Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: An unhealthy diet is an important modifiable risk factor for hyperuricemia and gout and is also associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome (MetS), known risk factors for gout as well as for cardiovascular disease (CVD). The prevalence of CVD is considerably elevated in patients with gout. A Mediterranean-style whole food plant-based diet (WFPD) has been shown to be effective for the treatment of other MetS- and obesity-related diseases. We therefore aimed to investigate the effect of a dietary intervention based on a WFPD on serum uric acid (SUA), gout disease activity and cardiovascular risk in patients with gout.
Methods: In the DIEGO (A DIEt for the treatment of GOut) pilot randomized clinical trial, patients with gout, hyperuricemia (♂ ≥ 0,42 mmol/L and ♀ ≥ 0,36 mmol/L), abdominal obesity (waist circumference ♂ ≥ 102 cm and ♀ ≥ 88 cm), and not receiving urate lowering therapy were assigned to the DIEGO WFPD intervention group or a usual care control group. The DIEGO group received individual counseling from a registered dietitian (60 min. at baseline, 30 min. in week 2, 4, 8, 12) and followed a Mediterranean-style WFPD for 16 weeks. Participants were allowed to use their usual gout flare medication during a gout flare. The primary outcome was the SUA level. Secondary outcomes included gout disease activity, cardiovascular risk factors and several other metabolic markers. An intention-to-treat analysis with a linear mixed model, adjusted for baseline values was used to analyze the between-group differences of primary and secondary continuous outcomes at 16 weeks.
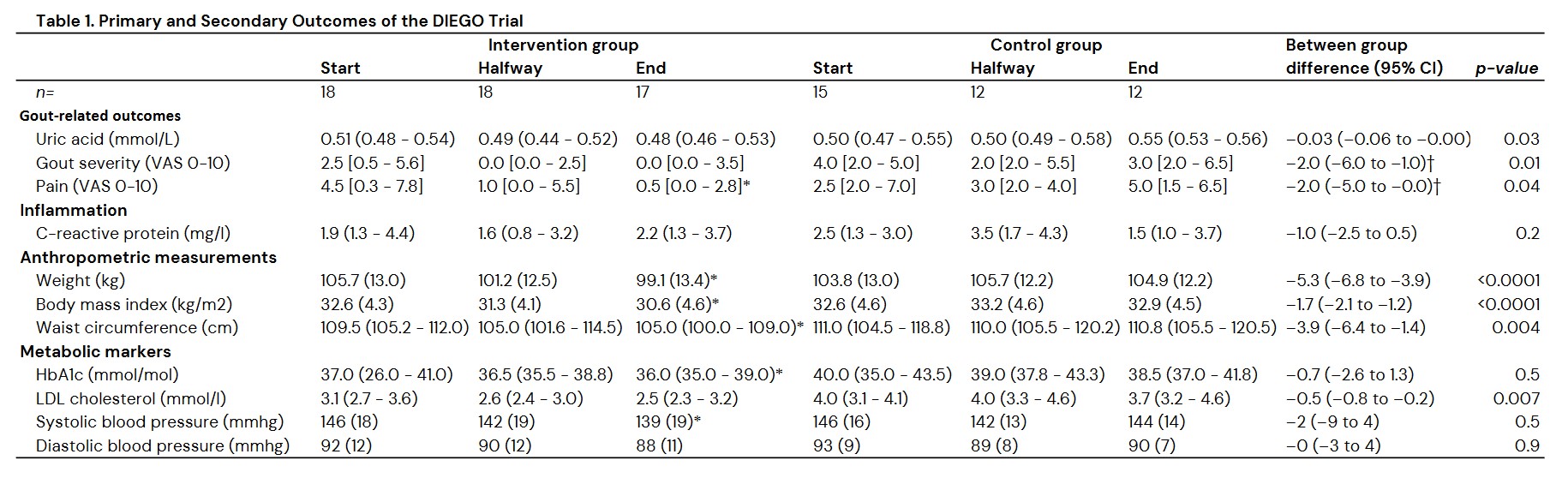
Results: Of 54 people screened, 36 were randomized and 31 completed the study (DIEGO group: n=18). Overall, 92% of participants were male, with a mean (SD) age of 52 (12) years and a mean (SD) BMI of 33 (4) kg/m2. After 16 weeks the DIEGO group had significantly lower SUA levels (–0.03 mmol/L 95% CI –0.06 to –0.00, p=0.03; –0.05 mmol/L 95% CI –0.08 to –0.02; p=0.004 after adjustment for age, sex and BMI) as compared to the control group (Table 1). In total 23 gout flares occurred during the study, 11 in the DIEGO group and 12 in the control group. The mean (SD) duration (days) and flare intensity (VAS range 0 least to 10 worst) in the DIEGO group were 5.6 (2.3) and 6.2 (1.8) respectively vs 4.6 (2.7) and 6.7 (1.6) in the control group. Overall gout severity and pain (VAS range 0 least to10 worst) were significantly lower in the DIEGO group vs. control group: –2.0 (95% CI –6.0 to –1.0) and –2.0 (95% CI –5.0 to –0.0) respectively. Compared to the control group, the DIEGO group had a lower body weight, reduced waist circumference and improved LDL cholesterol at the end of the study. The change in systolic blood pressure (SBP) was not different between the groups, however the SBP reduced significantly within the DIEGO group and not in the control group. HbA1c, CRP, and diastolic blood pressure remained unchanged. No serious adverse events occurred during the study.
Conclusion: The Mediterranean-style WFPD significantly decreased SUA in patients with gout and abdominal obesity. In addition, following the Mediterranean-style WFPD resulted in decreased gout severity and pain, significant weight loss, decreased waist circumference, and improved LDL cholesterol, thus reducing the risk for CVD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kretova A, Wagenaar C, Walrabenstein W, Vedder D, van Schaardenburg D, Gerritsen M. Effect of a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet in Patients with Gout: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-a-whole-food-plant-based-diet-in-patients-with-gout-a-pilot-randomized-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-a-whole-food-plant-based-diet-in-patients-with-gout-a-pilot-randomized-controlled-trial/