Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Persistent fatigue can be debilitating for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Although fatigue partially improves after the initiation of DMARDs, suggesting an inflammatory process, it does not fully resolve with control of the disease activity. There is a glaring need for effective treatment options for the management of fatigue in patients with RA. This study is aimed to evaluate the efficacy of aerobic exercise intervention programs on lowering fatigue levels in patients with RA.
Methods: A systematic review of the literature was conducted through Pubmed, Embase and Cochrane Library from April 2014 to March 2020. This research was partially drawn from a prior meta-analysis/systematic review of the literature in which five studies were identified from 1985 to April 2014. Rongen-van Dartel, S. A., Repping-Wuts, H., Flendrie, M., Bleijenberg, G., Metsios, G. S., van den Hout, W. B., van den Ende, C. H., Neuberger, G., Reid, A., van Riel, P. L., & Fransen, J. (2015). Effect of Aerobic Exercise Training on Fatigue in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Arthritis care & research, 67(8), 1054–1062. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.22561 Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the effect of supervised land-based aerobic moderate-to-high physical activity on clinical outcomes of adult patients who meet the ACR/EULAR classification criteria of RA were considered for inclusion. Those studies implementing exercise interventions for less than 15 minutes duration in each session, less than two sessions per week, or less than four weeks follow up duration were excluded. Meta-analyses were conducted using fixed-effects modeling to estimate the pooled effect sizes. Standardized mean difference (SDM) and 95%Confidence intervals (CI) are reported at short-term follow up (4-12 weeks) and long-term follow-up (20-24 weeks) after enrollment. Heterogeneity was further explored with I-squared testing and sub-group analyses.
Results: Eight RCTs were selected with a total of 713 participants. There were five and seven studies, respectively, conducting short-term and long-term analyses. Aerobic land-based physical activity interventions were found to improve fatigue score at short-term follow-up (-0.42, 95%CI [-0.65, -0.19], p < 0.001) (Figure 1) and long-term follow-up (-0.37, 95%CI [-0.53, -0.21], p < 0.001) (Figure 2). Heterogeneity was moderately elevated in the short-term analysis and significantly elevated in the long-term analysis. The high heterogeneity in the long-term analysis was markedly reduced when excluding studies that selected special populations (n=2), including only women in one study or only elderly in the other study.
Conclusion: Moderate-to-high land-based aerobic exercise for at least 4 weeks is an effective intervention to improve fatigue in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Physical activity may have a more potent effect on fatigue in women and elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis. More RCTs are needed to evaluate the effect of exercise in these special populations.
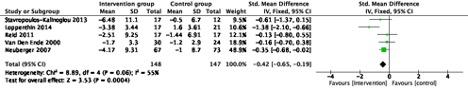 Figure 1. Forest plot of the short-term analysis for the effect of physical activity intervention on fatigue level on patients with rheumatoid arthritis. SD: standard deviation. IV: inverse variance. CI: confidence interval.
Figure 1. Forest plot of the short-term analysis for the effect of physical activity intervention on fatigue level on patients with rheumatoid arthritis. SD: standard deviation. IV: inverse variance. CI: confidence interval.
 Figure 2. Forest plot of the long-term analysis for the effect of physical activity intervention on fatigue level on patients with rheumatoid arthritis. SD: standard deviation. IV: inverse variance. CI: confidence interval.
Figure 2. Forest plot of the long-term analysis for the effect of physical activity intervention on fatigue level on patients with rheumatoid arthritis. SD: standard deviation. IV: inverse variance. CI: confidence interval.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aboulenain S, Farhangi A, Donath E, Pala O. Effect of Aerobic Land-based Exercise Intervention on Fatigue in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-aerobic-land-based-exercise-intervention-on-fatigue-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-aerobic-land-based-exercise-intervention-on-fatigue-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/
