Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with poor prognostic factors (PPF) are at risk for RA progression if disease activity is not rapidly controlled. In FINCH 3 (NCT02886728), filgotinib (FIL) — an oral, potent, selective JAK1 inhibitor — was effective relative to methotrexate monotherapy (MTX mono) in MTX-naïve patients with ≥1 PPF—erosions, seropositivity for rheumatoid factor (RF) or anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP), or hsCRP ≥4 mg/L.1 This post hoc analysis examined FIL efficacy in FINCH 3 pts with multiple PPF.
Methods: The global, phase 3, double-blind, active-controlled FINCH 3 study randomized MTX-naïve pts with moderately to severely active RA 2:1:1:2 to oral FIL 200 mg once daily + MTX ≤20 mg weekly, FIL 100 mg + MTX, FIL 200 mg mono, or PBO + MTX up to week (W)52. This subgroup analysis included pts with all 4 of the following PPF at baseline (PPF pts): erosions, seropositivity for RF or anti-CCP, hsCRP ≥4 mg/L, and DAS(28)CRP >5.1. Comparisons were not adjusted for multiplicity.
Results: Of 1249 pts randomized and treated in FINCH 3, 510 had all 4 PPF. At baseline, relative to the overall FINCH 3 population, PPF pts had longer mean disease duration (2.4 vs
2.2 years); higher mean hsCRP (27.9 vs 17.5 mg/L), mTSS (17.9 vs 13.3), DAS28(CRP) (6.3 vs 5.7), HAQ-DI (1.76 vs 1.56), CDAI (44.3 vs 39.8), and SDAI (47.1 vs 41.5); and greater frequency of seropositivity for RF (90.6% vs 67.9%), anti-CCP (92.4% vs 68.5%), or both
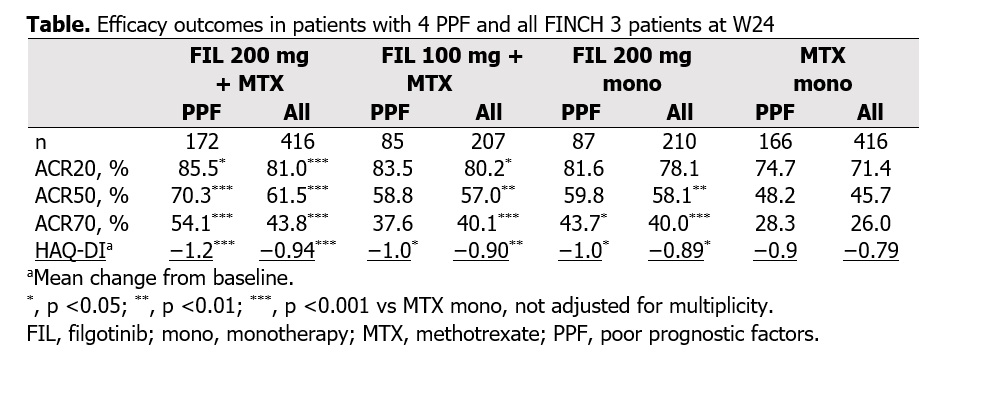
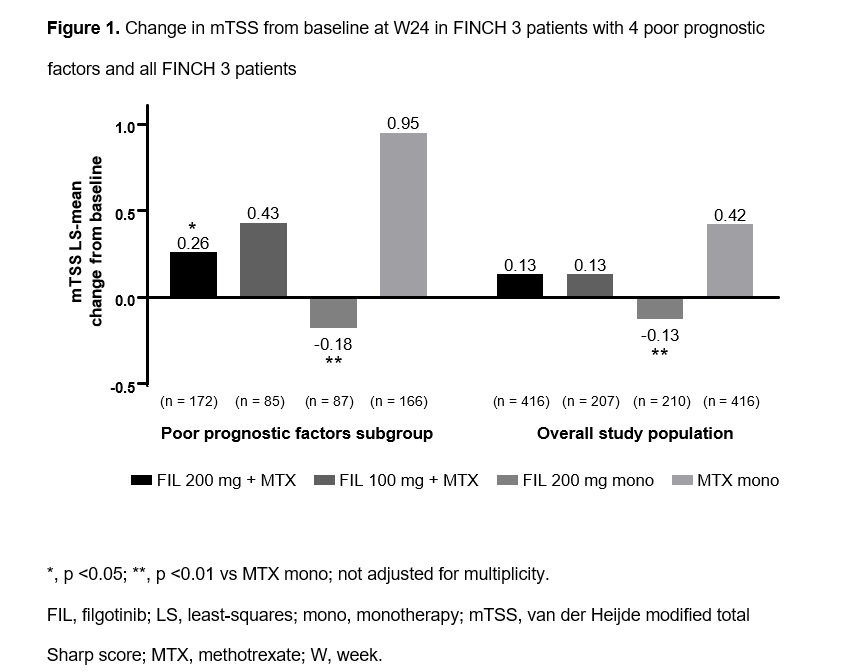
