Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic fibroinflammatory disease often associated with elevated serum IgG4 levels. High dose corticosteroids are the cornerstone of treatment, but relapses and side-effects are frequent, requiring synthetic and/or biologic immunosuppressants. Rituximab (RTX) seems to be effective in IgG4-RD.
Methods: Multicentre retrospective observational study of patients with IgG4-RD treated with RTX. Outcomes were clinical and serologic response, as well as safety.
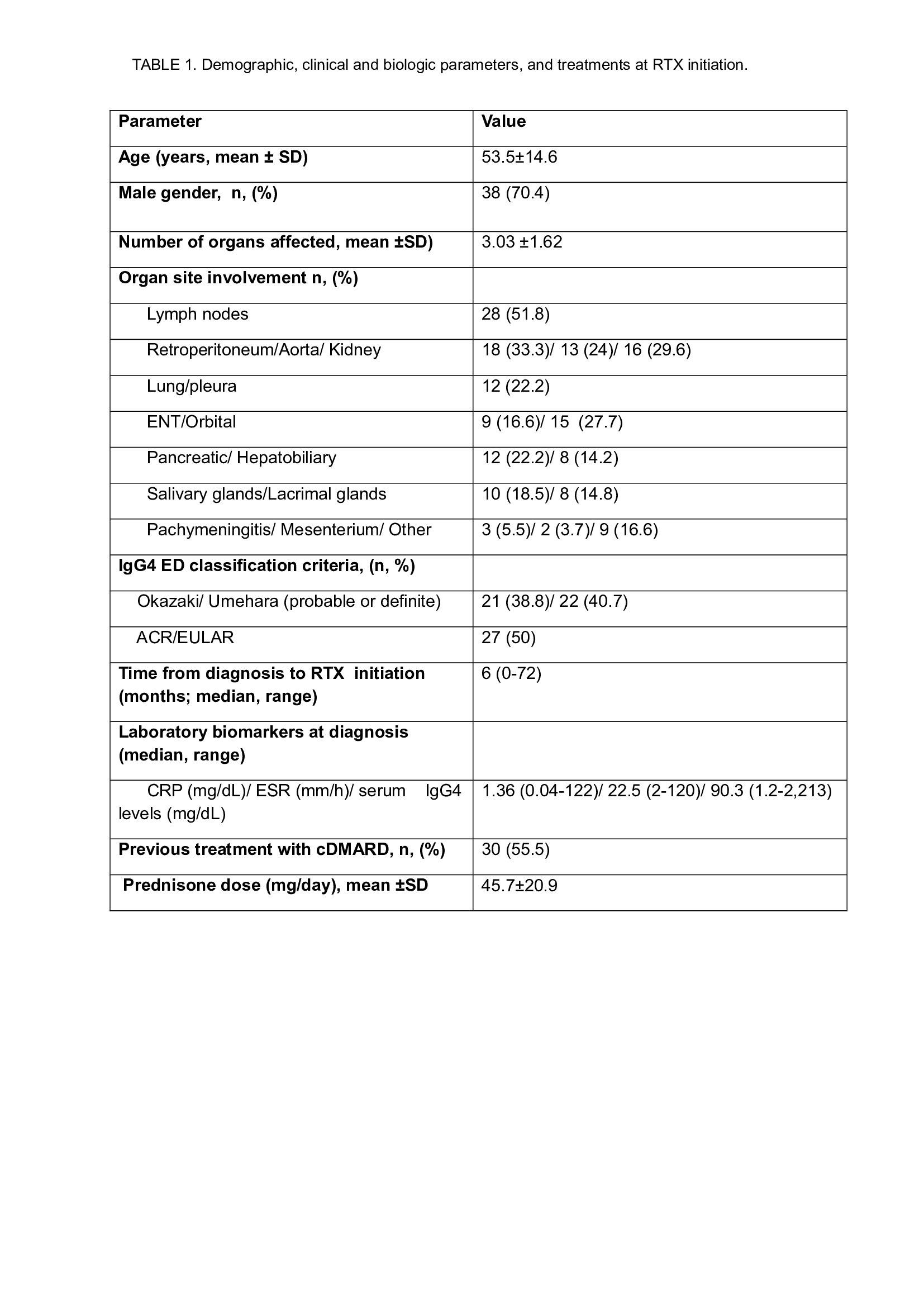
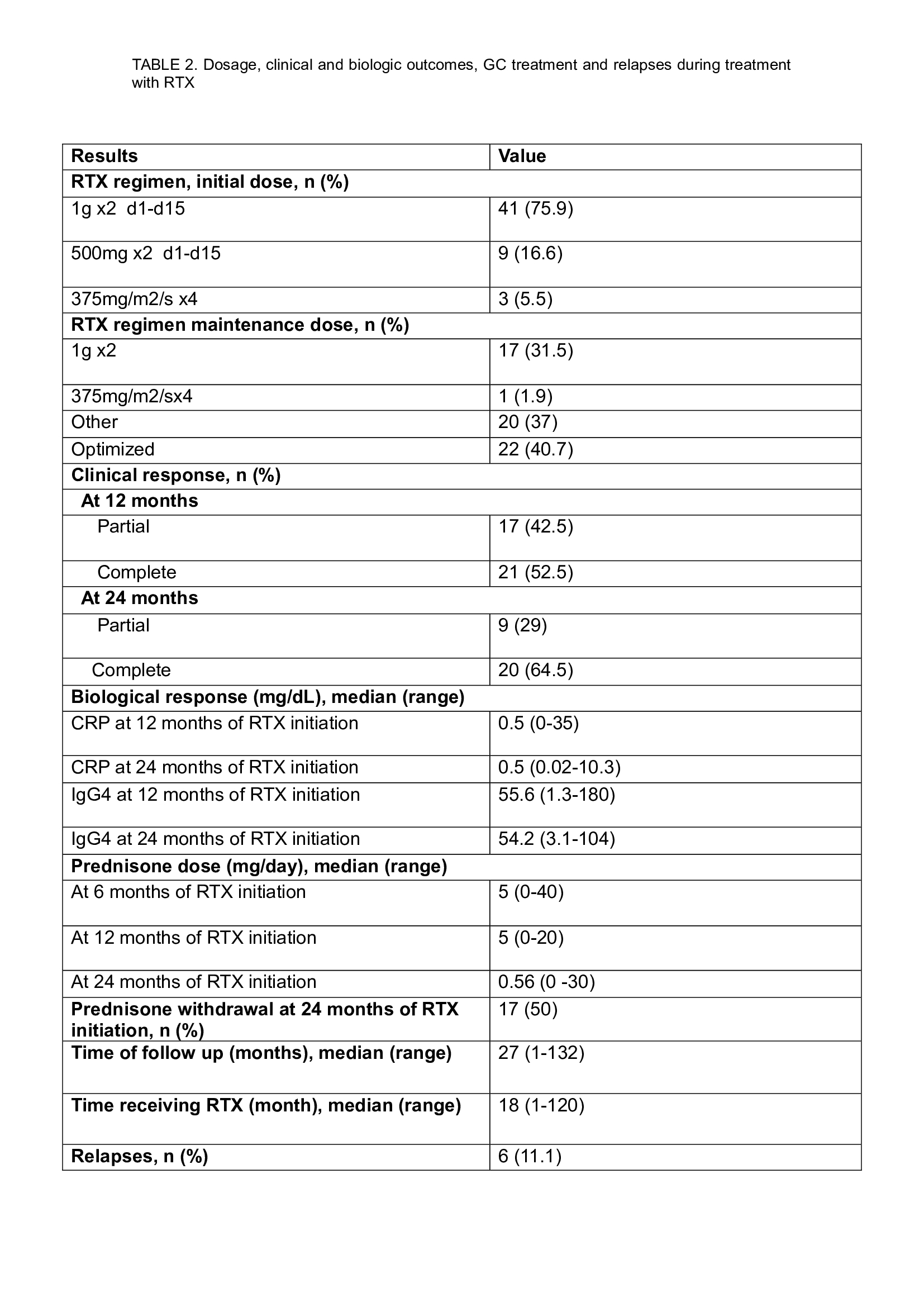
Results: We included 54 patients (38 men/16 women; mean age±SD 53.5±14.6 years) with IgG4-RD, treated with RTX (Table 1). The most affected organs were lymph nodes (n=28; 51.8%), retroperitoneum (n=18; 33.3%), kidney (n=16; 29.6%), orbit (n=15; 27.7%), aorta (n=13; 24.07%), lung/pleura (n=12; 22.2%), pancreas (n=12; 22.2%), salivary glands (n=10; 18.5%), ear nose and throat (n=9; 16.6%), lacrimal glands (n=8; 14.8%), , liver/biliary duct (n=8; 14.8%), pachymeninges (n=3; 5.5%) and mesenterium (n=2; 3.7%). All but 4 patients (7.4%) had received oral corticosteroids, and 15 (27.7%) patients also received corticosteroid boluses. 30 (55.5%) patients received conventional cDMARDs: methotrexate (MTX) (n=17; 31.5%), azathioprine (n=11; 20.4%), and mycophenolate mophetil (n=2(3.7%). Median time from diagnosis to RTX initiation was 6 (range 0-72) months, with a median time of follow-up of 27 (range 1-132) months. Main induction treatment schedule with RTX was 1g x2, two weeks apart (n=41; 75.9%), 500mg x2, two weeks apart (n=9; 16.6%) and 375 mg/m2 weekly x4 (n=3; 5.5%). 