Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: Inflammatory Arthritis – RA, SpA, & Gout (0560–0593)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase inhibitor, which is orally applied and is approved for rheumatoid arthritis among other indications. ESCALATE-RA is the first prospective, non-interventional study with tofacitinib in Germany. The first patient was enrolled end of 2017 and results of the first interim analysis were published in 2020.
Methods: The enrollment of the planned 1500 patients takes place Germany-wide (87 recruiting sites as of 08 May 2021). Adult patients eligible for tofacitinib therapy are documented quarterly in a standardized manner from the first tofacitinib intake up to 24 months and remain within the study even after switching to another DMARD or combination of DMARDs. This second interim analysis (cut-off date 29 Jan 2021) describes patients, who reached visit M12 after 12 months as well as patients who reached the final visit M24 after 24 months. Missing observations were not taken into account. Since this is an ongoing study, small changes in numbers may occur after the final data quality checks.
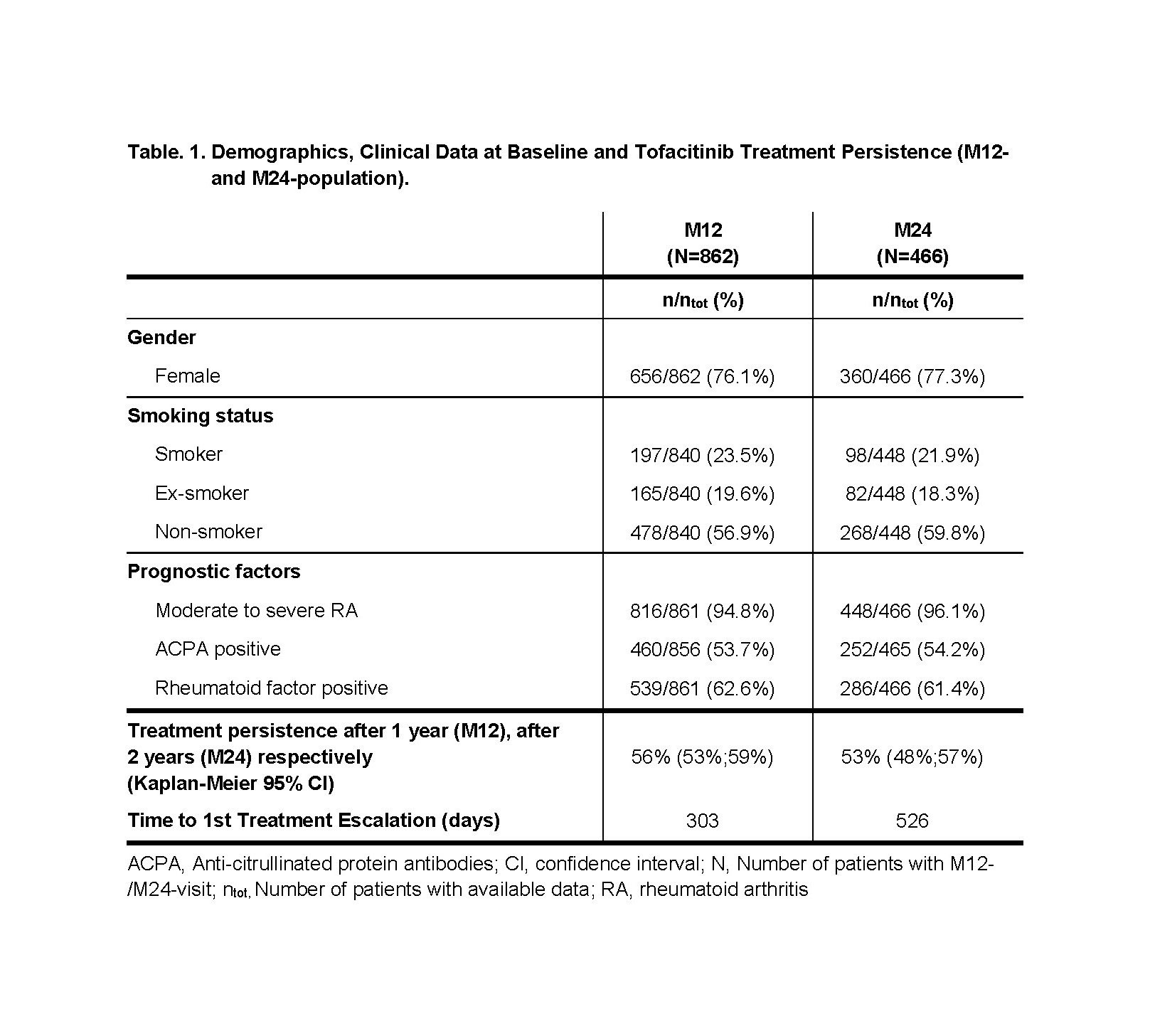
Results: At data cut-off, 1227 patients were enrolled, 862 (70.3%) patients reached M12 and 466 (38.0%) patients reached M24. In both populations mean age was 59 years, approx. three quarters of patients were female and over 60% were seropositive. 52.5% of M12- and 54.7% of M24-population were treated with a bDMARD immediately prior to enrollment. Tofacitinib treatment persistence was 56% after 1 year in M12-population and 53% after 2 years in M24-population (Table 1).
