Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: To retrospectively evaluate drug survival and reasons for discontinuation of eight biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients using the Niigata Orthopedic Rheumatoid Arthritis Database (NOSRAD).
Methods: Of 1,517 RA patients registered in NOSRAD from May 2001 to August 2022, 1,182 who received at least one of the following bDMARDs were included: abatacept (ABT), adalimumab (ADA), certolizumab pegol (CZP), etanercept (ETN), golimumab (GLM), infliximab (IFX), sarilumab (SAR), and tocilizumab (TCZ). We analyzed patient backgrounds, drug survival, and discontinuation reasons in three groups: the overall cohort, bDMARDs-naïve group, and switch group. The chi-square test and Kruskal–Wallis test were used for categorical and continuous variables, respectively. Drug survival was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method, and compared by log-rank test. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using EZR (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan).
Results: In the naïve group (n = 784), significant inter-drug differences were observed in sex, age, disease duration, the 28-joint Disease Activity Score with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR), concomitant methotrexate (MTX) use, concomitant prednisolone (PSL) use, and PSL dose. In the switch group (n = 398), significant differences were found in age, disease duration, DAS28-ESR, MTX use, PSL dose, and whether the drug was used as a second or fourth-line agent. Among the naïve group, TCZ showed the highest drug survival rate (50.8% at 5 years and 37.6% at 10 years). The 5-/10-year survival rates of other bDMARDs were as follows: ABT 46.6%/24.0%, IFX 25.0%/18.5%, ETN 36.6%/18.1%, GLM 22.6%/17.0%, ADA 32.3%/13.7%, and CZP 33.0%/10.8%. In the switch group, ABT had the highest survival rate (42.6% at 5 years and 21.3% at 10 years), followed by TCZ (38.2%/21.1%), ADA (18.3%/18.3%), ETN (15.1%/8.1%), CZP (17.3% at 5 years; 10-year data unavailable), GLM (14.8%; 10-year data unavailable), and IFX (10.0%; 10-year data unavailable). The proportion of discontinuation due to insufficient efficacy was 40.5% for IFX, 34.3% for ETN, 16.7% for TCZ, 38.4% for ADA, 22.8% for ABT, 28.4% for GLM, 41.5% for CZP, and 23.7% for SAR. Discontinuation due to adverse events was 20.3%, 20.0%, 16.7%, 17.4%, 13.1%, 16.8%, 24.5%, and 8.5%, respectively. Discontinuation due to non-adverse reasons (remission or good response, patient preference, transfer, others, or unknown) was 29.7%, 34.3%, 25.4%, 18.6%, 18.6%, 25.3%, 13.2%, and 13.6%, respectively.
Conclusion: In the naïve group, TCZ had the highest survival; in the switch group, ABT did. Switching was associated with lower survival. ABT was often used in older patients and had fewer discontinuations due to adverse events, suggesting its potential utility in elderly RA. This large-scale, single-center, long-term study highlights the importance of selecting and dosing bDMARDs appropriately to maintain long-term efficacy.
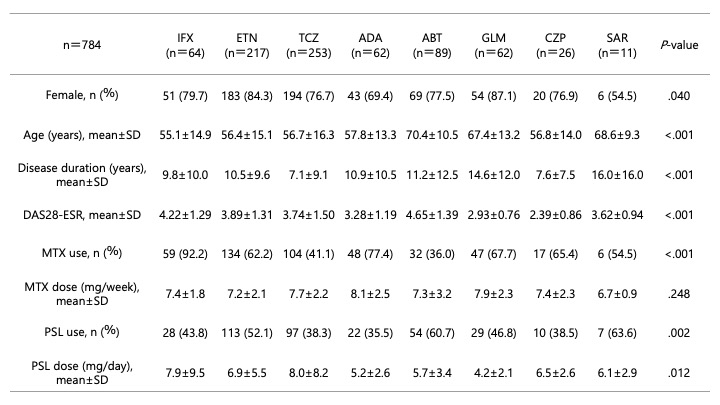 Table 1. Patient backgrounds of bDMARDs-naïve group.
Table 1. Patient backgrounds of bDMARDs-naïve group.
.jpg) Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier drug-survival rates for each drug in bDMARDs-naïve group.
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier drug-survival rates for each drug in bDMARDs-naïve group.
.jpg) Table 2. Reasons for discontinuation.
Table 2. Reasons for discontinuation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hao N, Kondo N. Drug Survival and Discontinuation Reasons of Eight Biological Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in 1,182 Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Retrospective Study Using the Niigata Orthopedic Rheumatoid Arthritis Database (NOSRAD) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-survival-and-discontinuation-reasons-of-eight-biological-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-1182-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-retrospective-study-using-the-niigata-orthopedic-rheu/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-survival-and-discontinuation-reasons-of-eight-biological-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-1182-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-retrospective-study-using-the-niigata-orthopedic-rheu/
