Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Blockade of JAK, preferably JAK1, by upadacitinib is a feasible approach to achieve erosion repair as it 1) is approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 2) effectively controls the inflammation and 3) targets pathogenic pathways that influence local bone homeostasis in the joint. To address the question whether inhibition of JAK1 could lead to erosion repair in patients with active RA, we performed a pilot non-randomized study comparing the changes in bone erosions on high-resolution peripheral quantitative computer tomography (HR-pQCT) before and after upadacitinib.
Methods: This is a 24-week, single-centered, prospective, non-randomized pilot study. We enrolled 20 adult patients with active RA (Disease activity score 28-C-reactive protein [DAS28-CRP] > 3.2) and ≥1 bone erosion on HR-pQCT. They were given upadacitinib 15mg once daily for 6 months. HR-pQCT of the 2-4 metacarpophalangeal (MCP) head was done at baseline and 6 months. The primary outcome was the change of erosion volume on HR-pQCT. Secondary outcomes included change in RA disease activity and predictors of response to treatment. Erosion regression was defined as decrease in volume exceeding the smallest detectable change.
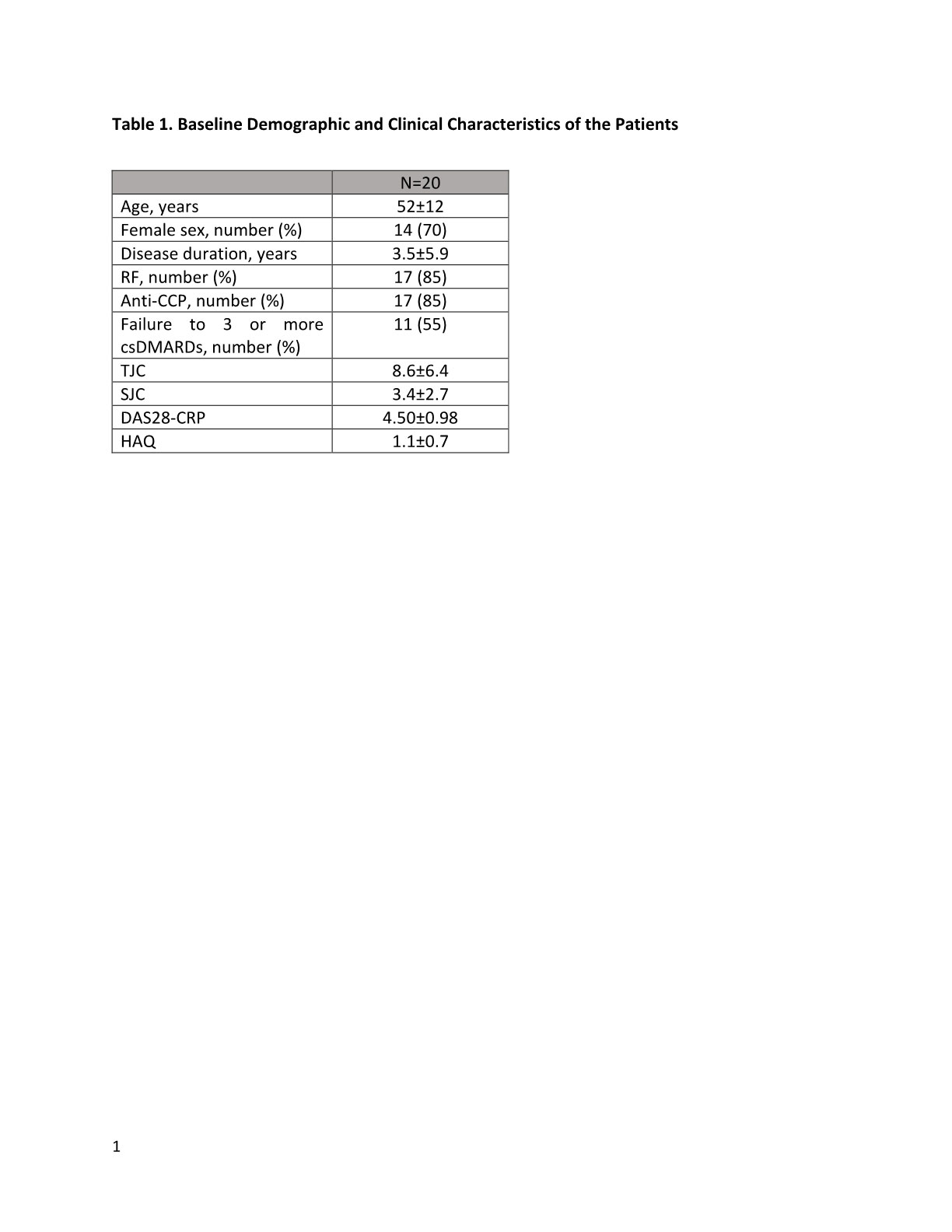
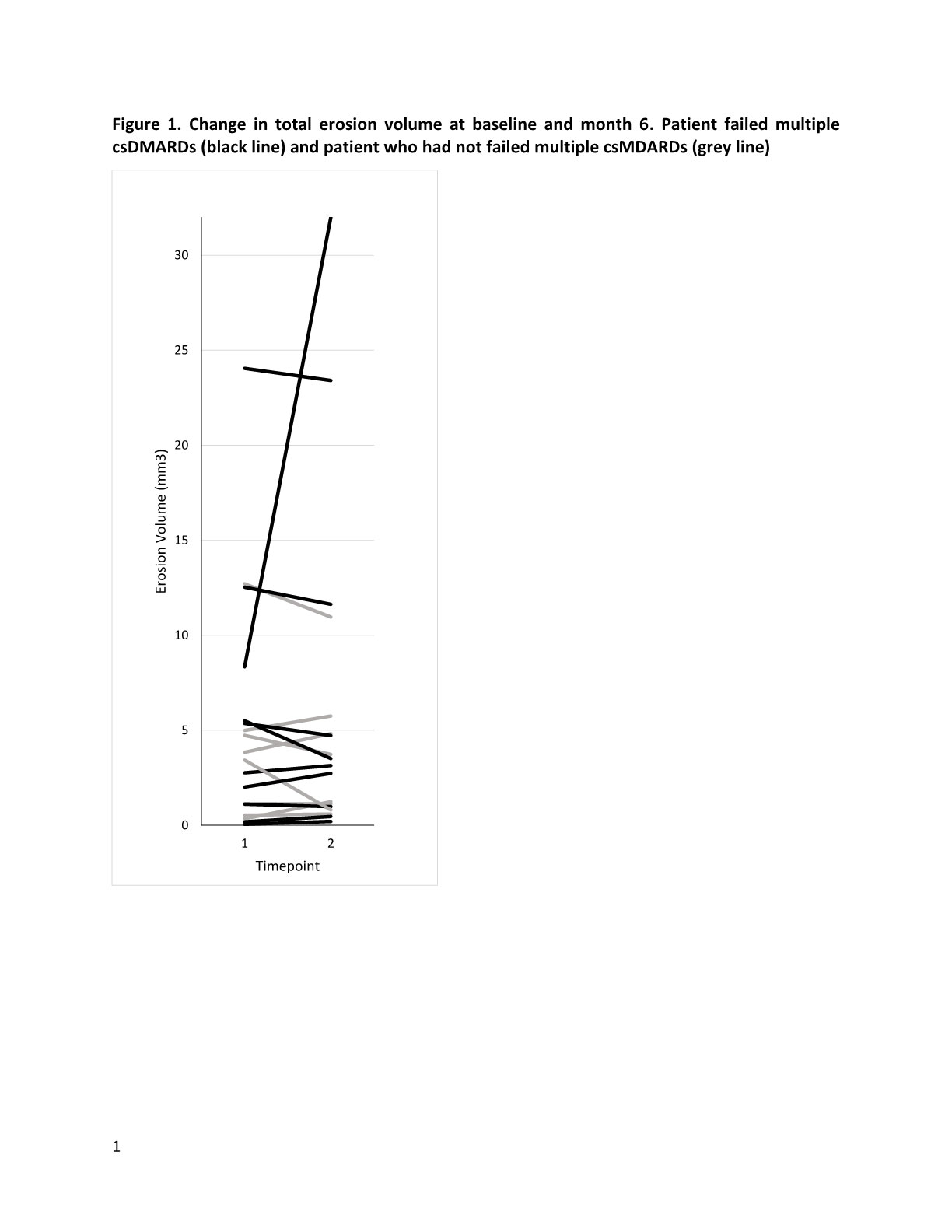
Results: The baseline clinical characteristics of the recruited patients were shown in table 1. Of the 20 patients, 11 (55%) patients failed to respond to 3 or more csDMARDs. At 24-week, there was significant improvement in mean DAS28 (-1.75, p< 0.001). Erosion regression was seen in 8 (40%) patients on HR-pQCT. Although no