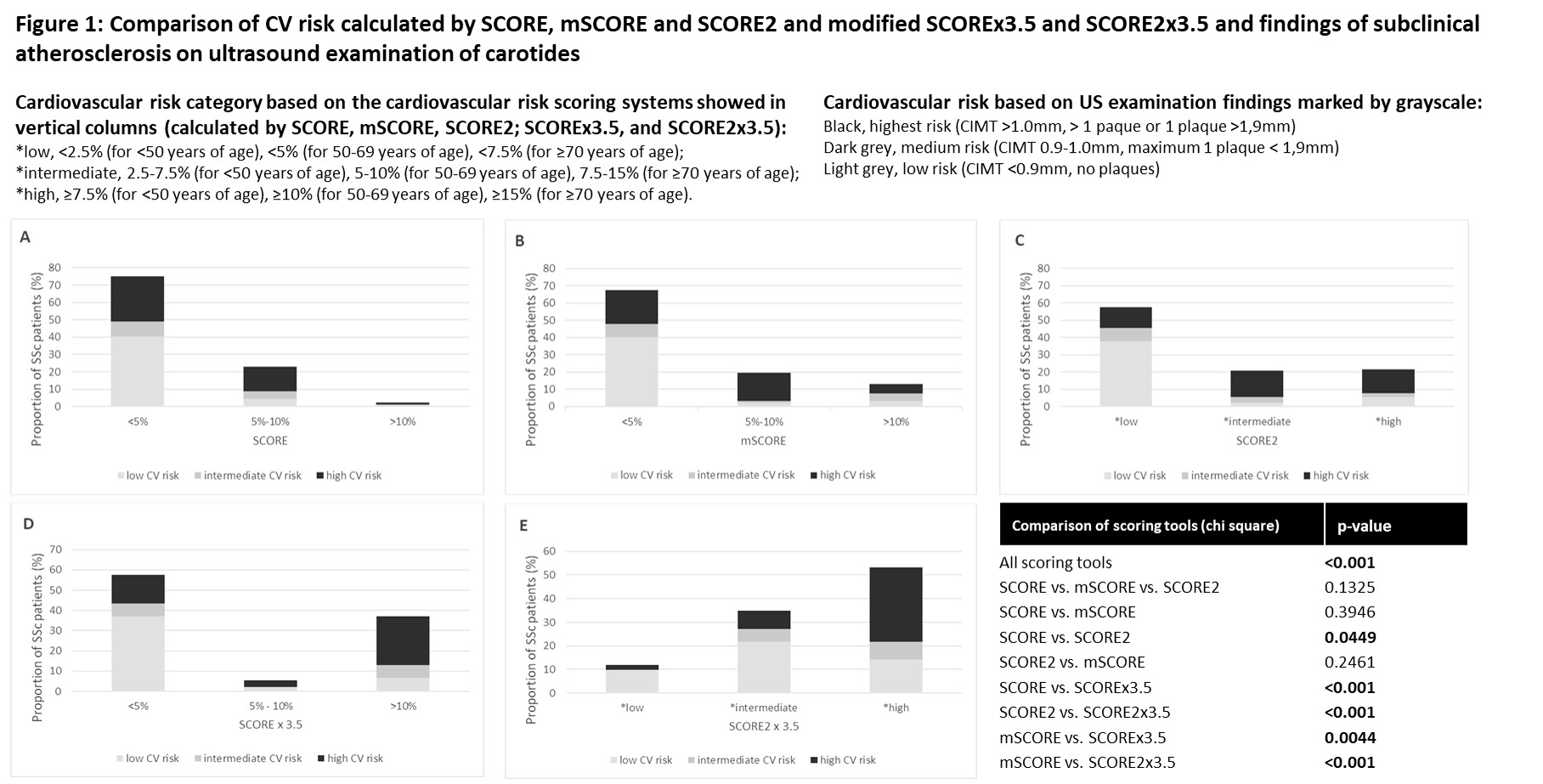
A comparison of calculated CV risk with US examination showed inaccuracy of the SCORE, mSCORE and SCORE2. On the other hand, modification of SCORE and SCORE2 by coefficient 3.59, showed significantly higher accuracy in estimation of CV risk, when compared to carotid US finding (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This cross-sectional case-control study demonstrated a significantly increased risk of subclinical ATS in SSc compared to HC, although there was an opposite trend in CV risk estimated by calculated SCORE. The CV risk in SSc was associated especially with age, disease duration, and HbA1c levels. Scoring systems SCORE and SCORE2 recommended for the European general population underestimated the CV risk when comapred to US examination. Using the coefficient 3.59 based on estimated CV risk for SSc (1) sigificantly increases the accuracy of available CV risk scoring systems.
Supported by MHCR (023728; NV18-01-00161A; NU21-01-00146).
Reference: Conrad N et al. Lancet. 2022;400(10354):733-743.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Oreská S, Prokopcová A, Storkanova H, Kudlicka J, Tuka V, Mikes O, Krupickova Z, Satny M, Chytilova E, Kvasnicka J, Spiritovic M, Hermankova B, Cesak P, Rybar M, Pavelka K, Šenolt L, Becvar R, Vencovský J, Vrablik M, Tomcik M. Estimation of Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis – Accuracy of Tools Based on SCORE and Its Modifications Compared to Ultrasound Examination of Subclinical Atherosclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/estimation-of-cardiovascular-risk-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-accuracy-of-tools-based-on-score-and-its-modifications-compared-to-ultrasound-examination-of-subclinical-atherosclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/estimation-of-cardiovascular-risk-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-accuracy-of-tools-based-on-score-and-its-modifications-compared-to-ultrasound-examination-of-subclinical-atherosclerosis/