Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: As biologic agents including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitors (TNFi) have been proven to improve enormously clinical outcomes for patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), treat-to-target (T2T) is an emerging management strategy in AS. According to the concept of T2T strategy, clinical remission, which means mainly achievement of ASDAS inactive disease (ASDAS-ID) or, alternatively, low BASDAI with normal CRP (BASDAI-CRP) or ASAS partial remission, should be accomplished and then be maintained throughout TNFi therapy. In this study, we evaluated to determine the possibility of achieving clinical remission and to investigate the predictors of attainment of clinical remission in AS patients treated with TNFi.
Methods: This was a retrospective observational study in 139 adult AS patients treated with TNFi up to 33 months. All outcome measures were performed at baseline and month 3, and then every six month up to month 33. Clinical remission selected were ASDAS-ID and BASDAI < 2 with normal CRP level (BASDAI-CRP). The longitudinal relationship between early improvement in clinical parameters and achievement of clinical remission was assessed using generalized estimating equations (GEEs).
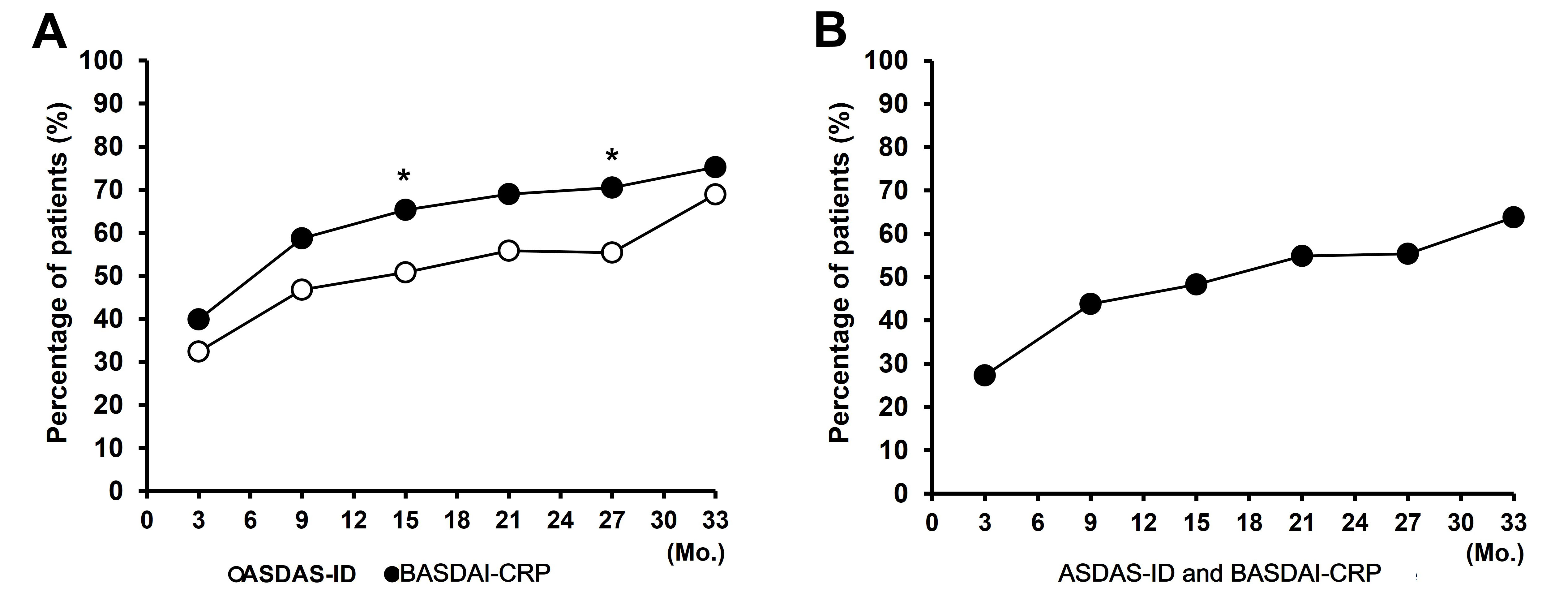
Results: Responders of ASDAS-ID increased from 32.4 at month 3 to 68.9% at month 33 and that of BASDAI-CRP increased from 39.9% at month 3 to 75.2% at month 33. Patients satisfied with ASDAS-ID or BASDAI-CRP were almost redundant. The responders of ASDAS-ID or BASDAI-CRP showed a significantly better functional and metrological indices than the non-responders.
The analysis using univariable GEE model demonstrated that age [OR: 0.71 (95% confidence interval (CI), 0.54-0.92)] and all of 3-month improvement in ASDAS-CRP [OR: 1.57 (CI, 1.11-2.23)], BASDAI [OR: 1.78 (CI, 1.40-2.26)], physician’s global assessment (PhGA) [OR: 1.47 (CI, 1.26-1.71)], patient’s global assessment (PtGA) [OR: 1.40 (CI, 1.26-1.71)], and pain [OR: 1.32 (CI, 1.13-1.53)] were significant variables. On the multivariable GEE analysis, age [OR: 0.67 (CI, 0.49-0.93)] and 3-month BASDAI improvement [OR: 1.70 (CI, 1.19-2.41)] were associated with achievement of ASDAS-ID.
On the univariable GEE analysis, age [OR: 0.76 (CI, 0.60-0.96)], 3-month improvement in BASDAI [OR: 1.66 (CI, 1.32-2.10)], PhGA [OR: 1.23 (CI, 1.06-1.42), PtGA [OR: 1.19 (CI, 1.04-1.38)], and pain [OR: 1.25 (CI, 1.09-1.45)], and normalized ESR [OR: 2.87 (CI, 1.26-6.55)] and CRP [OR: 2.56 (CI, 1.22-5.34)] at month 3 were independent predictors of achievement of BASDAI-CRP. On the multivariable GEE analysis, age [OR: 0.75 (CI, 0.59-0.96)], 3-month BASDAI improvement [OR: 1.75 (CI, 1.29-2.36)], normalized ESR [OR: 2.93 (CI, 1.20-7.16)] and CRP at month 3 [OR: 2.98 (CI, 1.30-6.83)] were independent predictors of attainment of BASDAI-CRP.
Conclusion: The proportion of achievement of BASDAI-CRP was higher than that of ASDAS-ID during long-term TNFi therapy and patients satisfied with ASDAS-ID and BASDAI-CRP were almost redundant. On the analysis of multivariable GEE model, age and 3-month BASDAI improvement were independent predictors of achievement of both clinical remission criteria and normalized ESR and CRP at month 3 were predictors of achievement of BASDAI-CRP.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee S, Kim N, Nam E. Early Improvement in Disease Activity Indices Predicts Achievement of Long-term Clinical Remissions, ASDAS Inactive Disease and Low BASDAI with Normal CRP, During TNF-α-inhibitor Therapy in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-improvement-in-disease-activity-indices-predicts-achievement-of-long-term-clinical-remissions-asdas-inactive-disease-and-low-basdai-with-normal-crp-during-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitor-therapy-in-patie/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-improvement-in-disease-activity-indices-predicts-achievement-of-long-term-clinical-remissions-asdas-inactive-disease-and-low-basdai-with-normal-crp-during-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitor-therapy-in-patie/