38 (70.3%) patients received maintenance treatment with RTX (Table 2). After 12 and 24 moths of follow up, complete and partial clinical improvement was observed in 21 (52.5%) and 17 (42.5%), and in 20 (64.5%) and 9 (29%) patients, respectively. Only 6 relapses were observed. Prednisone could be discontinued at 24 months in 17 (50%) patients. 3 patients died during follow up (1 of acute coronary syndrome, 1 of respiratory tract infection and one of cancer related complications). One patient needed ICU admission because of Influenza pneumonia, and 2 developed a larynx and a breast cancer, respectively.
Conclusion: RTX seems to be an effective and relatively safe therapy in IgG4-RD. Maintenance treatment with RTX seems to be associated with a low rate of relapse.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lopez-Gutierrez F, Loricera J, Hormigos C, Freites Nuñez D, Rodriguez-Laguna M, Moya Albarado P, López I Gómez M, Corominas H, Silva-Díaz M, GONZALEZ ARRIBAS G, Garcia-Aparicio A, Font Urgelles J, Casafont-Sole I, Martínez Calabuig P, Castaneda E, Merino C, Zas R, Molina-Collada J, Melero-Gonzalez R, Galindez-Agirregoikoa E, Hernández-Martín A, Pantoja L, Brana Abascal I, Jovani V, Valls-Pascual E, Mena Vázquez N, Gallego- Flores A, Cabaleiro Raña N, Veroz R, Andres M, Castañeda S, Blanco-Alonso R. Effectiveness of Rituximab in IgG4 Related Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-rituximab-in-igg4-related-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-rituximab-in-igg4-related-disease/