Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Mucosal surfaces may be involved in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (1). IgA is the most abundant class of immunoglobulin at mucosal sites and has an important function in intestinal homeostasis. Therefore, it is worthwhile to study this isotype in more detail in the context of RA. Humans have two IgA subclasses, IgA1 and IgA2, which are not evenly distributed. IgA1 is dominant in serum, whereas IgA1 and IgA2 are more balanced at mucosal surfaces (2). Besides these differences in location, IgA2 has also been ascribed pro-inflammatory properties (3). As IgA subclasses might provide insights into mucosal involvement and potential pro-inflammatory mechanisms in RA, we measured total and autoantibody specific IgA subclasses in sera of rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Methods: RA patients from two cohorts, the IMPROVED and the EAC, were selected based on previous autoantibody measurements. Samples were collected at baseline in the IMPROVED study and at the 1-year visit in the EAC. All patients fulfilled the 1987 (EAC) or 2010 (IMPROVED) ACR criteria for RA. Rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) and total IgA subclasses were measured in these sera using in-house ELISA’s, and compared to healthy donors. The association of IgA subclass levels with CRP, disease activity score (DAS) and smoking was investigated using Spearman’s rank correlation and Mann–Whitney U tests.
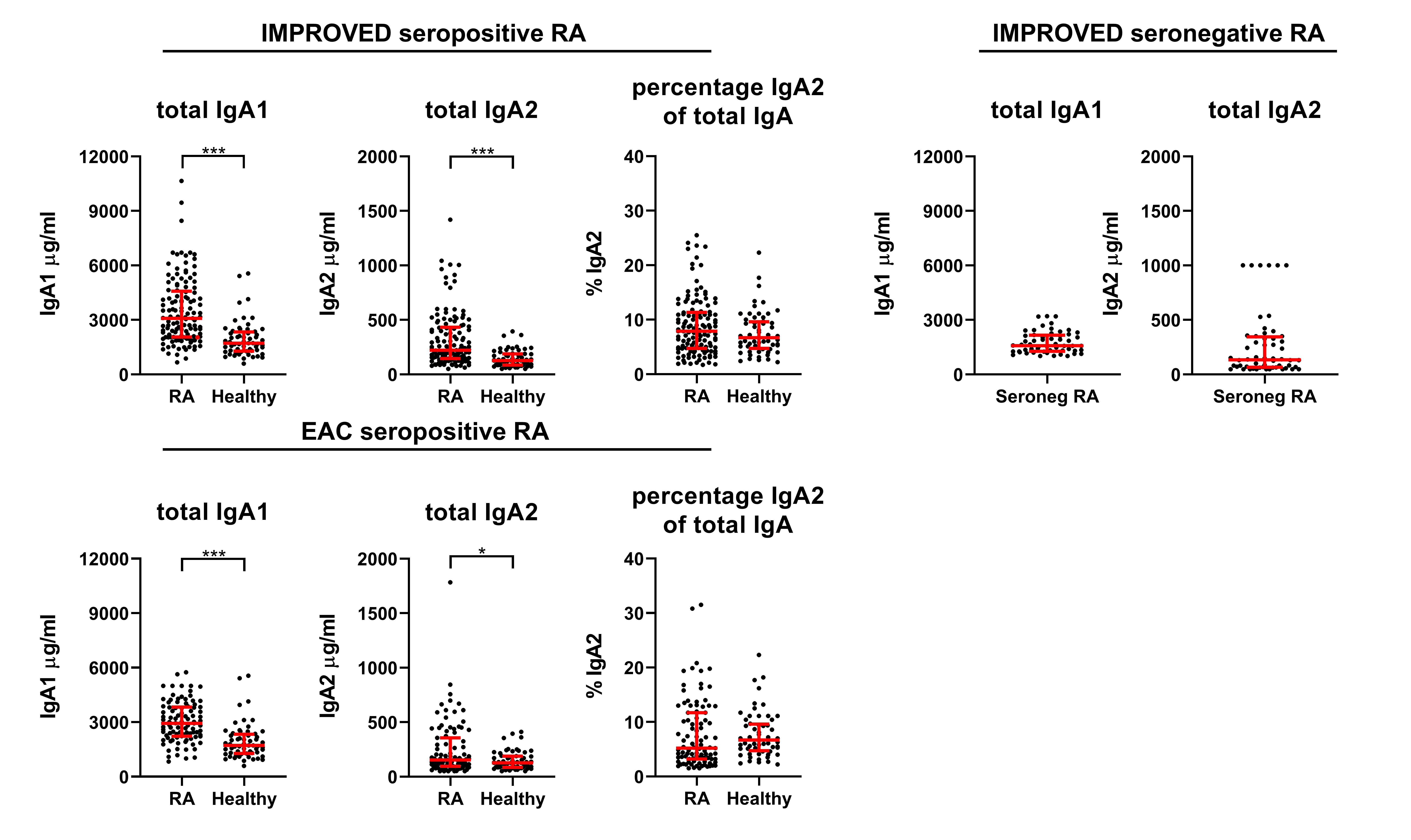
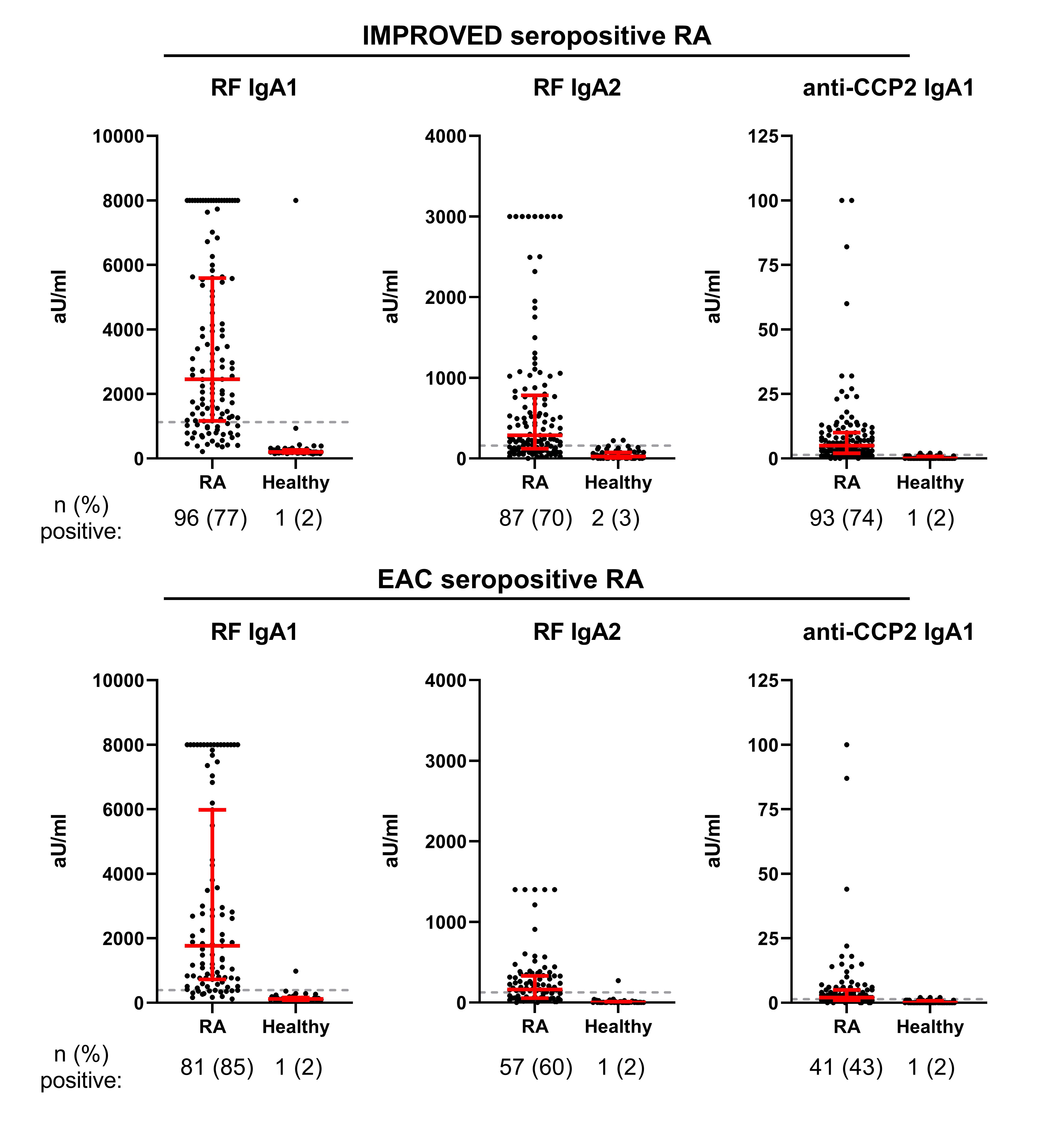
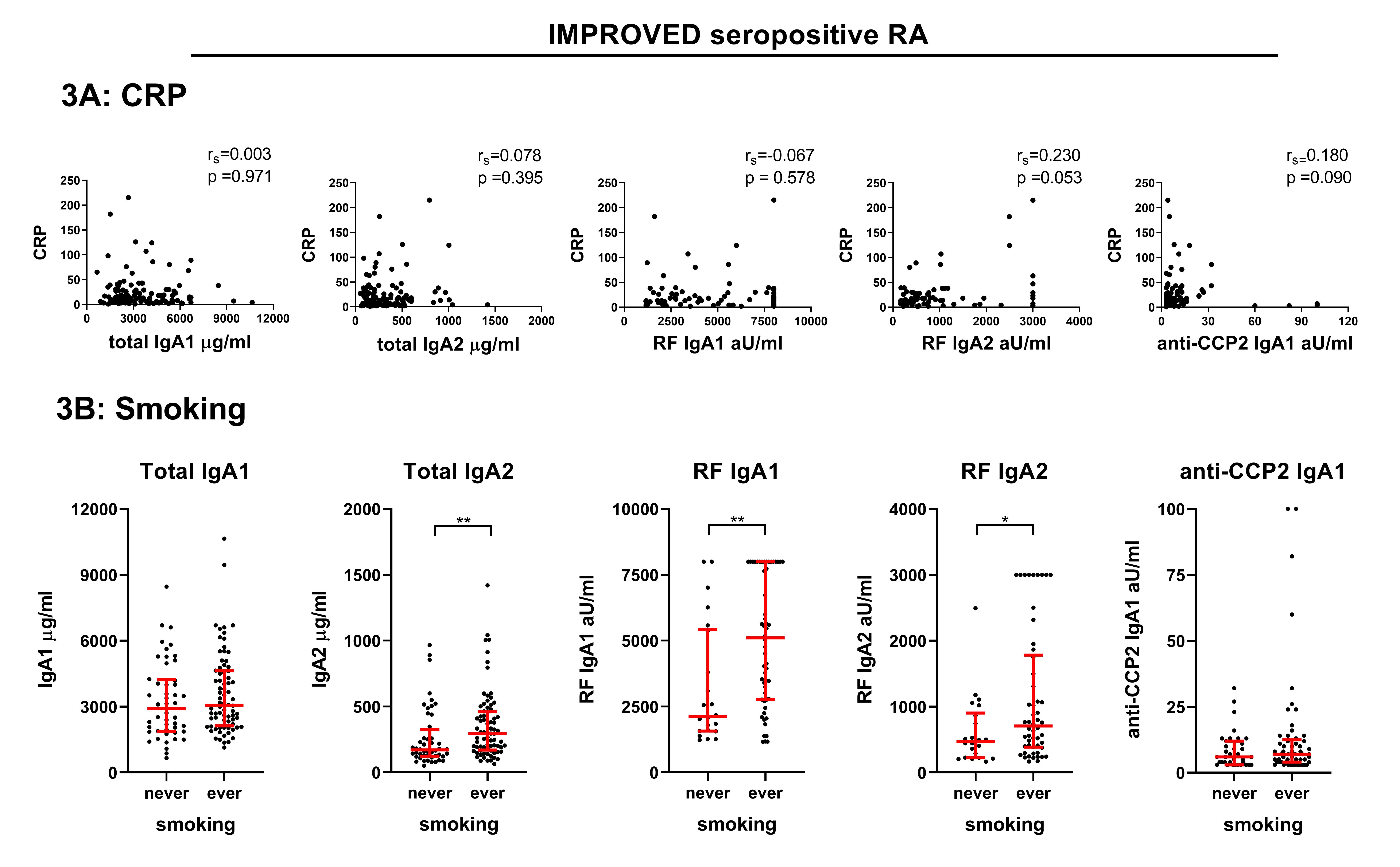
Results: Both total IgA1 and IgA2 were increased in seropositive RA, but not in seronegative RA patients in the IMPROVED (Figure 1). In seropositive RA, both IgA subclasses were raised to the same extent. RF and ACPA IgA1 and IgA2 were also detected in seropositive RA patients (Figure 2), but measurements of ACPA IgA2 levels proved challenging due to interference of RF IgA and are therefore not depicted. Although IgA2 has been postulated to be more proinflammatory, no relevant associations were found between total, RF and ACPA IgA subclass levels and CRP (Figure 3A, IMPROVED only) or DAS. In smoking seropositive RA patients, a selective minor increase in total IgA2, RF IgA1 and RF IgA2 was seen in both cohorts (Figure 3B, IMPROVED only), although all were non-significant in the EAC.
Conclusion: Seropositive RA patients have equally raised IgA1 and IgA2 levels and can also harbor RF and ACPA IgA subclasses. No indications of a mucosal source, such as a predominance of total IgA2, were found, although smokers might have slightly increased total IgA2. However, these results do consolidate the concept that seropositive versus seronegative RA have different pathophysiological traits, with seropositive patients perhaps displaying more aspecific B cell hyperreactivity.
References:
(1) Holers, Nat rev rheumatol 2018
(2) Woof, Mucosal immunol 2011
(3) Steffen, Nat commun 2020
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Derksen V, Allaart C, van der Helm-van Mil A, Huizinga T, Toes R, van der Woude D. Elevated IgA Subclass Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Indications of a Mucosal Origin? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-iga-subclass-levels-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-indications-of-a-mucosal-origin/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-iga-subclass-levels-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-indications-of-a-mucosal-origin/