Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), subcutaneous tocilizumab (TCZ-SC) is administered every 2 weeks (q2w) or every week (qw), based on the patient’s weight and clinical response. This study evaluated the effects on disease activity at week 24 when the dosing schedule of TCZ-SC was escalated from q2w to qw in patients who did not achieve low disease activity (LDA; Disease Activity Score in 28 Joints [DAS28] > 3.2) at week 12 in COMP-ACT compared with patients who did not achieve LDA and did not escalate dosing in SUMMACTA and BREVACTA.
Methods: US patients in COMP-ACT who weighed < 100 kg at baseline and who received TCZ-SC 162 mg q2w + methotrexate escalated to qw if they did not achieve LDA at week 12. In the primary analysis, DAS28 remission (< 2.6) and LDA (≤ 3.2), Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) remission (≤ 2.8) and LDA (≤ 10) and Simple Disease Activity Index (SDAI) remission (≤ 3.3) and LDA (≤ 11) at week 24 were compared between patients who switched from q2w to qw and North American patients in SUMMACTA who initiated TCZ qw + conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and continued a qw dose (baseline body weight < 100 kg and DAS28 > 3.2 at week 12). A secondary analysis compared COMP-ACT patients who escalated from q2w to qw with all SUMMACTA patients who continued a qw dose and all patients in BREVACTA who initiated a TCZ-SC q2w dose + csDMARDs and continued a q2w dose (baseline body weight < 100 kg and DAS28 > 3.2 at week 12). DAS28 was standardized to DAS28-ESR, and comparisons were calculated using a mixed model with repeated-measures logistic regression, including the following covariates: CDAI, SDAI and/or DAS28 at the reference visit (week 12), as well as study baseline values of CDAI, SDAI and/or DAS28, baseline age, sex, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor use prior to the study (yes or no) and weight category.
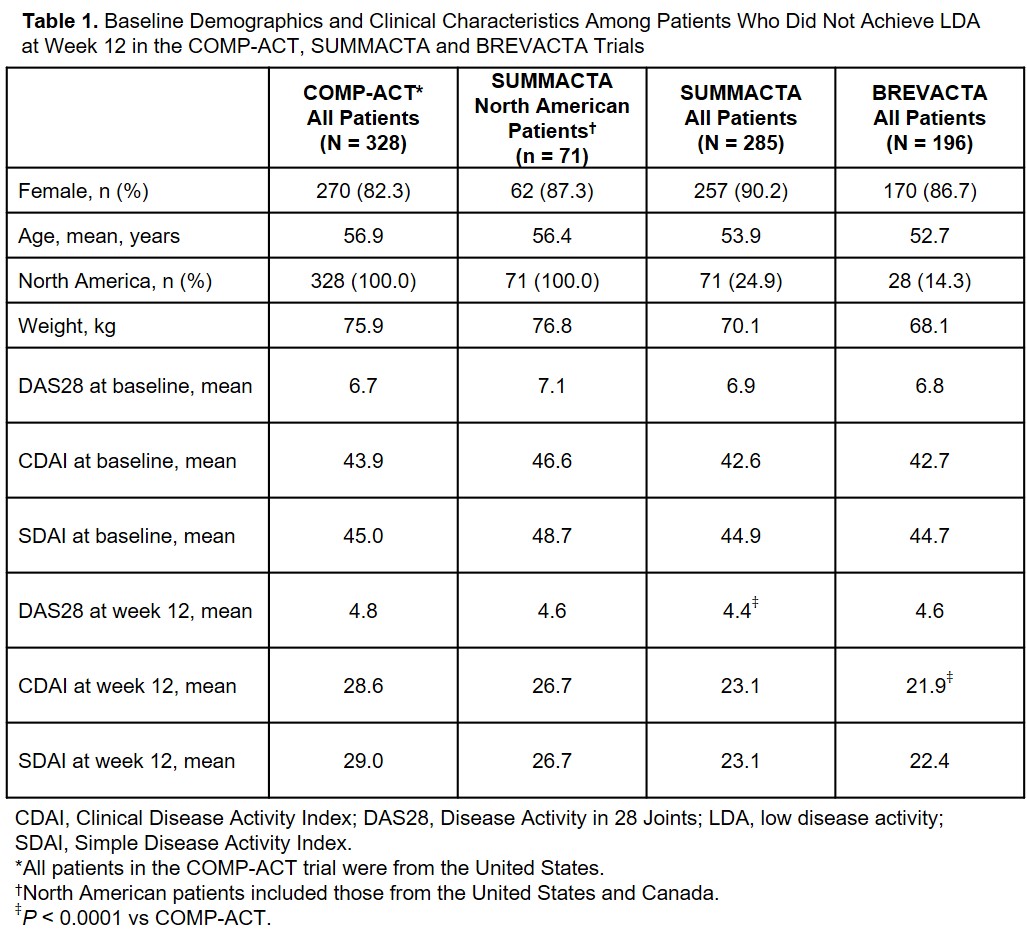
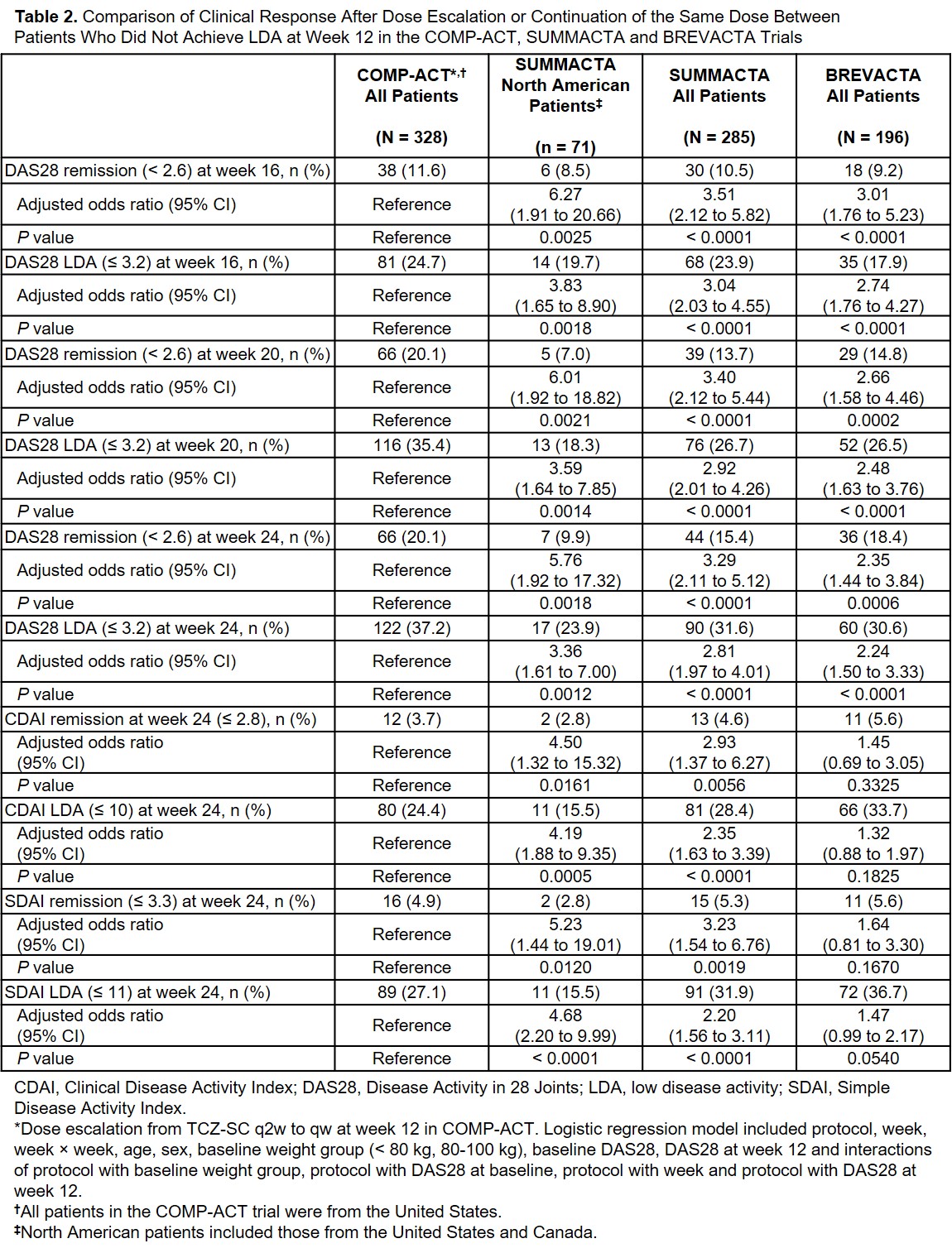