significant change in overall median erosion volume before and after upadacintinib (0.07 [-0.90-0.76mm3] mm3, p=0.904) was noted, the deterioration was less obvious compared to a historic cohort of 20 patients with similar age and disease activity on csDMARDs (median erosion volume change in 6 months: 0.67 mm3). When patients were stratified according to whether or not they had failed multiple csDMARDs, significantly high proportion of patients in the non-multiple-DMARDs failure group had volume regression in at least one erosion compared to those in the failure group (75% vs 25%, p=0.04) (Figure 1). There was improvement in mean total erosion volume in the non-failure group (-0.33±1.33 mm3), whereas mean erosion volume in the failure group worsened (2.09±7.62 mm3). One patient developed chest infection requiring hospitalization and withdrew from the study. No other serious adverse event was noted.
Conclusion: The results of the study suggest upadacitinib is clinically efficacious in refractory RA disease and can retard erosion progression. Regression of erosion is possible, particularly in those with limited csDMARDs exposure. Whether early JAK1 inhibition could lead to better structural outcome warrants further investigations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
SO H, Cheng I, Hung V, Tam L. Effect of Upadacitinib on Bone Erosion Repair in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-upadacitinib-on-bone-erosion-repair-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-pilot-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-upadacitinib-on-bone-erosion-repair-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-pilot-study/