Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Enthesitis (inflammation where the tendon, ligament, or joint capsule insert into the bone) has been associated with higher disease activity and reduced quality of life in patients (pts) with PsA,1 and is therefore recognized as an important domain to consider during treatment.2 Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of PsA, has been associated with improvements in enthesitis.3, 4 Here, we assessed the effects of tofacitinib on enthesitis by location and severity in pts with active PsA.
Methods: This post hoc analysis pooled data from 2 Phase 3 studies: OPAL Broaden (12 months; NCT01877668)4 and OPAL Beyond (6 months; NCT01882439)3, in pts with active PsA receiving tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily (BID) or placebo (up to Month [M]3); pts received a stable background dose of a single conventional synthetic DMARD. Enthesitis at baseline (BL) was defined as Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI)5 > 0 (no enthesitis: BL LEI=0); pts were stratified by BL enthesitis location (for each site, both left and right sides were assessed and results were combined) and severity (LEI site counts: 1/2/3–6 sites). Endpoints (assessed at M1/3/6) included change from BL in LEI score and presence of enthesitis. The proportion of pts without BL enthesitis (LEI=0) developing enthesitis at each location was also assessed.
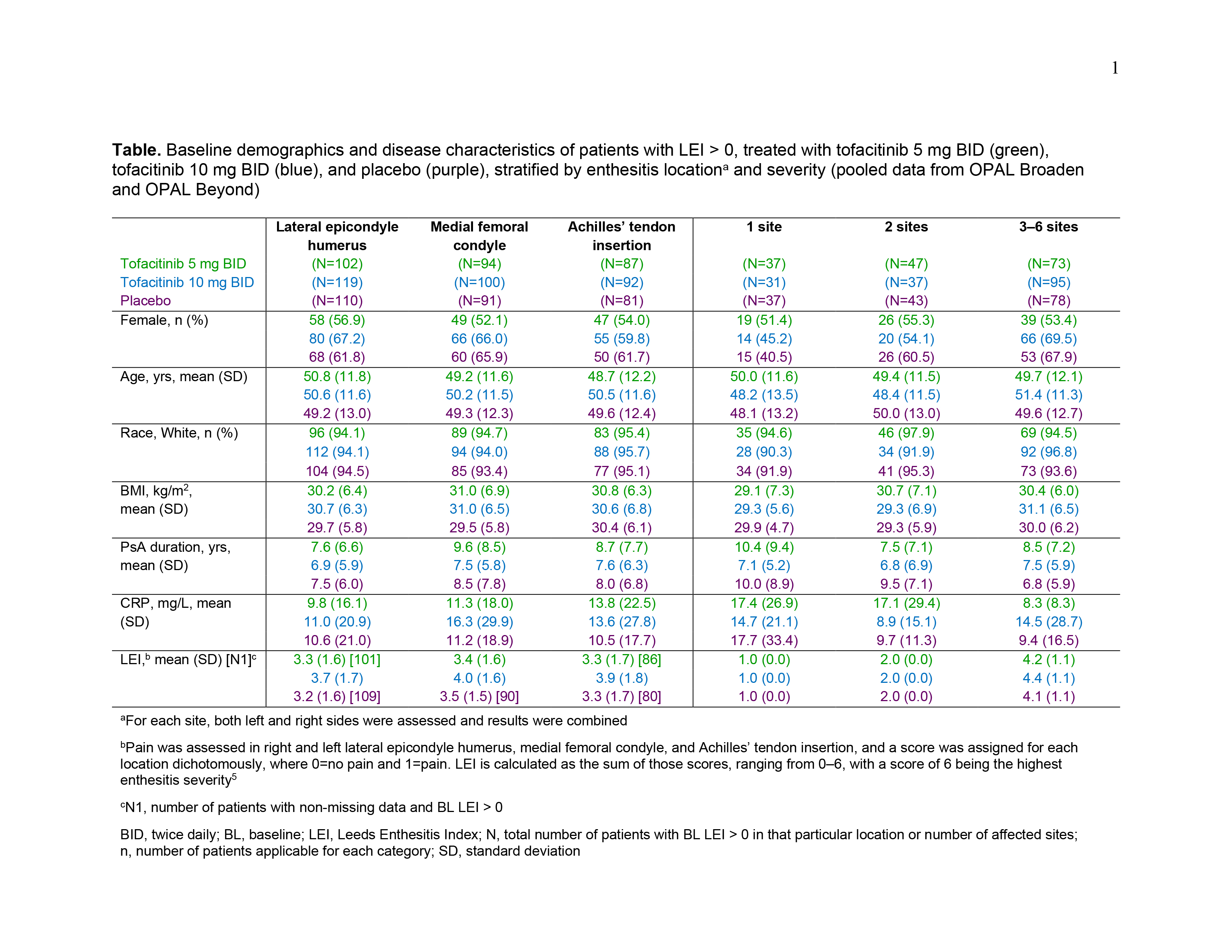
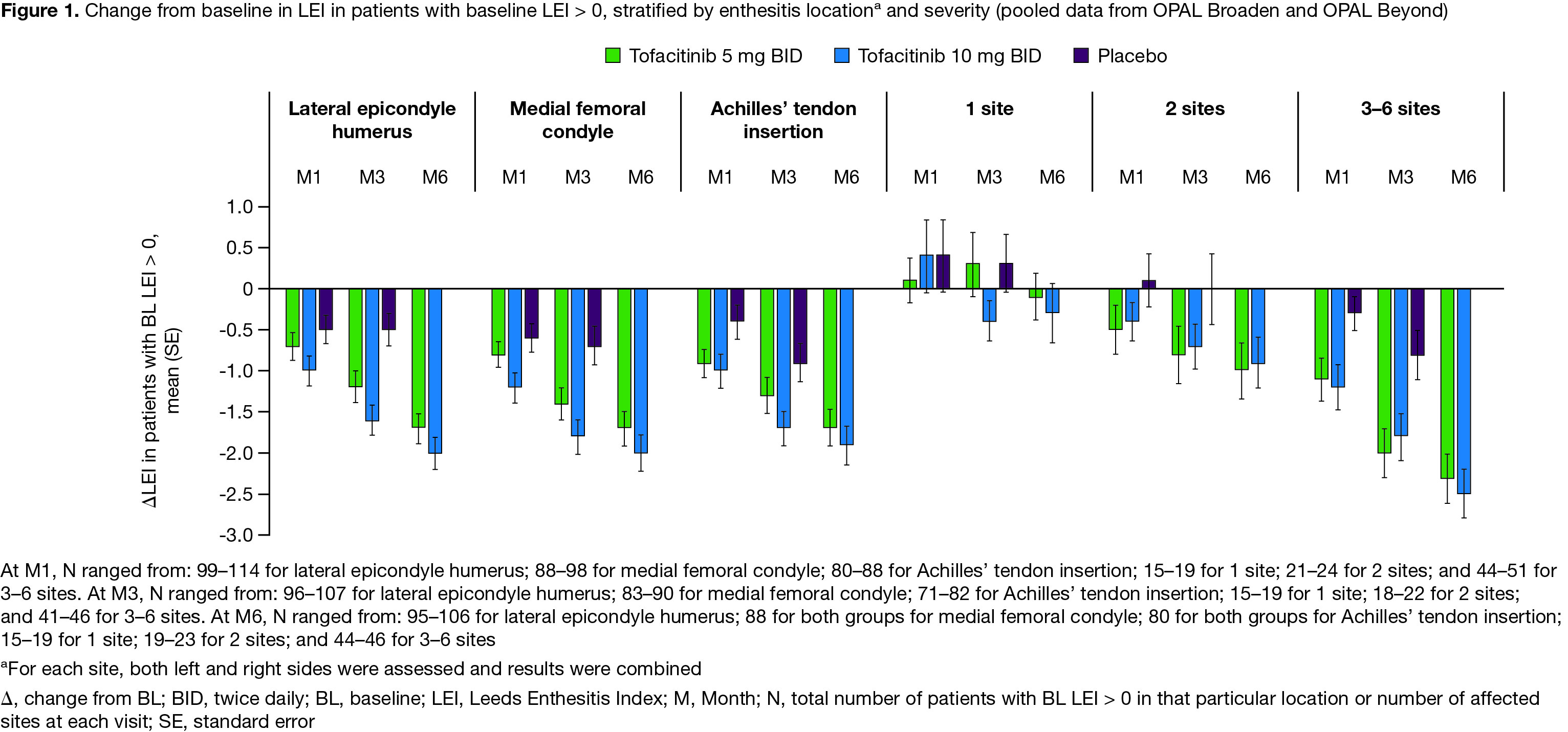
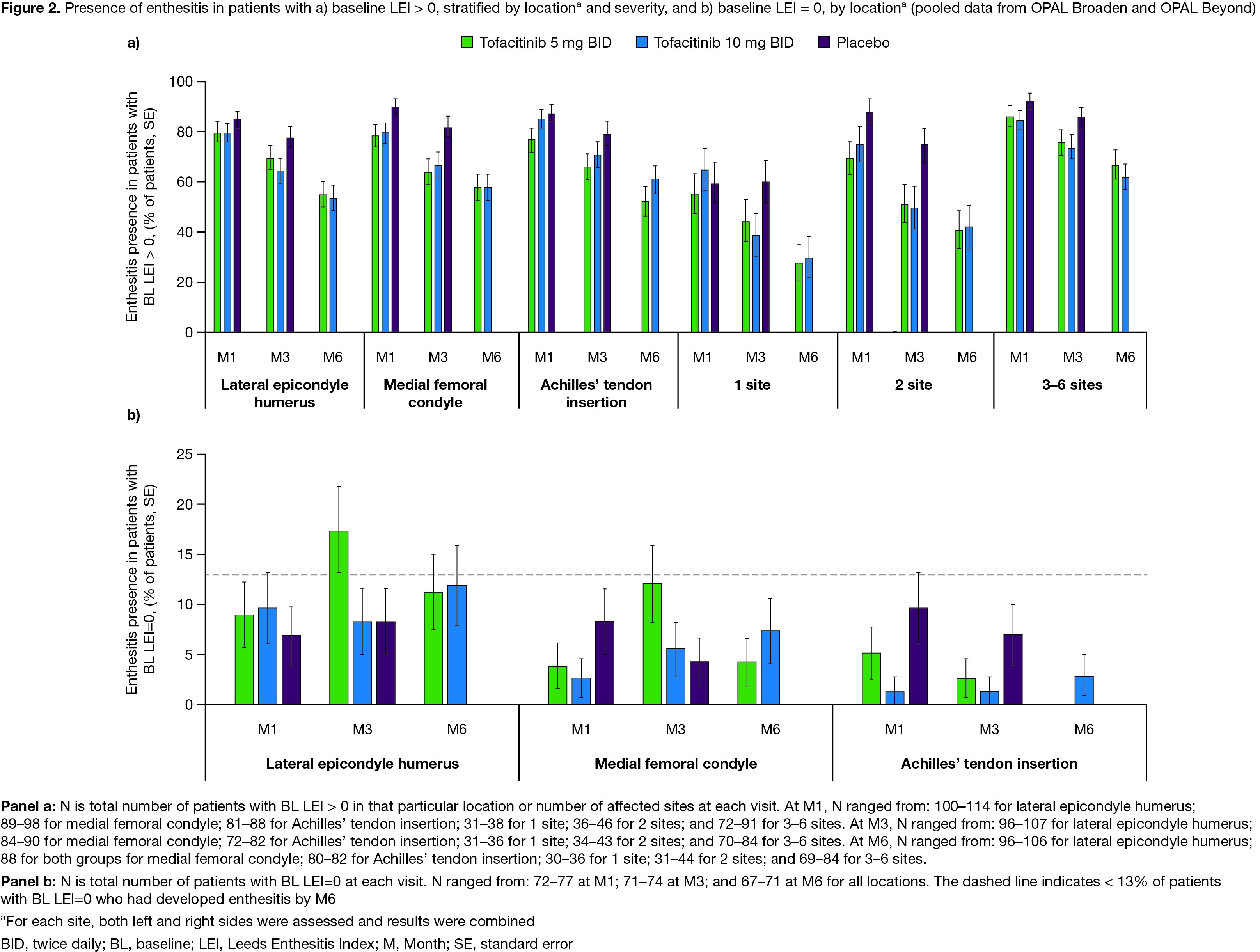
Results: Data were pooled from 479 pts with LEI > 0 and 227 pts with LEI=0 at BL. For pts with BL LEI > 0, demographics and disease characteristics were generally similar across treatment groups (Table). BL LEI scores across all locations were higher in pts treated with tofacitinib 10 mg BID; BL CRP was higher in pts with 2 affected sites treated with tofacitinib 5 mg BID and in pts with 3–6 affected sites treated with tofacitinib 10 mg BID compared with other treatment groups (Table). Improvements in LEI with tofacitinib were observed as early as M1 and maintained up to M6 across all locations and in pts with greater BL enthesitis severity (≥ 2 sites affected; Figure 1). By M3, fewer pts treated with tofacitinib vs placebo had enthesitis, regardless of BL location or severity (Figure 2a). At M6, the proportion of pts with enthesitis at the specified locations was generally reduced by ~ 50%; similar results were reported for pts with lower BL severity (1 or 2 affected sites; Figure 2a). For pts with high BL disease severity (3–6 affected sites), while the proportion of pts with enthesitis decreased over time from BL, enthesitis was present at M6 in about 2/3 of pts (Figure 2a). By M6, < 13% of pts with BL LEI=0 in each treatment group had developed enthesitis (Figure 2b).
Conclusion: In pts with PsA, tofacitinib treatment resulted in improvements in enthesitis, regardless of location or severity. Therefore, tofacitinib is a treatment option for pts with PsA who have enthesitis.
1. Kaeley GS et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2018; 48: 35-43.
2. Coates LC et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016; 68: 1060-71.
3. Gladman D et al. N Engl J Med 2017; 377: 1525-36.
4. Mease P et al. N Engl J Med 2017; 377: 1537-50.
5. Healy PJ, PS Helliwell. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 59: 686-91.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by J Juana, CMC Connect, funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Orbai A, FitzGerald O, Bedaiwi M, Fleishaker D, Mundayat R, Young P, Helliwell P. Efficacy of Tofacitinib on Enthesitis in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tofacitinib-on-enthesitis-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tofacitinib-on-enthesitis-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/