Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (0934–0964) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells represent a potentially curative strategy for B cell malignancies. A first successful clinical experience has been recently reported in systemic lupus erythematosus, suggesting that CD19-targeted CAR-T cell transfer was feasible and tolerable. Since systemic sclerosis (SSc) and SLE are both severe diseases sharing B cell implication in their pathogenesis, we aimed at assessing the efficacy and tolerance of two B cell depletion strategies, including one with CD19-targeted CAR-T cells, in a preclinical model mimicking the severe lung damages observed in SSc.
Methods: B cell depletion strategies were evaluated in the Fra-2 transgenic (Tg) mouse model. We considered a first group of 16 untreated mice, a second group of 15 mice receiving a single intravenous (IV) dose (50 mg) of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb) at day 1 and a third group of 8 mice receiving 50 mg anti-CD20 mAb IV at day 1 followed by the IV injection of 20*106CD19-targeted CAR-T cells at day 3. After 6 weeks of clinical evaluation, different validated markers of inflammation, lung fibrosis and pulmonary vascular remodeling were assessed.
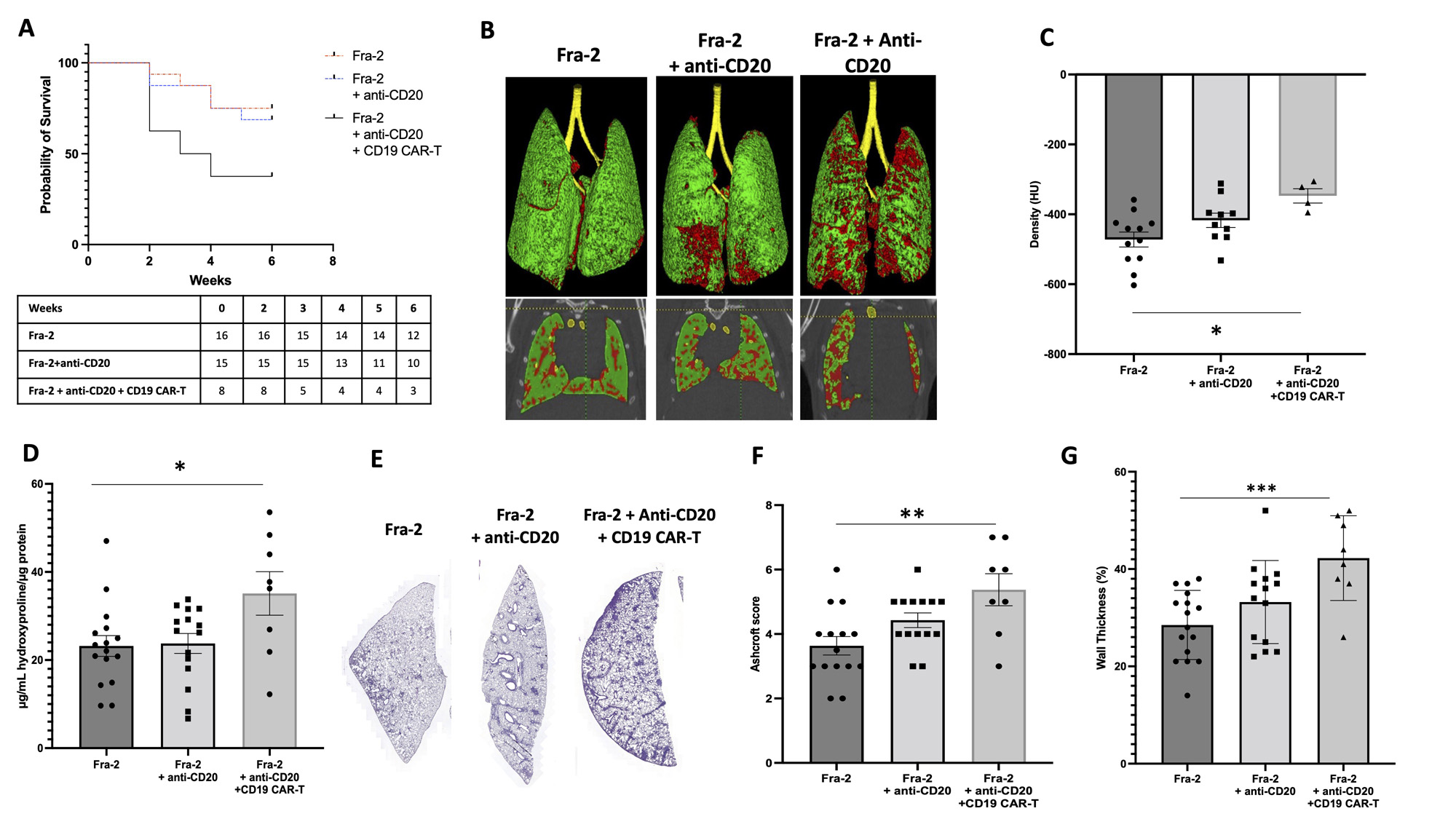
Results: Following treatment with anti-CD20 mAb, CD19 expression was significantly decreased in peripheral blood and lesional lungs of Fra-2 Tg mice by 59% (p< 0.001) and 40% (p=0.019), respectively, compared to control Fra-2. B cell depletion was even more pronounced in mice treated with CD19-targeted CAR-T cells: CD19 expression was decreased in peripheral blood and lungs of Fra-2 Tg mice by 92% (p< 0.001) and 85% (p< 0.001), respectively, compared to control Fra-2. CAR-T cell infusion worsened clinical score and increased mortality in Fra-2 Tg mice (Figure 1A). In line with the above findings, mice receiving CD19-targeted CAR-T cells displayed a significant increase in lung density (mean difference of 55±28 Hounsfield Units, p=0.038) (Figure 1B-C) and a marked reduction of functional residual capacity(mean difference of 25±9%, p=0.041) as compared to control Fra-2 when assessed by chest micro-CT imaging. CAR-T cell infusion significantly increased lung collagen content (mean