Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical (0496–0501)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:45PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: INCREASE was a 16-week trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of inhaled treprostinil (iTRE) in patients with pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD). The study met its primary efficacy endpoint of change in 6-minute walking distance (6MWD), demonstrated by a 31m improvement from baseline (260m). Secondary endpoints, including change in N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and time to clinical worsening, were also met. Post-hoc analyses were conducted to investigate clinical endpoints within patient subgroups.
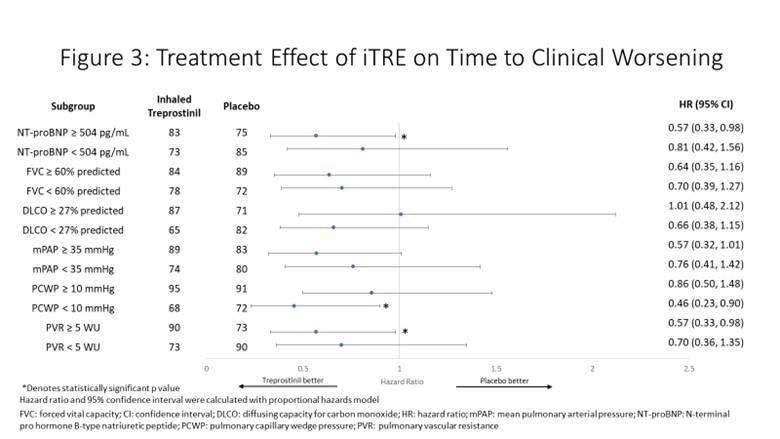
Methods: All 326 patients randomized in INCREASE were included in the present analyses, of which 72 patients (iTre 40, placebo 32) had connective tissue disease as the cause of their underlying lung disease. Patient subgroups were delineated by median values of the following baseline characteristics: PVR (< 5 WU, ≥5WU), PCWP (< 10 mmHg, ≥10 mmHg), mPAP (< 35 mmHg, ≥35 mmHg), DLCO (< 27% predicted, ≥27% predicted), FVC (< 60% predicted, ≥60% predicted) and NT-proBNP (< 504 pg/mL, ≥504 pg/mL). Clinical worsening was defined as any of the following: cardiopulmonary hospitalization, decrease in 6MWD >15% from baseline, all-cause death, or lung transplantation.
Results: 6MWD improvements were demonstrated in all subgroups. Statistically significant improvements occurred in patients with above median PVR, PCWP, mPAP; lower than median DLCO; and in both above median and below median FVC and NT-proBNP cohorts (p≤0.013 for all). Statistically significant reductions in NT-proBNP were demonstrated in all subgroups (p≤0.028 for all). Statistically significant benefit in time to clinical worsening with iTRE was observed in above median PVR, mPAP, and NT-proBNP; and lower PCWP (p≤0.0493 for all). Overall, response separation in clinical endpoints indicated greater improvement for patients with above median NT-proBNP and PVR. A similar trend of benefit was observed in lower DLCO and higher mPAP subgroups.
Conclusion: These analyses demonstrate improvements in clinical endpoints with inhaled treprostinil across patient subgroups. Patients with more advanced pulmonary vascular disease stand to gain the most benefit with inhaled treprostinil therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tapson V, Nathan S, Girgis R, Runo J, Bag R, Talwar A, Smith P, Edwards L, Park C, Waxman A. Efficacy in Patient Subgroups in the INCREASE Trial, a Phase III Trial to Evaluate Inhaled Treprostinil in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Parenchymal Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-in-patient-subgroups-in-the-increase-trial-a-phase-iii-trial-to-evaluate-inhaled-treprostinil-in-patients-with-pulmonary-hypertension-due-to-parenchymal-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-in-patient-subgroups-in-the-increase-trial-a-phase-iii-trial-to-evaluate-inhaled-treprostinil-in-patients-with-pulmonary-hypertension-due-to-parenchymal-lung-disease/