Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients are at high risk for pulmonary hypertension (PH), a leading cause of death in this population. Chloroquine is a pulmonary vasodilator shown to attenuate hypoxia-induced PH in mouse models (1). In culture with pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMC), chloroquine increases BMPR-II protein expression and inhibits proliferation of PASMC via inhibition of autophagy (2). Our objective was to evaluate whether treatment with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) was associated with a lower rate or longer time to onset of PH in SSc patients.
Methods: We performed a survival analysis using a prospective, observational SSc cohort from a US SSc Center. We identified SSc patients seen for an initial visit between 1990 and 2015. Individuals exposed to HCQ for a minimum of 90 days were in the treatment group and all others were controls. Additional chart review and use of electronic medical record coding was performed to confirm HCQ exposure dates and PH evaluations. Descriptive analysis plus Cox Proportional-Hazards modeling with time-dependent covariates to account for duration of HCQ exposure was performed. We analyzed all HCQ exposure, with separate analysis for early (< 18 months of disease) HCQ use.
Results: Eligible were 228 with HCQ exposure and 977 controls; 21 had missing onset of HCQ use, symptoms, or PH diagnosis and were excluded from analysis. Baseline characteristics for the 208 cases and 976 controls are shown in Table 1. HCQ-treated patients were younger, more often female and non-Caucasian. HCQ patients had a higher rate of limited cutaneous disease with more joint involvement at baseline, but lower rates of pulmonary fibrosis, PH and renal crisis. HCQ patients had significantly higher frequencies of anti-centromere (ACA) and anti-U1RNP antibodies, both of which are recognized to be associated with increased risk of PH.
In time to event analysis of the entire group, there was no difference in development of PH between those treated with HCQ, and those not. However, when we evaluated those treated early in their disease, defined as within 18 months of their initial SSc symptom (approximately 25% of HCQ-exposed patients), the time to development of PH was slower (p=0.04), as shown in Figure 1.
Conclusion: Patients with SSc treated with HCQ are younger, more frequently female and more often have limited SSc, joint symptoms and ACA and U1-RNP antibody positivity. Although limited SSc and these antibodies are linked to higher rates of PH, our findings suggest that when HCQ is initiated early in disease (< 18 months) there is a reduced rate of progression to PH. This is in keeping with the plausible biologic actions of HCQ on preventing PH. This early stage of SSc may represent a critical period for therapeutic intervention with HCQ.
References:
1) Wu, K. et al. Chloroquine is a potent pulmonary vasodilator that attenuates hypoxia‐induced pulmonary hypertension. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174: 4155– 4172.
2) Long L. et al. Chloroquine prevents progression of experimental pulmonary hypertension via inhibition of autophagy and lysosomal bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor degradation. Circ Res. 2013;112(8):1159-1170.
 Table 1. Baseline Characteristics
Table 1. Baseline Characteristics
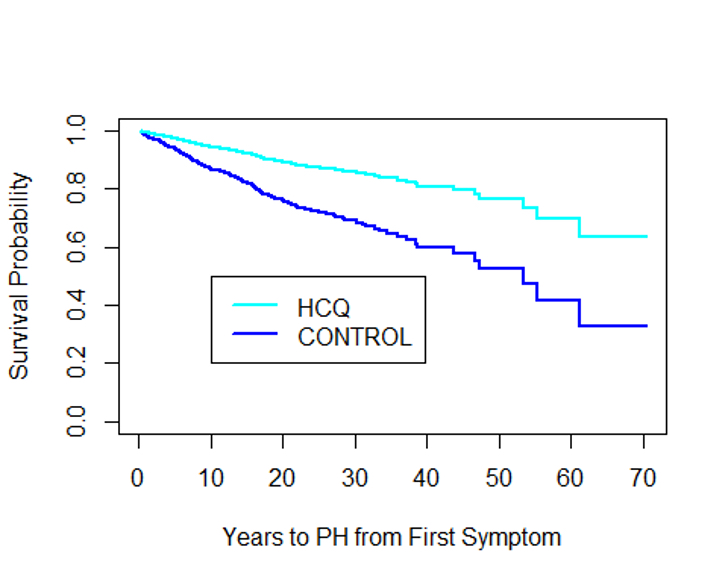 Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curve of pulmonary hypertension survival probability in SSc patients exposed with HCQ during the first 18 months of disease and SSc patients who were not exposed to HCQ. p=0.04
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curve of pulmonary hypertension survival probability in SSc patients exposed with HCQ during the first 18 months of disease and SSc patients who were not exposed to HCQ. p=0.04
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Boucher A, Park Y, Zalewski S, Laffoon M, Medsger T, Lafyatis R, Domsic R. Early Hydroxychloroquine Use May Reduce Risk for SSc-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-hydroxychloroquine-use-may-reduce-risk-for-ssc-associated-pulmonary-hypertension/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-hydroxychloroquine-use-may-reduce-risk-for-ssc-associated-pulmonary-hypertension/