difference of 11.93±4.44 mg/mL, p=0.020) (Figure 1D), histological fibrosis score (mean difference 1.74±0.48, p=0.002) (Figure 1E-F) and right ventricular systolic pressure (mean difference 8.52±2.70 mmHg, p=0.013) (Figure 1G). CAR-T cells accumulated in lesional lungs and promoted T-cell activation, with a significant increase of CD4+ effector memory T cells and the fraction of CD69 and PD1-expressing cells within the CD4+ and CD8+ subsets. Moreover, in the lung of CD19-targeted CAR-T cell-treated Fra-2 Tg mice. Moreover, the levels of inflammatory cytokines IL6, TNF-a and IFNg were markedly elevated in lesional lungs of mice treated with CAR-T cells. Treatment with anti-CD20 mAb in monotherapy had no impact on lung inflammation-driven fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension.
Conclusion: B-cell therapies failed to show efficacy in the Fra2 transgenic mice. The exacerbated Fra-2 lung inflammatory burden stimulated accumulation and expansion of activated CD19-targeted CAR-T cells, secondarily inducing T-cell activation and systemic inflammation, finally leading to disease worsening.
A, Survival curves of Fra_2 mice after anti-CD20 mAb and CD19-targeted CAR-T cell infusion. Significance was determined by log rank (Mantel-Cox; p=0.031). B, Representative pictures of micro-computed tomography. C, Y-axis shows the lung density at micro-computed tomography. D, Y-axis shows the content of collagen in a lung fragment (μg) evaluated by Sircol assay. E, Representative HES 4-μm lung sections (magnification × 8). F, Y-axis shows the Ashcroft histological score. G, Y-axis shows the right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP). All data are shown as the mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, ***p<0.001 determined by one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s post hoc test.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Avouac J, Cauvet A, Orvain C, boulch M, Bousso P, ALLANORE Y. Effects of B Cell Depletion by CD19-targeted CAR-T Cells in a Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-b-cell-depletion-by-cd19-targeted-car-t-cells-in-a-murine-model-of-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-b-cell-depletion-by-cd19-targeted-car-t-cells-in-a-murine-model-of-systemic-sclerosis/