Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although exacerbated morbidity and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is frequently seen in women, the etiology of this sexual dimorphism remains unclear. Previously, we showed that the TNF-Tg mouse model of RA displays similar unexplored sex differences in the severity of inflammatory-erosive arthritis, interstitial lung disease (ILD) and early mortality from cardiopulmonary disease (female median life span = 165 vs. 226 days for males). Thus, the goal of this study was to elucidate the mechanisms that underlie these sex differences.
Methods: WT and TNF-Tg male and female mice in a C57BL/6 background (n = 3-12) were evaluated for weight and grip strength at 2, 3, 4, 5 and 5.5 months. At 5.5 months mice underwent in vivo micro-CT of the lung and a novel analysis technique was used to measure tissue (cells, fluid and ECM) volume within the lung. Mice were euthanized at 5.5 months for lung immunohistochemistry (CD3, B220 and F4/80), or flow cytometry (CD3, CD19, CD11b and CD11c).
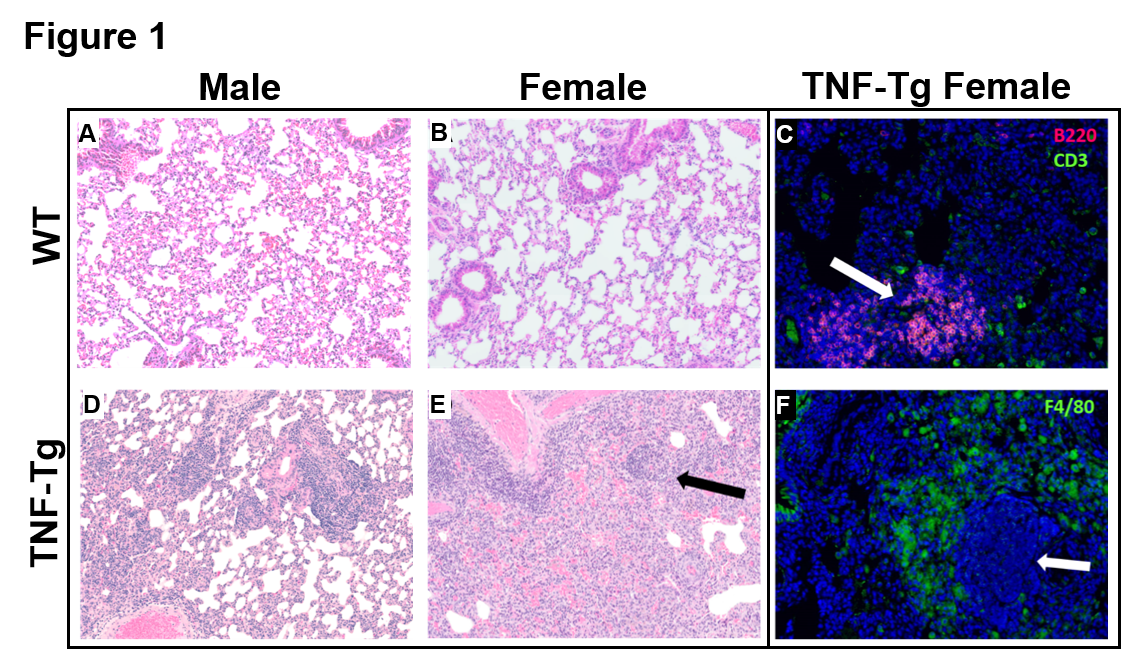
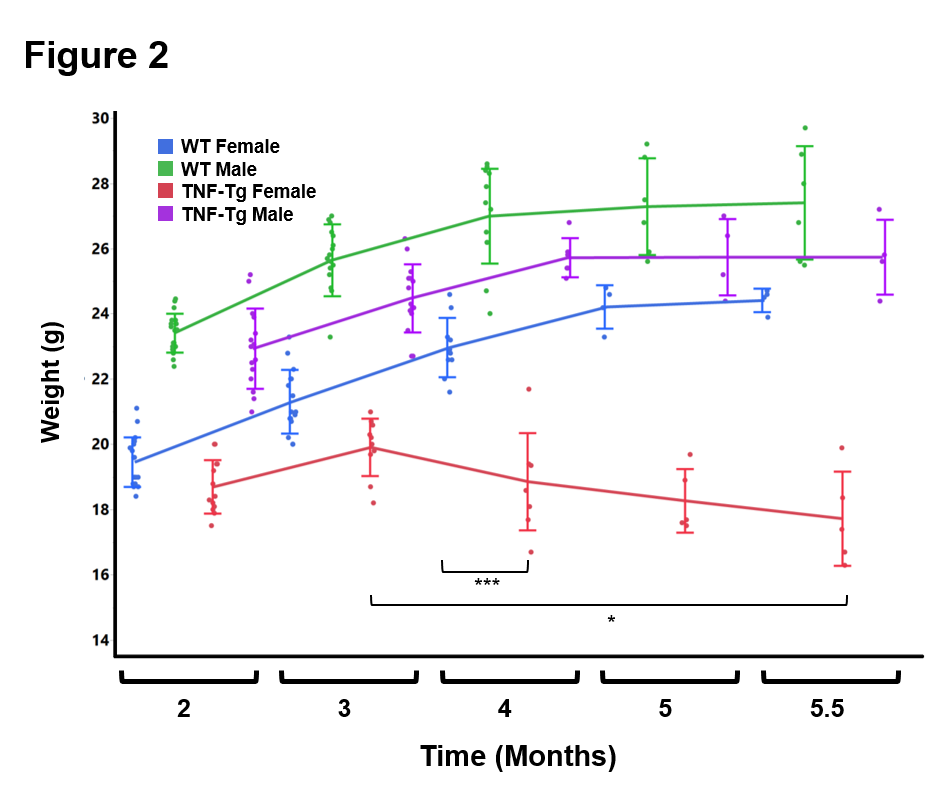
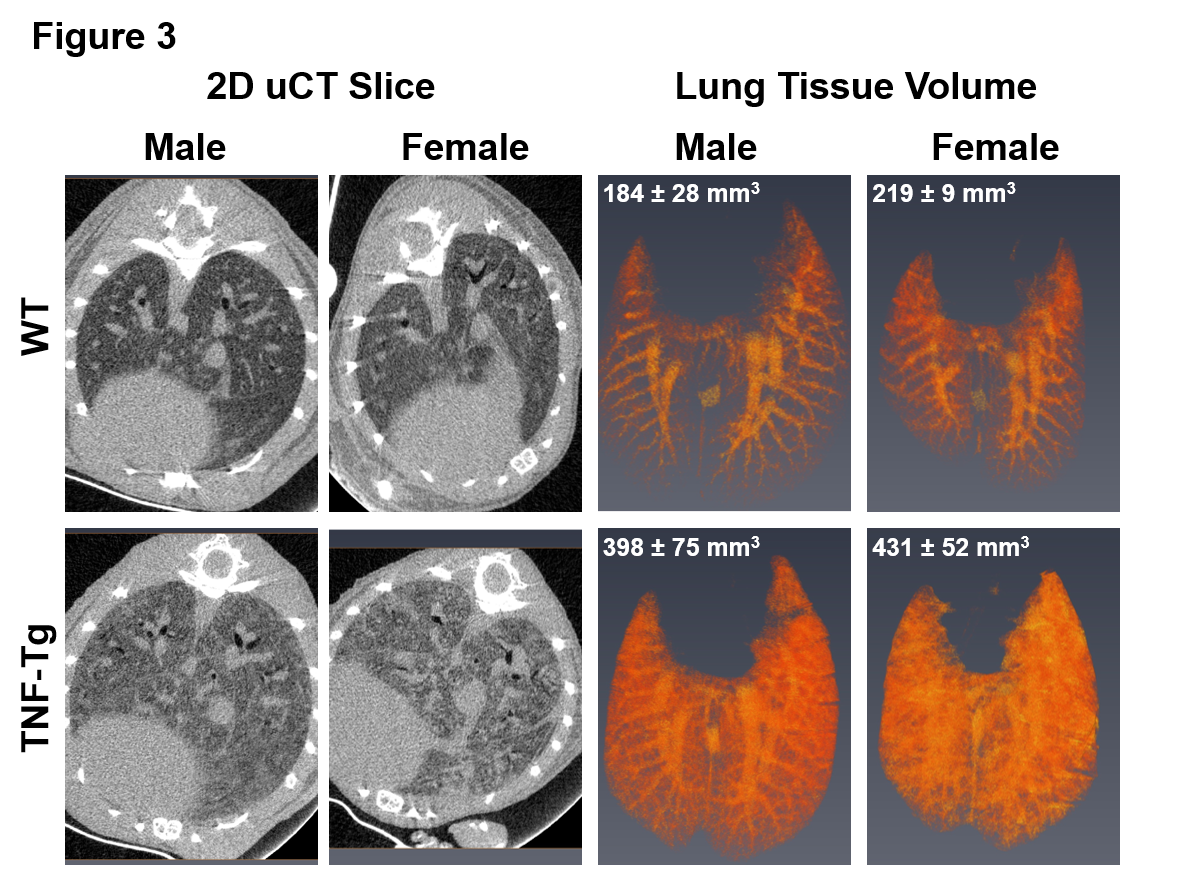
Results: ILD lesions contained B-cells, T-cells, and macrophages, and showed signs of pulmonary arterial hypertension (Fig. 1). At 4 months, female TNF-Tg mice were significantly smaller vs. WT littermates (18.9 ± 1.5g vs. 23.0 ± 0.9g, p<0.01); and TNF-Tg females displayed significant weight loss from 3 to 5.5 months (19.9 ± 0.9g vs 17.7 ± 1.4g, p<0.05; Fig. 2). Female TNF-Tg grip strength was also significantly decreased starting at 2 months vs. WT females (1.9 ± 0.4N vs 2.2 ± 0.2N, p<0.01), while male WT and TNF-Tg mice did not differ until 3 months (2.0 ± 0.3N vs 2.7 ± 0.3N, p<0.01). Both female and male TNF-Tg mice had significantly greater tissue volume via μCT vs. WT animals (431 ± 52 vs 398 ± 75 vs 219 ± 9 vs 184 ± 28 mm3; p<0.05; Fig. 3). Female and male TNF-Tg lungs also had significantly increased numbers of immune cells, in particular CD11b+/CD11c+ cells (105.5 ± 7.5, 345.0 ± 263.1 vs 8.6 ± 3.5, 4.5 ± 2.4 cells/lung x 103; p<0.05).
Conclusion: Here we describe a novel model of RA-associated ILD that recapitulates the sexual dimorphism known to occur in patients. While further work is necessary to elucidate the interactions of the comorbidities and their contributing factors, the significant weight loss observed in females may account for their early onset of arthritis and mortality.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bell R, Wu E, Wood R, Chakkalakal J, Rangel-Moreno J, Garcia-Hernandez MDLL, Ritchlin CT, Schwarz E, Rahimi H. Early Onset Morbidity and Mortality in Female Tumor Necrosis Factor Transgenic Mice with Inflammatory-Erosive Arthritis and Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-onset-morbidity-and-mortality-in-female-tumor-necrosis-factor-transgenic-mice-with-inflammatory-erosive-arthritis-and-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-onset-morbidity-and-mortality-in-female-tumor-necrosis-factor-transgenic-mice-with-inflammatory-erosive-arthritis-and-interstitial-lung-disease/