Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1412–1441) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II: SpA
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The prevalence of cardiometabolic diseases including obesity and diabetes is higher in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) than those without PsA. Apremilast (APR) is associated with weight loss and a reduction in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c). The objective of this analysis was to evaluate the effects of APR on cardiometabolic parameters over 52 weeks in patients with active PsA.
Methods: Data from 5 randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies (PALACE 1–4 and ACTIVE) in patients with active PsA receiving APR 30 mg twice daily were pooled. Included in this analysis were patients who were treated with APR for 52 weeks. Changes from baseline to Week 52 in low- and high-density lipoprotein (LDL, HDL), body mass index (BMI), and HbA1c were assessed and stratified by baseline level of these parameters and Week 52 disease activity (Clinical Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis [cDAPSA] remission/low disease activity [REM/LDA] vs moderate/high disease activity [ModDA/HDA]).
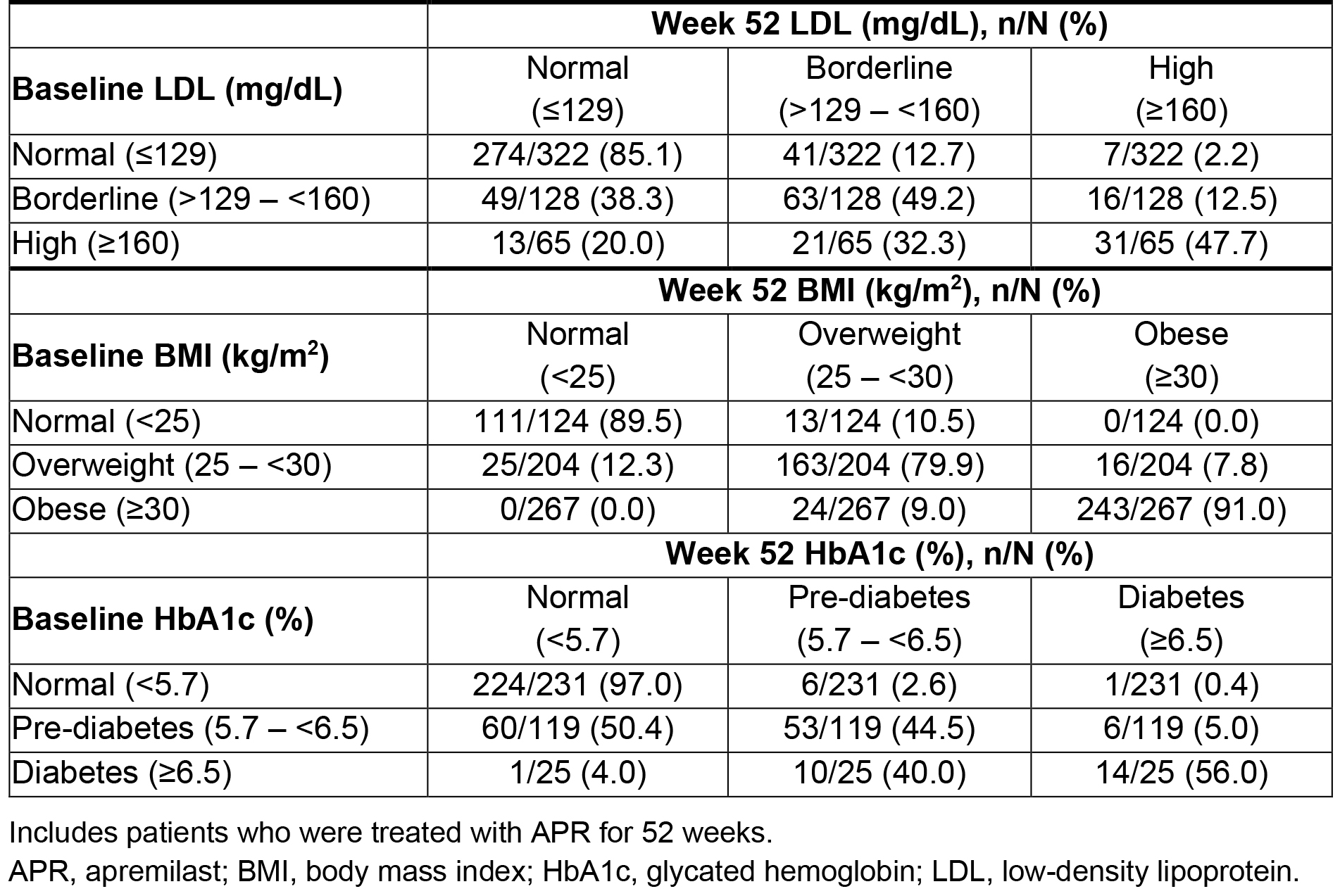
Results: Data from 781 patients with PsA who received APR were pooled (mean age: 50 years, 55% female). Mean LDL was 119.6 mg/dL in the overall population at baseline and decreased by 2.0 mg/dL on average at Week 52 (Figure). The greatest decreases in LDL were seen in patients with the highest LDL levels at baseline (Figure). Similar favorable changes in HDL were observed. A total of 34/65 (52.3%) moved from the high LDL category (≥160 mg/dL) at baseline to borderline ( >129 – < 160 mg/dL) or normal (≤129 mg/dL) at Week 52 and 49/128 (38.3%) changed from borderline high to normal LDL levels (Table).
Mean BMI was 30.3 kg/m2 in the overall population at baseline and decreased by 0.5 kg/m2 at Week 52 (Figure). A trend was again seen where patients with higher BMI at baseline saw greater decreases in BMI at Week 52 (Figure). Additionally, 24/267 (9.0%) patients changed from the obese category (≥30 kg/m2) to the overweight category (25 – < 30 kg/m2), and 25/204 (12.3%) patients changed from the overweight category to the normal category (< 25 kg/m2) (Table).
Mean HbA1c was 5.6% in the overall population at baseline and decreased by 0.1% at Week 52 (Figure). Greater changes in HbA1c were seen in patients who were pre-diabetic (HbA1c 5.7% – < 6.5%) and diabetic (HbA1c ≥6.5%) at baseline vs those who had normal HbA1c (HbA1c < 5.7%) (Figure). Furthermore, 60/119 (50.4%) patients who had pre-diabetes changed to normal HbA1c levels, and 10/25 (40.0%) moved from diabetes to pre-diabetes (Table).
Results were consistent across Week 52 cDAPSA psoriatic disease activity subgroups; greater changes in cardiometabolic parameters were seen in patients with higher baseline LDL, BMI, HbA1c, or lower baseline HDL regardless of whether REM/LDA was achieved at Week 52.
Conclusion: APR treatment was associated with improvement in cardiometabolic parameters observed across psoriatic disease activity groups. The most favorable changes were seen in patients with high LDL, low HDL, obesity, or diabetes at baseline. These findings suggest that those with a high burden of comorbid cardiometabolic diseases and active PsA treatment may gain benefit beyond joint disease with APR. However, these findings require larger, prospective studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Gladman D, McInnes I, Cheng S, Colgan S, Klyachkin Y, Teng L, Mehta N. Effects of Apremilast on Changes in Cardiometabolic Parameters by Diabetes and Obesity Status in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-apremilast-on-changes-in-cardiometabolic-parameters-by-diabetes-and-obesity-status-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-apremilast-on-changes-in-cardiometabolic-parameters-by-diabetes-and-obesity-status-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/