Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: 5T107 ACR Abstract: Pediatric Rheum–Clinical II: Treatment Update (2862–2867)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
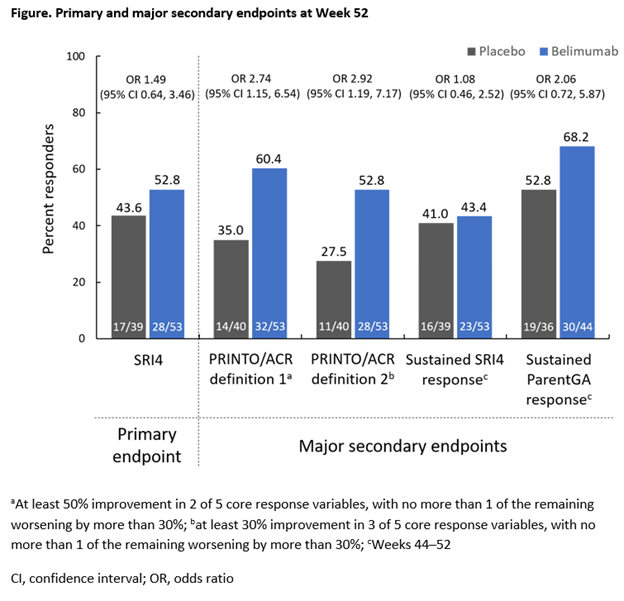
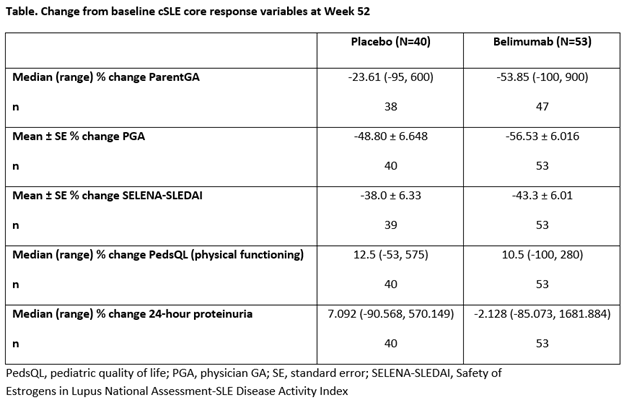
<>Background/Purpose: Belimumab (BEL) is approved in adults with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). There are no approved biologic therapies for pediatric patients with childhood-onset SLE (cSLE). This Phase 2, multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial (NCT01649765) evaluated the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of intravenous (IV) BEL vs placebo (PBO), plus standard therapy (SoC), in cSLE. <>Methods: Patients with cSLE aged 5–17 years were randomized to BEL 10 mg/kg IV or PBO every 4 weeks, plus SoC. The primary endpoint was SLE Responder Index 4 (SRI4) at Week (Wk) 52. Major secondary endpoints were: proportion of patients achieving the Pediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organization/ACR (PRINTO/ACR) cSLE Evaluation criteria for improvement using two definitions at Wk 52; cSLE core response variables at Wk 52 (Table); and sustained SRI4 and Parent Global Assessment (ParentGA) responses (Wks 44–52). Other secondary endpoints included time to first severe flare (modified SELENA-SLEDAI Flare Index). Safety and PK were assessed. The study was not powered for statistical testing.
Disclosure: H. I. Brunner, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), F. Hoffman-La Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi Aventis, Merck Serono, 5,AbbVie, Amgen, Biogenidec, Alter, AstraZeneca, Baxalta Biosimilars, Biogenidec, Boehringer, BMS, Celgene, CrescendoBio, EMD Serono, F. Hoffman-La Roche, Janssen, MedImmune, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi Aventis, Takeda, and UCB Biosciences GmbH, 5; C. Abud-Mendoza, None; D. I. Viola, None; I. Calvo, None; D. M. Levy, None; J. Calderon Gallegos, None; M. Ferrandiz, None; V. Chasnyk, None; V. Keltsev, None; J. Anton, None; M. Paz, None; M. Shishov, None; A. L. Boteanu, None; M. Henrickson, None; D. Bass, GSK, 1, 3; K. Clark, GSK, 1, 3; A. Hammer, GSK, 1, 3; B. Ji, GSK, 1, 3; D. Roth, GSK, 1, 3; H. Struemper, GSK, 1, 3; M. L. Wang, GSK, 1, 3; A. Martini, Abbvie, Biogen, Boehringer, Bristol Myers and Squibb, EMD Serono, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, R-Pharm on behalf of the Gaslini Institute, 5; D. J. Lovell, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Abbott, Pfizer, 5,Wyeth Pharma, 8; N. Ruperto, Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, Biogenidec, Astellas, Alter, AstraZeneca, Baxalta Biosimilars, Boehringer, BMS, CD-Pharma,Celgene, CrescendoBio, EMD Serono, Hoffman-La Roche, Italfarmaco, Janssen, MedImmune, Medac, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rewind Arms, 5, 6, 7, 8,R-Pharma, Sanofi Aventis, Servier, Sinergie, Takeda, Vertex, UCB Biosciences GmbH., 5, 6, 7, 8,BMS, "Francesco Angelini", GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Hoffman-La Roche, Italfarmaco, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi Aventis, Schwarz Biosciences, Sobi, Xoma, Wyeth., 2.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brunner HI, Abud-Mendoza C, Viola DI, Calvo I, Levy DM, Calderon Gallegos J, Ferrandiz M, Chasnyk V, Keltsev V, Anton J, Paz M, Shishov M, Boteanu AL, Henrickson M, Bass D, Clark K, Hammer A, Ji B, Roth D, Struemper H, Wang ML, Martini A, Lovell DJ, Ruperto N. Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Belimumab in Children with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-intravenous-belimumab-in-children-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-intravenous-belimumab-in-children-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/