Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is a complication affecting ~40% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Belimumab (BEL), an anti–B-lymphocyte stimulator therapy, was approved in the USA and in the EU for active LN in adult patients. When given to patients without LN for 52 weeks, BEL reduced anti-double stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) by 41% in patients with anti-dsDNA at baseline (BL; BLISS-52 & -76). The aim of this study was to evaluate changes in autoantibodies, complement, and B-cell subsets in response to BEL plus standard therapy versus placebo (PBO) plus standard therapy in patients with LN enrolled in BLISS-LN.
Methods: BLISS-LN was a Phase 3, 104-week study (GSK Study BEL114054; NCT01639339) in adult patients with active LN. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive monthly BEL 10 mg/kg intravenous (IV) or PBO, plus standard therapy (high-dose corticosteroids plus either cyclophosphamide followed by azathioprine [CYC/AZA] or mycophenolate mofetil [MMF]). Changes from BL at Week 104 were determined for anti-dsDNA and anti-C1q antibodies (in patients with positive BL anti-dsDNA [≥30 IU/mL] or anti-C1q [≥22.2 IU/mL]), C3/C4, and B-cell subpopulations.
Results: Among patients with autoantibodies at BL, greater reductions in anti-dsDNA and anti-C1q levels were observed with BEL versus PBO in both standard therapy groups. There were notable increases in C3/C4 levels in favor of BEL in both standard therapy groups. BEL significantly reduced the total CD19+ and naïve B cells versus PBO, driven mainly by the MMF subgroup. However, the reduction in circulating memory B cells was numerically smaller with BEL versus PBO. BEL reduced plasmablasts versus PBO in both standard therapy groups (data in Table).
Conclusion: Treatment with BEL improved complement (numerically for C3) and anti-dsDNA and anti-C1q antibody levels in patients with LN to greater degrees than standard therapy alone, consistent with the mechanism of action of BEL. There were greater reductions in CD19+ B cells, naïve B cells and plasmablasts with BEL compared with PBO; however, there was a numerically smaller reduction in circulating memory B cells with BEL versus PBO.
Funding: GSK
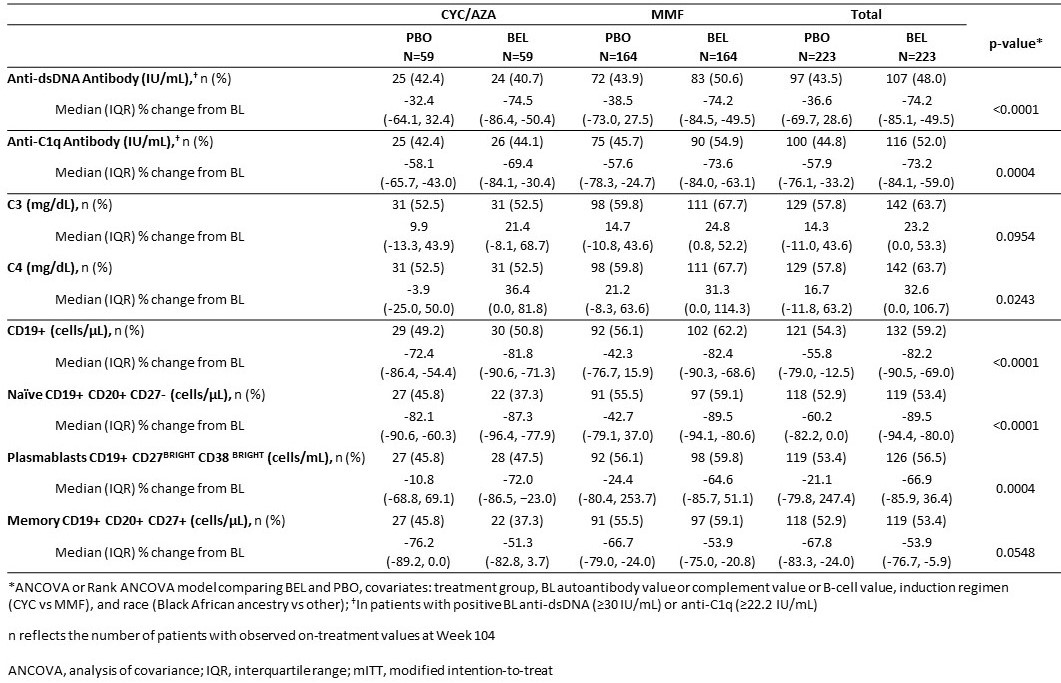 Table. Biomarker percent change from BL at Week 104 (mITT population)
Table. Biomarker percent change from BL at Week 104 (mITT population)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rovin B, Furie R, Malvar A, Aranow C, Pego-Reigosa J, Zakharova E, Schwarting A, Jones-Leone A, Madan A, Gilbride J, Roth D, Green Y, van Maurik A. Effect of Belimumab on Autoantibodies, Complement, and B-Cell Subsets in Patients with Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-belimumab-on-autoantibodies-complement-and-b-cell-subsets-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-belimumab-on-autoantibodies-complement-and-b-cell-subsets-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/