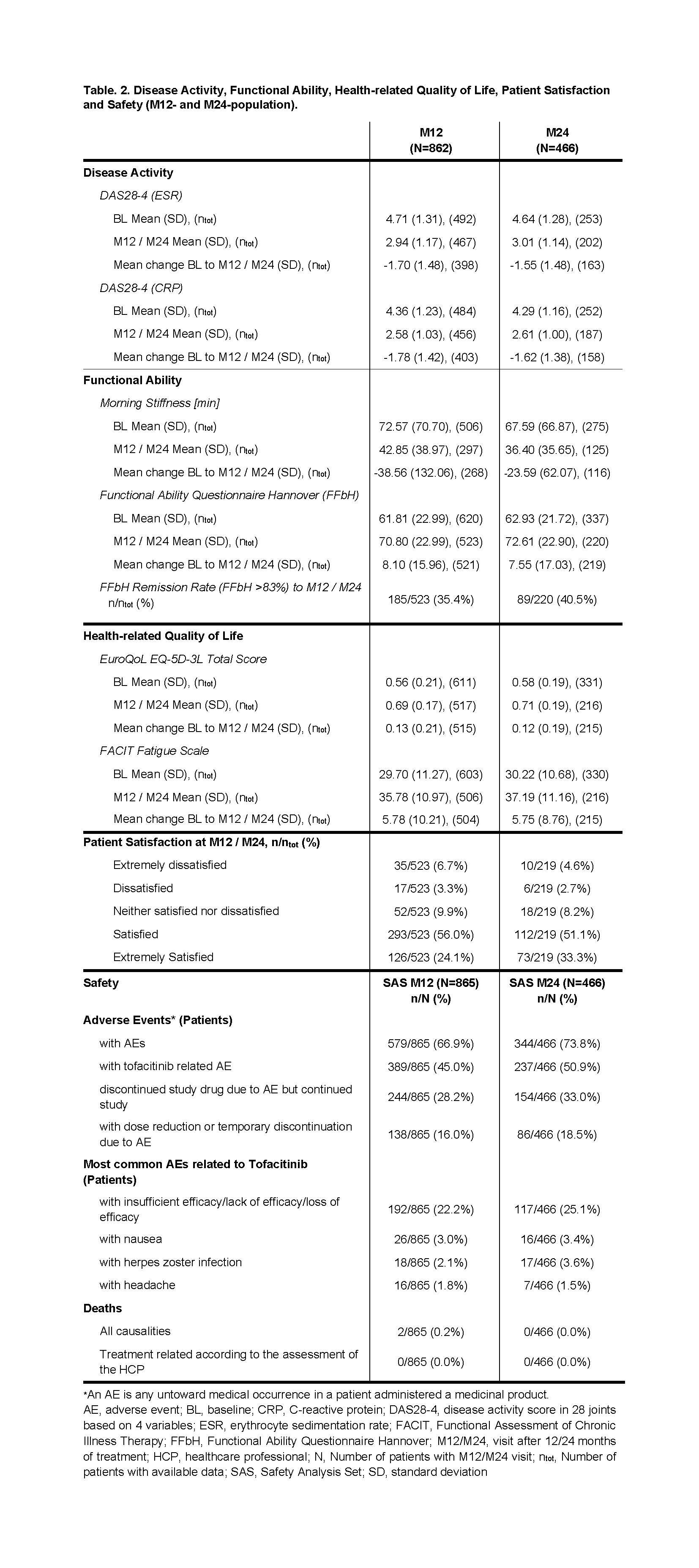
A reduction of disease activity and morning stiffness was observed in both populations over time while functional ability according to FFbH (Functional Ability Questionnaire Hannover, German short questionnaire for the assessment of patient functional capacity in the context of basic everyday activities (range: 0-100% functional capacity) [1]) increased in both populations. The mean change from BL of disease activity and morning stiffness as well as functional ability was somewhat more pronounced in M12- than in M24-population. Functional remission was achieved by more patients in the M24- (40.5%) than in M12-population (35.4%). Furthermore, patients in both populations showed a comparable improvement in self-reported quality of life and the majority of patients in both populations were satisfied or extremely satisfied with tofacitinib treatment (Table 2).
AEs occurred in 66.9% (M12-population), and 73.8% (M24-population) of patients, respectively. Approx. half of the M12- as well as the M24-population had AEs related to tofacitinib, less than one-third of patients in both populations discontinued study drug due to AE but remained in the study. Two deaths were reported in M12-population (Table 2).
Conclusion: This second interim analysis shows a good effectiveness and an increased quality of life with tofacitinib therapy. Safety results were consistent with the known safety profile of tofacitinib. These results are in line with those of the first interim analysis.
[1] Lautenschläger J, Mau W, Kohlmann T, Raspe HH, Struve F, Brückle W, et al. [Comparative evaluation of a German version of the Health Assessment Questionnaire and the Hannover Functional Capacity Questionnaire]. [Article in German] Z Rheumatol 1997;56:144–55
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Krüger K, Behrens F, Prothmann U, Klopsch T, Blindzellner L, Behmer O, Jobst J, Klaus P, Meng T, Löschmann P. Effectiveness, Safety, Quality of Life and Patient Satisfaction with Tofacitinib Treatment in Adult Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Under Routine Clinical Care: Second Interim Analysis of a German Non-Interventional, Prospective, Multi-Center Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-safety-quality-of-life-and-patient-satisfaction-with-tofacitinib-treatment-in-adult-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-under-routine-clinical-care-second-interim-analysis-of-a-german/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-safety-quality-of-life-and-patient-satisfaction-with-tofacitinib-treatment-in-adult-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-under-routine-clinical-care-second-interim-analysis-of-a-german/