Results: A total of 328 US patients in COMP-ACT did not achieve LDA at week 12 and escalated from q2w to qw TCZ-SC. In SUMMACTA, 285 patients did not achieve LDA at week 12 and continued TCZ-SC qw, of whom 71 were from North America. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were comparable between patients in COMP-ACT and North American patients in SUMMACTA (Table 1). A significantly higher proportion of patients in COMP-ACT achieved DAS28, CDAI and SDAI remission and LDA 12 weeks after TCZ dose escalation (week 24) than North American SUMMACTA patients (Table 2). In the secondary analysis, similar results were seen when the proportion of patients who achieved DAS28 remission and LDA was compared at week 24 between patients in COMP-ACT and patients from all geographic regions who did not escalate dosing in SUMMACTA and BREVACTA (N = 196) (Table 2). Comparable clinical responses were seen with CDAI and SDAI when the COMP-ACT patients and patients from all geographic regions in SUMMACTA were analyzed.
Conclusion: US patients with RA who did not achieve LDA and escalated from q2w to qw TCZ-SC at week 12 in COMP-ACT had better outcomes at week 24 than North American patients who did not achieve LDA and continued qw dosing in SUMMACTA. These results provide evidence that escalation from q2w to qw has more effect than would be expected without dose change for patients who do not achieve LDA by week 12.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Singer N, Mohan S, Yourish J, Han J, Edwardes M, Michalska M. Effect of Dose Escalation of Subcutaneous Tocilizumab on Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-dose-escalation-of-subcutaneous-tocilizumab-on-disease-activity-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-randomized-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-dose-escalation-of-subcutaneous-tocilizumab-on-disease-activity-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-randomized-controlled-trial/