Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment with methotrexate (MTX) has been shown to be associated with lower cardiovascular risk and lower blood pressure (BP) compared with other disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in cross-sectional and epidemiological studies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the evidence in longitudinal, randomized trials is lacking. We sought to address this issue by performing a randomized trial comparing the effect of MTX on BP against a control group on sulfasalazine.
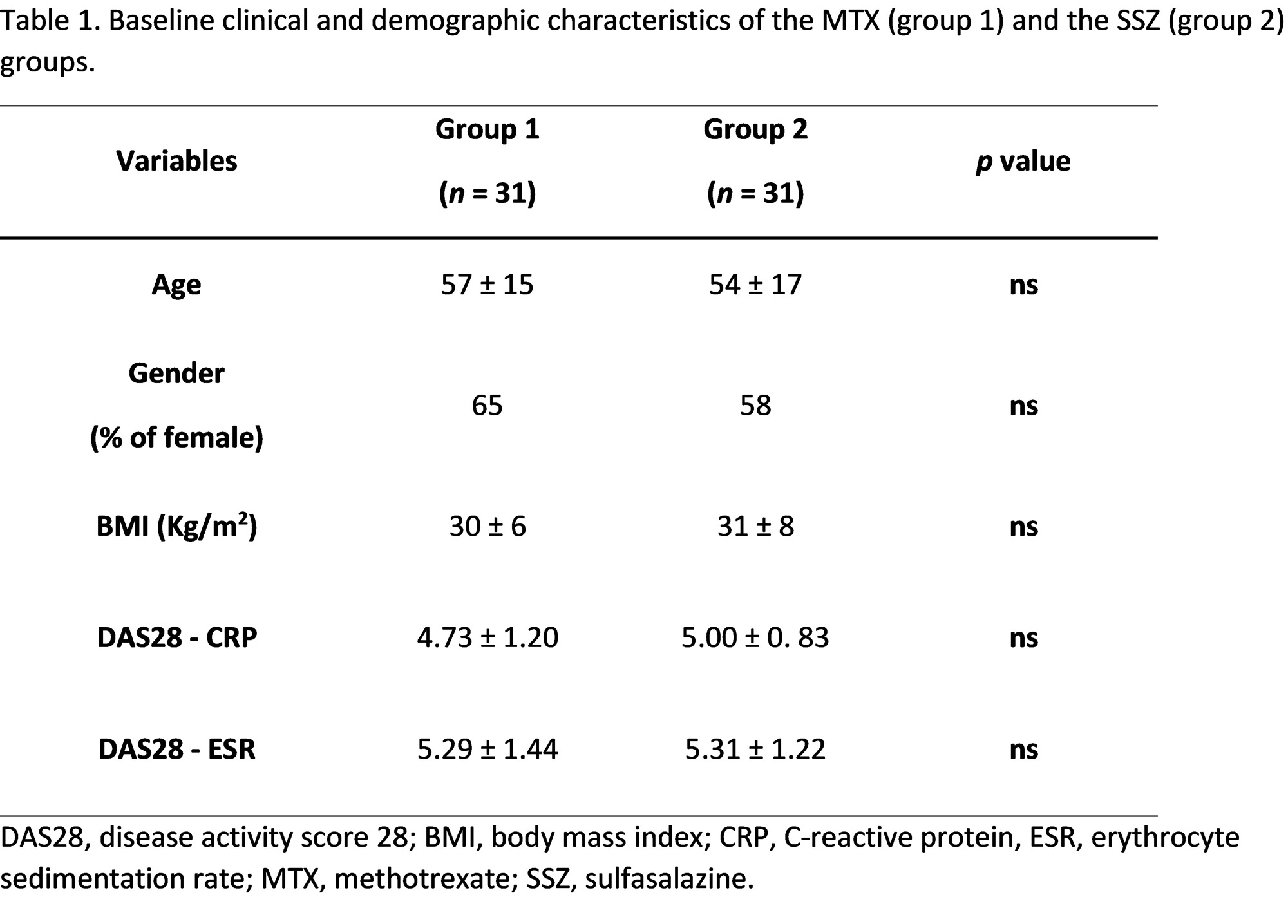
Methods: Adult treatment-naïve patients, recently diagnosed with RA according to the 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria, were randomized to clinically guided doses of subcutaneous MTX (Group 1, n=31, age 57±15 years, 65% females) or the DMARD sulfasalazine (SSZ, Group 2, n=31, age 54±17 years, 58% females). Clinic systolic (SBP, primary study endpoint), diastolic (DBP), and mean arterial pressure (MAP), and the augmentation index (AIx), (a marker of arterial wave reflection) were measured at baseline (before treatment), and after 1 and 6 months (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03254589).
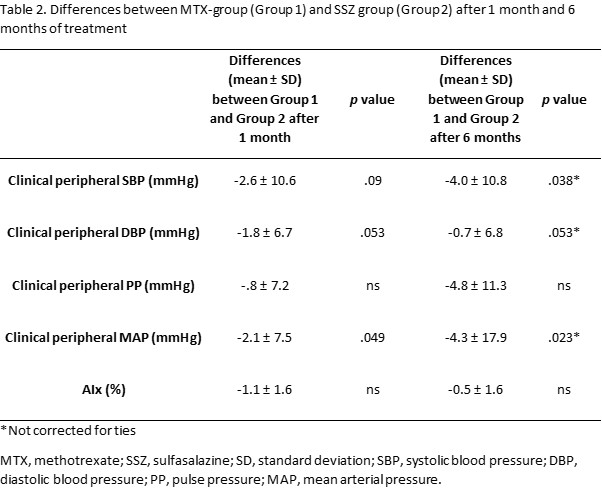
Results: At baseline, the two groups were matched for age, gender, body mass index, and 28-joint disease activity score (p>0.05 for all comparisons). After 1 month of treatment, group 1 had a trend towards a significant reduction in SBP (mean difference -2.6±10.6 mmHg, p=0.09) and DBP (mean difference -1.8±6.7 mmHg, p = 0.053) and a significant reduction in MAP (mean difference -2.1±7.5 mmHg, p=0.049) compared to Group 2. After 6 months of treatment, group 1 had a significant reduction in SBP (mean difference -4.0±10.8 mmHg, p=0.038) and MAP (mean difference -4.3±17.9 mmHg, p=0.023) and a trend towards a significant reduction in DBP (mean difference -0.7±6.82 mmHg, p=0.053). There were no significant between-group differences in AIx over time.
Conclusion: The results of this study provide the first evidence that MTX treatment causes a significant reduction in SBP (primary endpoint) at 6 months in RA patients in intervention studies. The effects of MTX on BP are not mediated by changes in arterial wave reflections. Further research is warranted to identify the mechanisms involved in the MTX-induced BP lowering effects and whether such effects account for the protective effects of MTX against cardiovascular disease observed in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tommasi S, Woodman R, Wiese M, Shanahan M, Mangoni A. Effects of Methotrexate on Blood Pressure in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-methotrexate-on-blood-pressure-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-randomized-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-methotrexate-on-blood-pressure-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-randomized-controlled-trial/