(82.9% vs 59.6%). Efficacy in PPF pts was comparable to data from all FINCH 3 pts (Table, Figures 1–2). PPF pts receiving FIL 200 mg with or without MTX vs MTX mono had higher frequencies of ACR20/50/70 response and greater improvement in HAQ-DI at W24; responses were numerically greater for FIL 200 mg + MTX vs FIL 100 mg + MTX or FIL 200 mg mono (Table) and were evident by W12 (data not shown). Radiographic progression at W24 was lower in PPF pts receiving FIL 200 mg + MTX or FIL 200 mg mono vs MTX mono (Figure 1).
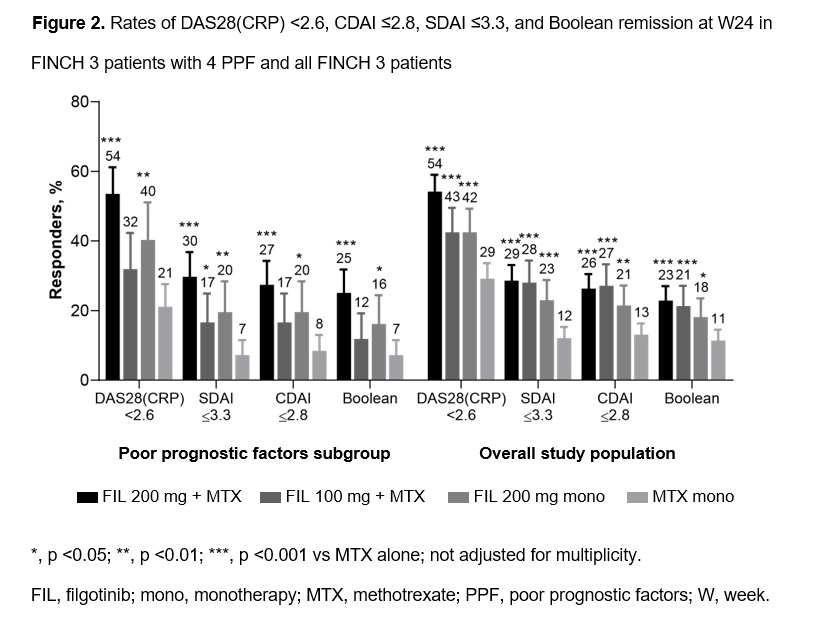
Proportions of PPF pts receiving FIL 200 mg with or without MTX who achieved DAS28(CRP) < 2.6, CDAI ≤2.8, SDAI ≤3.3, and Boolean remission at W24 (Figure 2) were larger vs pts receiving MTX mono and numerically greater vs pts receiving FIL 100 mg + MTX.
Conclusion: FIL treatment provided rapid and deep disease control including higher rates of remission and other clinical outcomes, improved physical function, and less radiographic progression compared with MTX alone in MTX-naïve pts with RA with 4 PPF, a population at risk for severe progressive disease. In pts with 4 PPF, W24 remission rates following FIL 200 mg with or without MTX were higher vs MTX mono and numerically higher vs FIL 100 mg + MTX.
- Westhovens et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78(Suppl2):259–60.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aletaha D, Westhovens R, Gaujoux-Viala C, Adami G, Matsumoto A, Bird P, Messina O, Buch M, Bartok B, Yin Z, Guo Y, Hendrikx T, Burmester G. Efficacy of Filgotinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Poor Prognostic Factors: Post Hoc Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-filgotinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-poor-prognostic-factors-post-hoc-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-filgotinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-poor-prognostic-factors-post-hoc-analysis/