Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Apremilast is an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor with a unique immunomodulatory mechanism of action and is approved for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) is a promising tool for inflammatory arthritis management and may provide a more thorough picture of total inflammatory burden than standard MRI or clinical assessment. Here, we evaluate the efficacy of apremilast 30 mg BID (APR) on peripheral and axial inflammation in patients with PsA.
Methods: The MOSAIC study was a phase 4, multicenter, single-arm, open-label trial that evaluated up to 48 weeks of APR treatment (monotherapy or with stable methotrexate) on MRI outcomes in patients with active PsA (≥3 months but ≤5 years since diagnosis, meeting the CASPAR criteria for PsA). Contrast-enhanced WB-MRI was performed at baseline, Week 24, and Week 48, and images were read and adjudicated by two blinded, experienced readers. Using the OMERACT MRI whole‑body scoring system for inflammation in peripheral joints and entheses (MRI‑WIPE), WB-MRI results were used to calculate the change from baseline in the peripheral enthesitis inflammation index (33 entheses), peripheral joint inflammation index (83 joints), and total peripheral inflammation index (enthesitis + joint inflammation). In patients deemed to have PsA spondylitis by the investigator and a baseline BASDAI Item 2 (pain) ≥4), MRI axial inflammation was assessed by calculating the change from baseline in the Canada-Denmark (CANDEN) spine score, the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) spine score, and the SPARCC sacroiliac joint (SIJ) inflammation score.
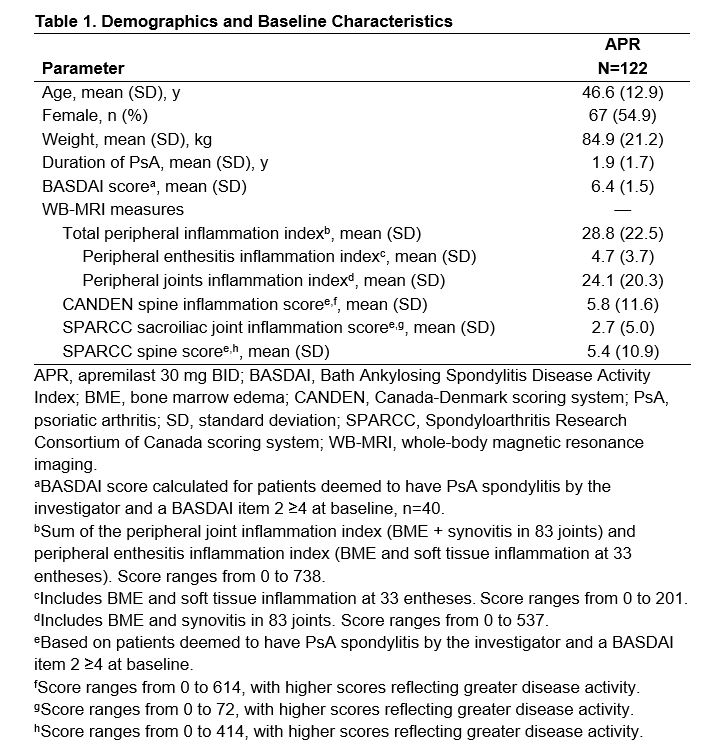
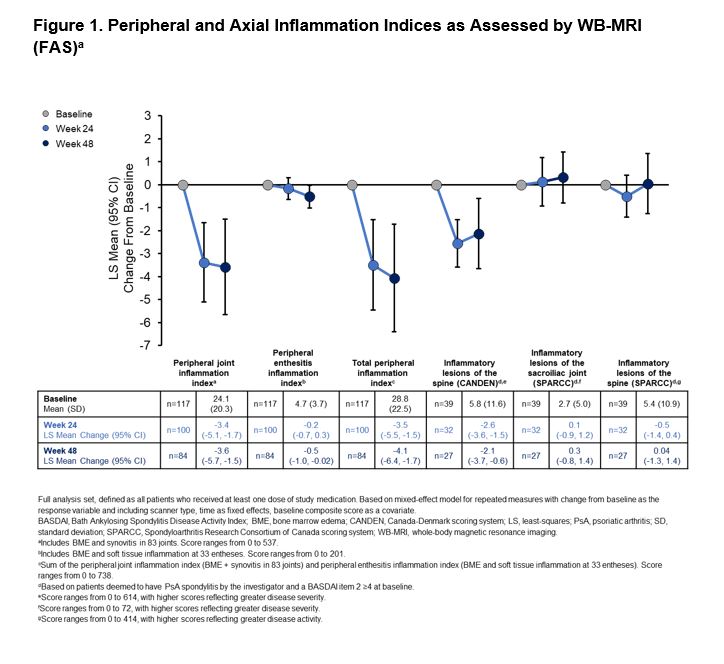
Results: A total of 122 patients were enrolled and treated with APR. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics are shown in Table 1. WB-MRI results showed significant reductions in peripheral joint inflammation at 24 and 48 weeks, and a significant reduction in peripheral enthesitis at 48 weeks (Figure 1). Taken together, a significant reduction in the total peripheral inflammation index was observed at both 24 and 48 weeks (Figure 1). At baseline, 40 patients were deemed by the investigator to have PsA spondylitis and a BASDAI Item 2 ≥4; 39 patients were analyzed for axial inflammation. WB-MRI using the CANDEN scoring system showed a reduction in axial inflammation at 24 and 48 weeks (Figure 1). There was no significant change in either SPARCC spine or SPARCC SIJ scores (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This is the first PsA study applying WB-MRI of both peripheral and axial joints and entheses. Patients treated with APR experienced significant improvement from baseline in peripheral joint and entheseal inflammation. These outcomes demonstrate the efficacy of APR on inflammatory manifestations of PsA and the value of using WB-MRI as an objective measure in PsA management.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Østergaard M, Boesen M, Maksymowych W, Lambert R, Valenzuela G, Bubb M, Kubassova O, Reddy J, Colgan S, Klyachkin Y, Deignan C, Zhou Z, Mease P. Efficacy of Apremilast on Peripheral and Axial Inflammation in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Based on Whole-Body Magnetic Resonance Imaging [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-apremilast-on-peripheral-and-axial-inflammation-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-based-on-whole-body-magnetic-resonance-imaging/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-apremilast-on-peripheral-and-axial-inflammation-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-based-on-whole-body-magnetic-resonance-imaging/