Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (SSc-PAH) has been known as a life-threatening manifestation in SSc. Earlier detection and subsequent interventions are important to improve the prognosis. DETECT algorithm was established in 2013, however Japanese patients were not included in the original study. The objective of this study was to verify the effectiveness of this algorithm in Japanese with old and new hemodynamic definition of PAH.
Methods: In this retrospective, single-center study, patients with SSc who fulfilled American College of Rheumatology criteria and underwent right heart catheterization (RHC) for the diagnosis of PAH from 2004 to 2019 were included. We analyzed their results of DETECT algorithm in old and new hemodynamic definition of PAH (Mean pulmonary pressure (mPAP) ≧25 mmHg in old definition and >20 mmHg in new definition, with mean pulmonary capillary wedge pressure ≦15 mmHg).
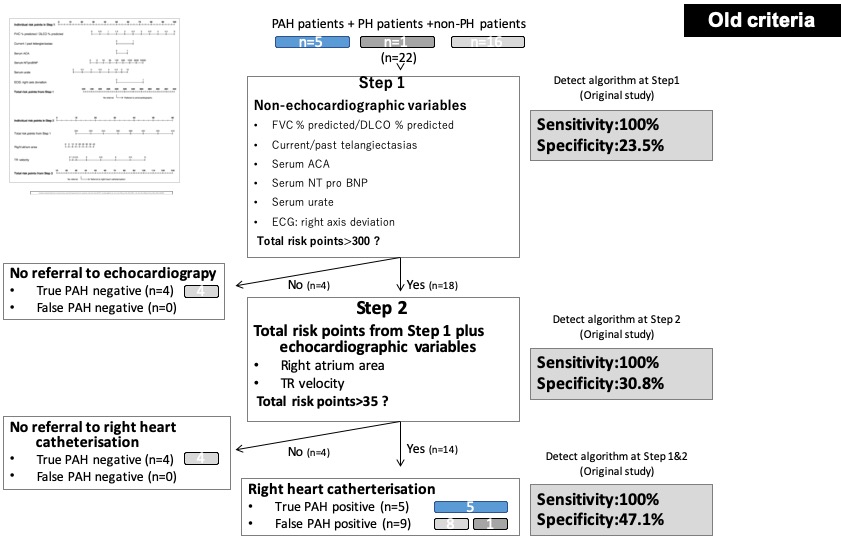
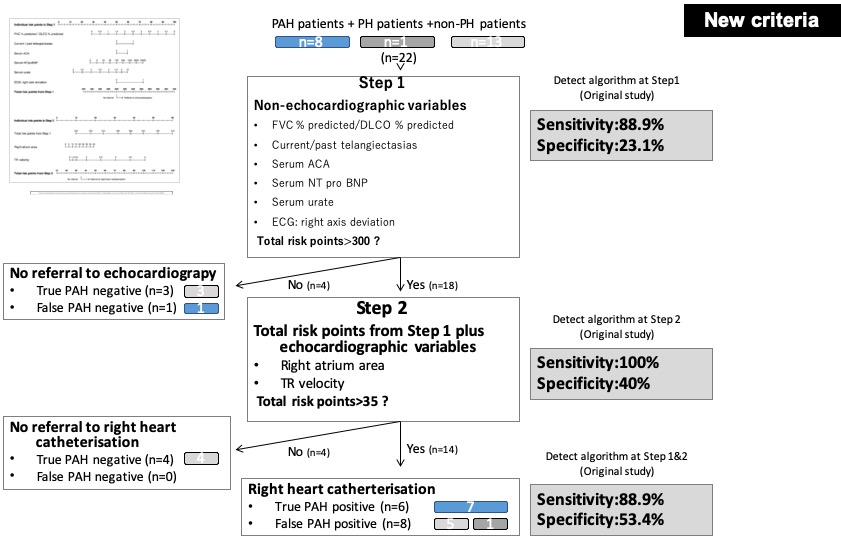
Results: Twenty-two patients were analyzed in this study. The mean age of enrolled patients was 59 years. The female patients were 73% and limited cutaneous SSc patients were 68%. Five and eight patients were diagnosed as PAH with old and new definition respectively. Overall sensitivity and specificity of DETECT algorithm to PAH in old criteria was 100% and 47.1% (Figure 1). On the other hand, 88.9% and 53.4% in new definition (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The DETECT algorithm was confirmed to be very sensitive and safely used in Japanese patients with SSc as a screening before RHC to minimize missed diagnosis of PAH. However, the algorithm should be used with caution, considering sensitivity was slightly lower with new PAH criteria.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ito T, Nakai T, Kidoguchi G, Fukui S, Ozawa H, Kawaai S, Ikeda Y, Shimizu H, Suyama Y, Nomura A, Tamaki H, Yamaguchi K, Okada M. Effectiveness of DETECT Algorithm in Japanese Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Old or New Hemodynamic Definition of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-detect-algorithm-in-japanese-systemic-sclerosis-patients-with-old-or-new-hemodynamic-definition-of-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-detect-algorithm-in-japanese-systemic-sclerosis-patients-with-old-or-new-hemodynamic-definition-of-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension/