Session Information
Session Type: ACR Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) accompanied by anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5)-positive dermatomyositis (DM) is often rapidly progressive and associated with poor life prognosis in Japanese patients. However, the standard treatment for such intractable cases had not been established, although some case reports have suggested possible efficacy of combined immunosuppressive therapy. Therefore, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of combined immunosuppressive regimen as a prospective trial for anti-MDA5-positive DM with ILD.
Methods: Anti-MDA5 was detected by protein-immunoprecipitation using 35S-methionine-labeled HeLa cells. Newly onset adult Japanese anti-MDA5-positive DM patients with ILD were enrolled in multi-centers from July 2014 to September 2017. They were treated with combined immunosuppressive regimen of high-dose glucocorticoids (GC), tacrolimus, and intravenous cyclophosphamide. Plasmapheresis was also added if the patients got worse and needed oxygenation even after the regimen started. As the primary endpoint, their six-month survival was compared with a historical control of anti-MDA5-positive DM with ILD who received step-up treatment started with high-dose GC and gradually intensified by the addition of immunosuppressants. The alteration of serum ferritin level, anti-MDA5 titer (MESACUP™ anti-MDA5 test), and respiratory functions were also compared before and after treatment.
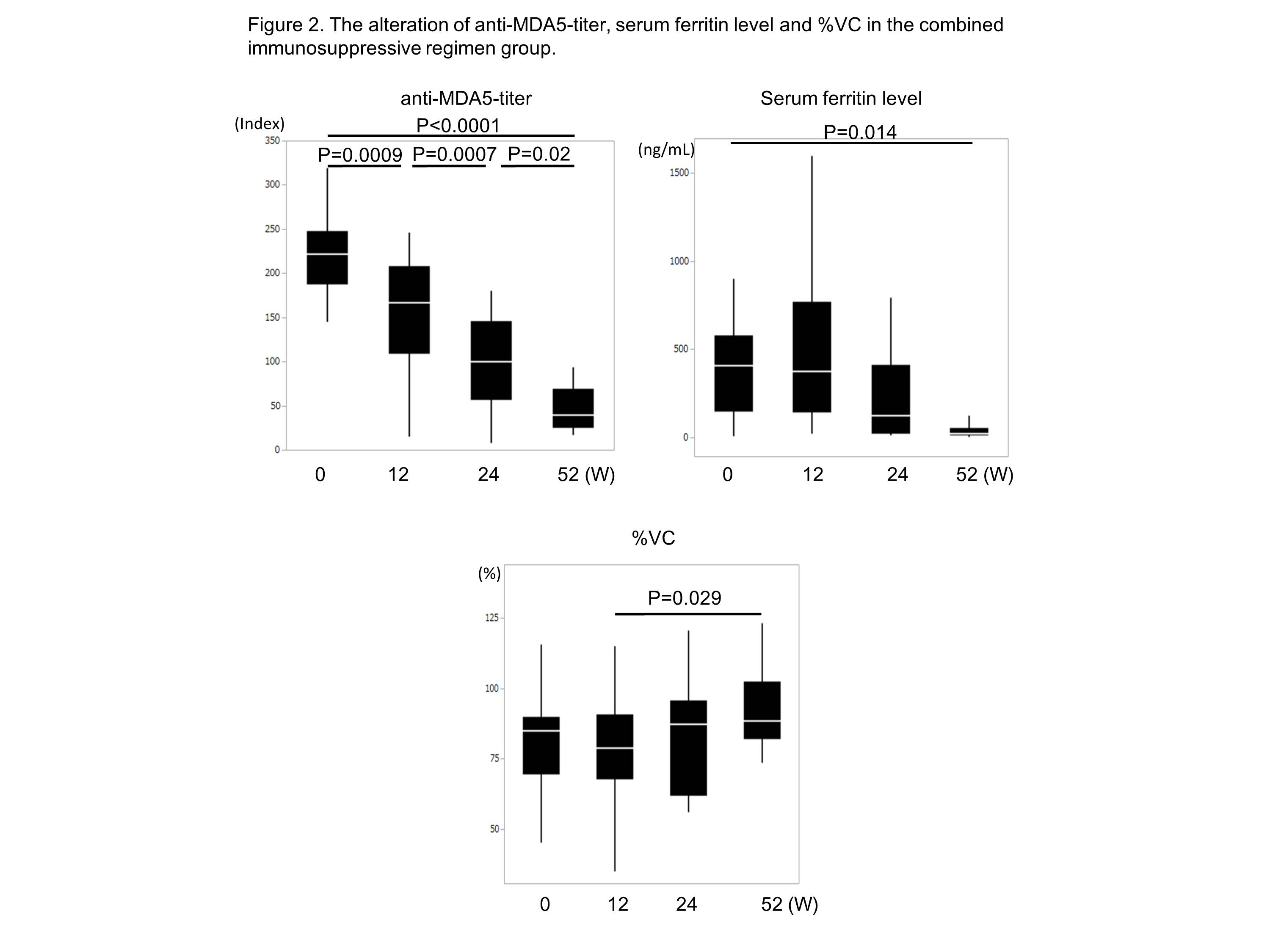
Results: The combined immunosuppressive regimen group (n=26) showed significantly better survival than the historical control (n=15) (6-month survival; 89% and 33%, respectively, p<0.0001) (Figure 1). At week 52, anti-MDA5-titer and serum ferritin level were decreased and %vital capacity was increased (Figure 2). During 52 weeks, cytomegalovirus reactivation was frequently observed in the combined immunosuppressive regimen group (90% vs 33%, respectively, p=0.0002). When the survived (18 cases) and the deceased (4 cases) in combined immunosuppressive regimen group were compared, frequency of skin ulcer (11% vs 75%, respectively, p=0.01), positivity of CRP (39% vs 100%, respectively, p=0.01), and serum ferritin level (468.3±561.8 ng/mL vs 2050.3±1772.8 ng/mL, respectively, p=0.01) before treatment were significantly higher in the deceased patients.
Conclusion: Early treatment with combination immunosuppressive therapy improves the survival of anti-MDA5-positive DM with ILD. Opportunistic infections such as cytomegalovirus reactivation should be carefully monitored and treated during the treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tsuji H, Nakashima R, Imura Y, Yagita M, Yoshifuji H, Hirata S, Nojima T, Sugiyama E, Hatta K, Taguchi Y, Katayama M, Akizuki S, Murakami K, Hashimoto M, Tanaka M, Ohmura K, Mimori T. Efficacy and Safety of Combined Immunosuppressive Therapy with High-Dose Glucocorticoid, Tacrolimus, and Cyclophosphamide in Interstitial Lung Disease Accompanied By Anti-MDA5-Positive Dermatomyositis -a Multicenter Prospective Study – [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-combined-immunosuppressive-therapy-with-high-dose-glucocorticoid-tacrolimus-and-cyclophosphamide-in-interstitial-lung-disease-accompanied-by-anti-mda5-positive-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-combined-immunosuppressive-therapy-with-high-dose-glucocorticoid-tacrolimus-and-cyclophosphamide-in-interstitial-lung-disease-accompanied-by-anti-mda5-positive-dermatomyositis/
