Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: T Cell Biology and Targets in Autoimmune Disease - Poster Session II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Methods:
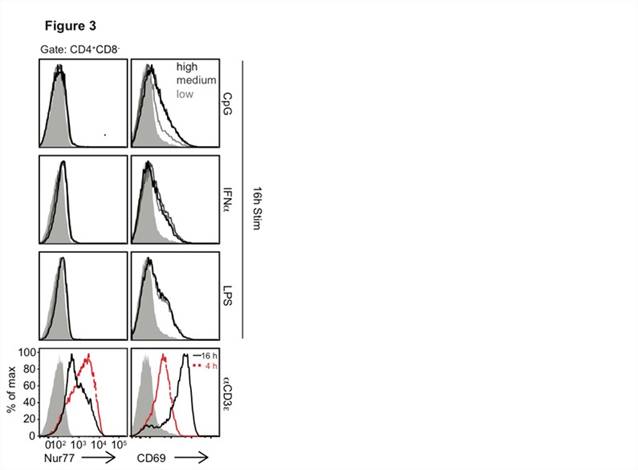
Results:
Conclusion: 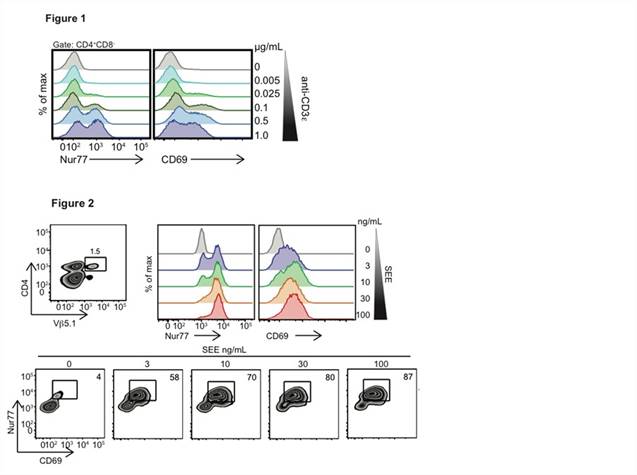
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ashouri J, Weiss A. Endogenous Nur77 Is a Specific Indicator of Antigen Receptor Signaling in Human T and B Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/endogenous-nur77-is-a-specific-indicator-of-antigen-receptor-signaling-in-human-t-and-b-cells/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/endogenous-nur77-is-a-specific-indicator-of-antigen-receptor-signaling-in-human-t-and-b-cells/
