Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1365–1382) Sjögren’s Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by systemic involvement and lacks effective treatment options. The Janus kinase (JAK) pathway plays a pivotal role in cytokine signaling pathways that contribute to the pathogenesis of SS. This study aims to investigate the underlying mechanisms and therapeutic efficacy of the JAK inhibitor, tofacitinib, in primary Sjögren’s syndrome.
Methods: We enrolled 10 patients with active pSS and administered oral tofacitinib, assessing disease activity scores, laboratory parameters, and immune cell subsets. Additionally, NOD mice were treated with either tofacitinib or vehicle, and we evaluate saliva flow rates, immune cell subsets, and submandibular gland (SMG) pathology.
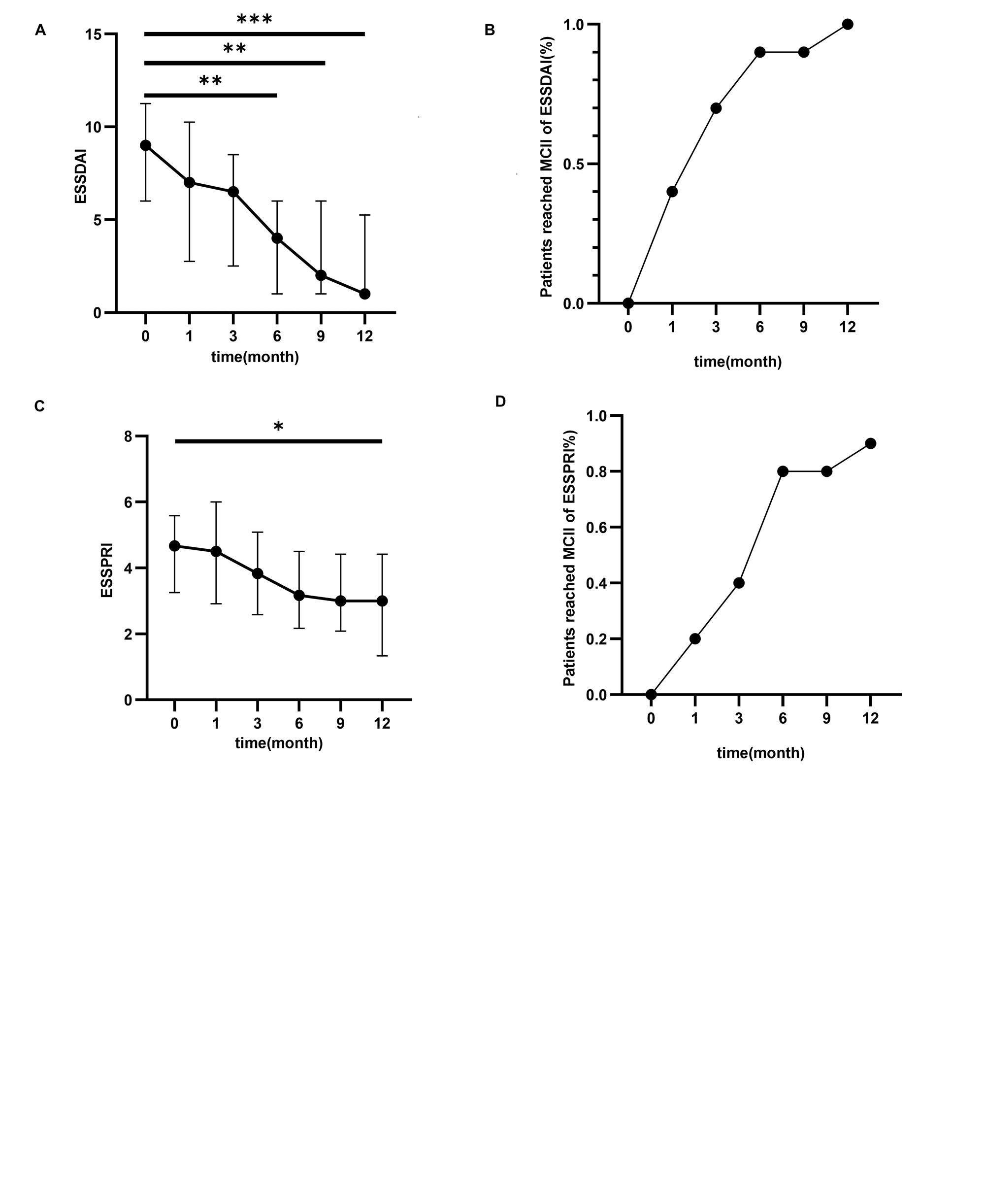
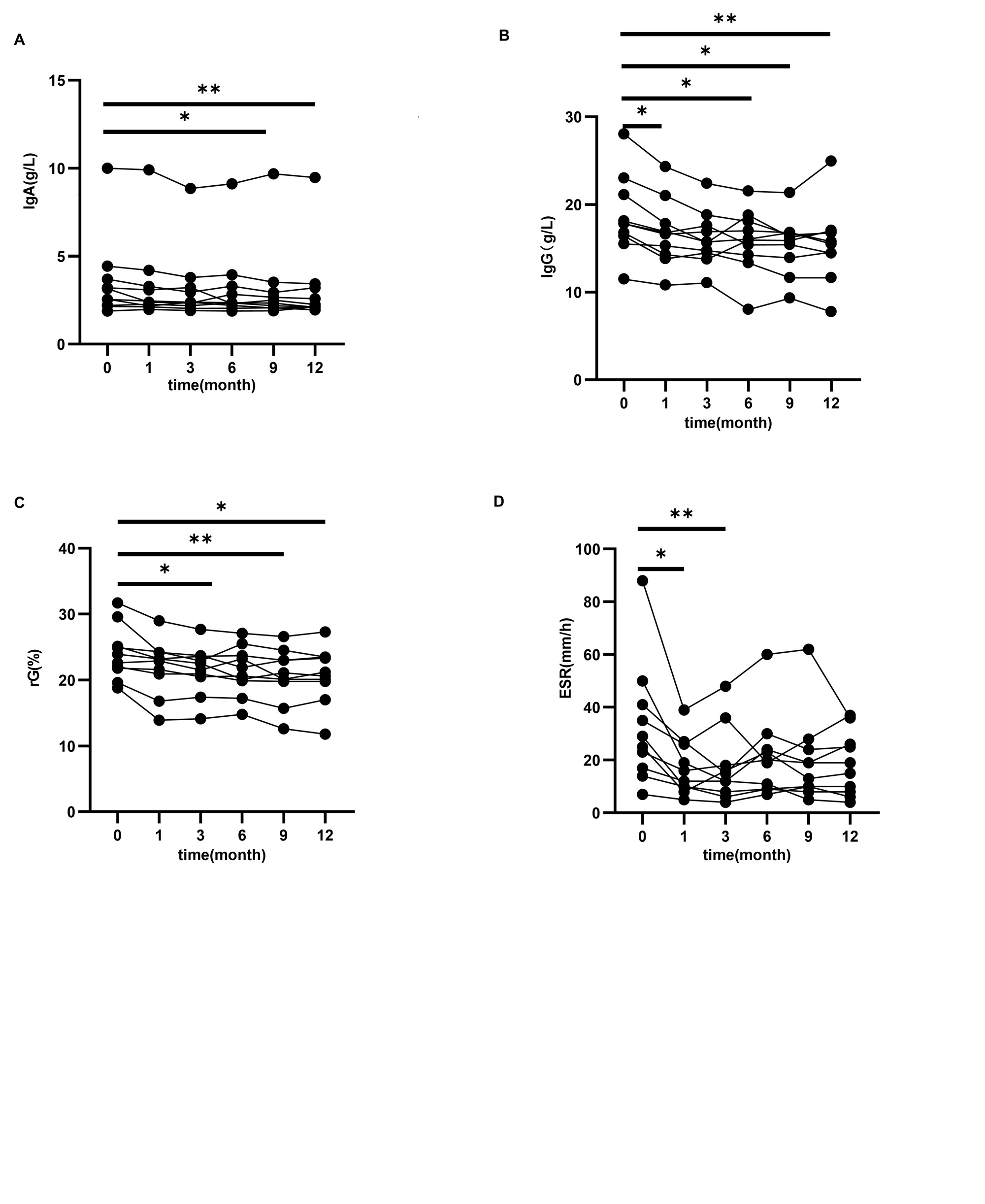
Results: Following tofacitinib treatment, a significant decrease in ESSDAI scores was observed at the 6th compared to baseline ( 9(6, 11.25) vs 4(1, 6), (p=0.002)).Additionally, at 6 months, 80% of patients achieved MCII of ESSPRI, which was defined as an improvement of ESSPRI at least one point or 15%.Notably, arthritis exhibited significant improvement at the 6th month compared to baseline (p=0.020). No serious adverse events were observed. In tofacitinib-treated mice, the results demonstrated a significant increase in saliva production compared to the control group from weeks 8 to 14 (4.20( 3.29, 4.41)mg/min vs 5.74( 4.44,6.15)mg/min, p=0.033), and SMGs exhibited fewer lymphocytic infiltrations and foci under a photomicroscope. Finally, immunological analysis revealed that both NOD mice and pSS patients exhibited a decrease in effector follicular helper T (Tfh) cells and peripheral helper T cells (Tph cells), which correlated positively with the level of pSTAT-3 in CD4+ T cells and disease activity scores.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that the dosage of 5 mg tofacitinib twice a day proven to be effective and safe for the management of pSS. Tofacitinib inhibits the progression of pSS in both murine models and patients, potentially through the regulation of T cell differentiation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liu Q, He J. Efficacy of Tofacitinib Immunotherapy Suppresses Tfh and Tph Cells in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tofacitinib-immunotherapy-suppresses-tfh-and-tph-cells-in-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tofacitinib-immunotherapy-suppresses-tfh-and-tph-cells-in-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome/