Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Little is known about the impact of upadacitinib (UPA) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) during the initial weeks of therapy in real-world clinical practice. Our objective was to evaluate the impact of UPA on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in patients with RA during the first 12 weeks of treatment using a mobile health application (app).
Methods: Participating rheumatologists from the CorEvitas RA Registry recruited patients across 17 sites between July 2020 and October 2021 who were initiating UPA treatment. A modified version of the ArthritisPower app was used to collect PROs, including RAPID3, PROMIS Fatigue-7a Short Form, and duration of morning joint stiffness, at baseline and weeks 1-4, 8, and 12. PROs are summarized as mean change from baseline (SD) for continuous outcomes (RAPID3 [including pain], PROMIS Fatigue, duration of morning stiffness) and as proportion of patients achieving response (RAPID3 low disease activity [LDA; defined as RAPID3 ≤ 6]) for binary outcomes. The treatment satisfaction questionnaire for medication (TSQM-9; range: 0-100 for effectiveness, convenience, and overall satisfaction subscales) and compliance questionnaire for rheumatology (CQR; range: 0-20) were assessed at weeks 8 and 12 and are summarized as mean (SD). RAPID3 responses over time were assessed using Kaplan-Meier estimation to determine the proportion of patients achieving disease activity improvement (defined as a reduction of at least one RAPID3 disease activity category) and minimally clinically important difference (MCID; defined as a decrease ≥ 3.8). Results were analyzed for all patients initiating UPA treatment, as well as for a subsample of TNF inhibitor (TNFi)-experienced patients with moderate to severe disease at baseline (defined as RAPID3 > 6).
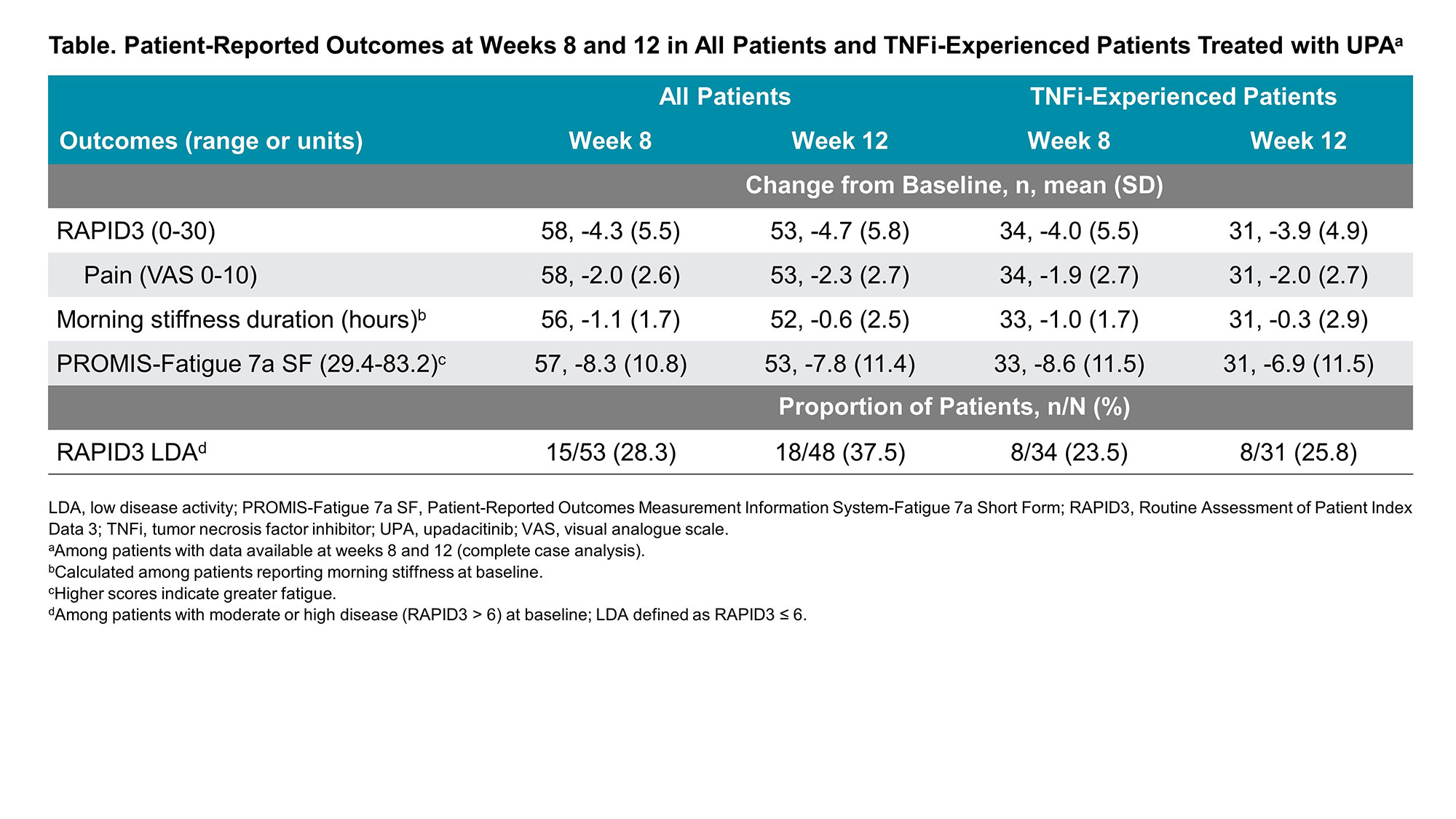
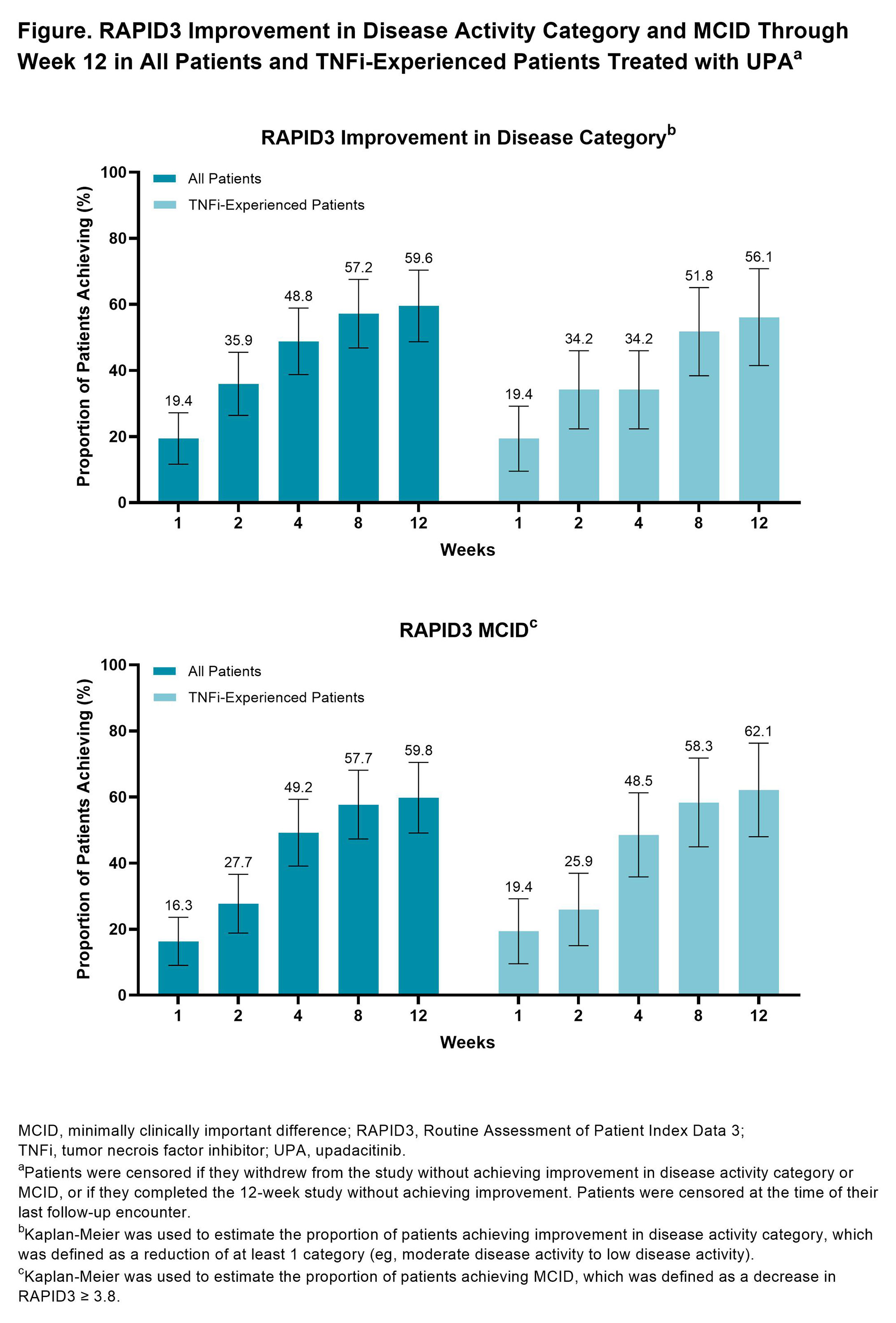
Results: In total, 103 RA patients initiating UPA (62.1% TNFi-experienced) were included in this analysis. At initiation, the mean age of patients was 59.9 years old, most were female (81.6%), and mean (SD) RAPID3 was 14.9 (5.2). At week 12, 53 patients (51.4%) completed the study and provided PRO data via the app. Amongst all patients initiating UPA treatment, improvements in RAPID3, pain, fatigue, and morning stiffness were observed at weeks 8 and 12 (Table). At week 12, 37.5% of patients achieved RAPID3 LDA. Starting at week 1, improvements in RAPID3 disease activity and achievement of MCID were reported, with nearly 50% of patients achieving these outcomes by week 4 and 60% by week 12 (Figure). Similar or slightly attenuated results were observed in patients with prior TNFi experience. Amongst all patients initiating UPA treatment, mean (SD) responses at week 12 for TSQM-9 for the effectiveness subscale was 66.8 (18.7), for convenience 83.6 (13.8), and for overall satisfaction 68.5 (20.3). Mean (SD) CQR at week 12 for all patients was 17.5 (2.1).
Conclusion: In this real-world cohort of RA patients, treatment with UPA was associated with improvement in RAPID3, pain, fatigue, and morning stiffness regardless of prior TNFi experience. Improvement in RAPID3 patient-reported disease activity was observed as early as week 1, with continued improvement reported through week 12.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harrold L, Zueger P, Nowell W, Blachley T, Lakin P, Curtis D, Stradford L, Venkatachalam S, Tundia N, Patel P. Early Real-World Effectiveness of Upadacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Patient-Reported Outcomes Collected via Mobile Application [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-real-world-effectiveness-of-upadacitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-patient-reported-outcomes-collected-via-mobile-application/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-real-world-effectiveness-of-upadacitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-patient-reported-outcomes-collected-via-mobile-application/