Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Takayasu’s arteritis (TA) is a large vessel vasculitis affecting mainly young women. Biologic agents are currently use to treat refractory TA patients but no data are available on drug retention rate (DRR) of biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) TA patients. We retrospectively investigated DRR and reasons for discontinuation of seven bDMARDs in TA patients in a real-world setting.
Methods: TA patients followed-up in our Centre fulfilling the 1990 ACR criteria and treated with ≥1 bDMARD were selected. Data about disease duration, number of bDMARDs, reasons for bDMARDs discontinuation, concomitant conventional synthetic (cs)DMARDs were collected. Survival curves were examined by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared using a stratified log-rank test. 24-month DRR was calculated. Hazard ratio (HR) for concomitant csDMARDs and for previous bDMARDs was evaluated. A comparative sub-analysis between anti-TNFα drugs and tocilizumab was performed.
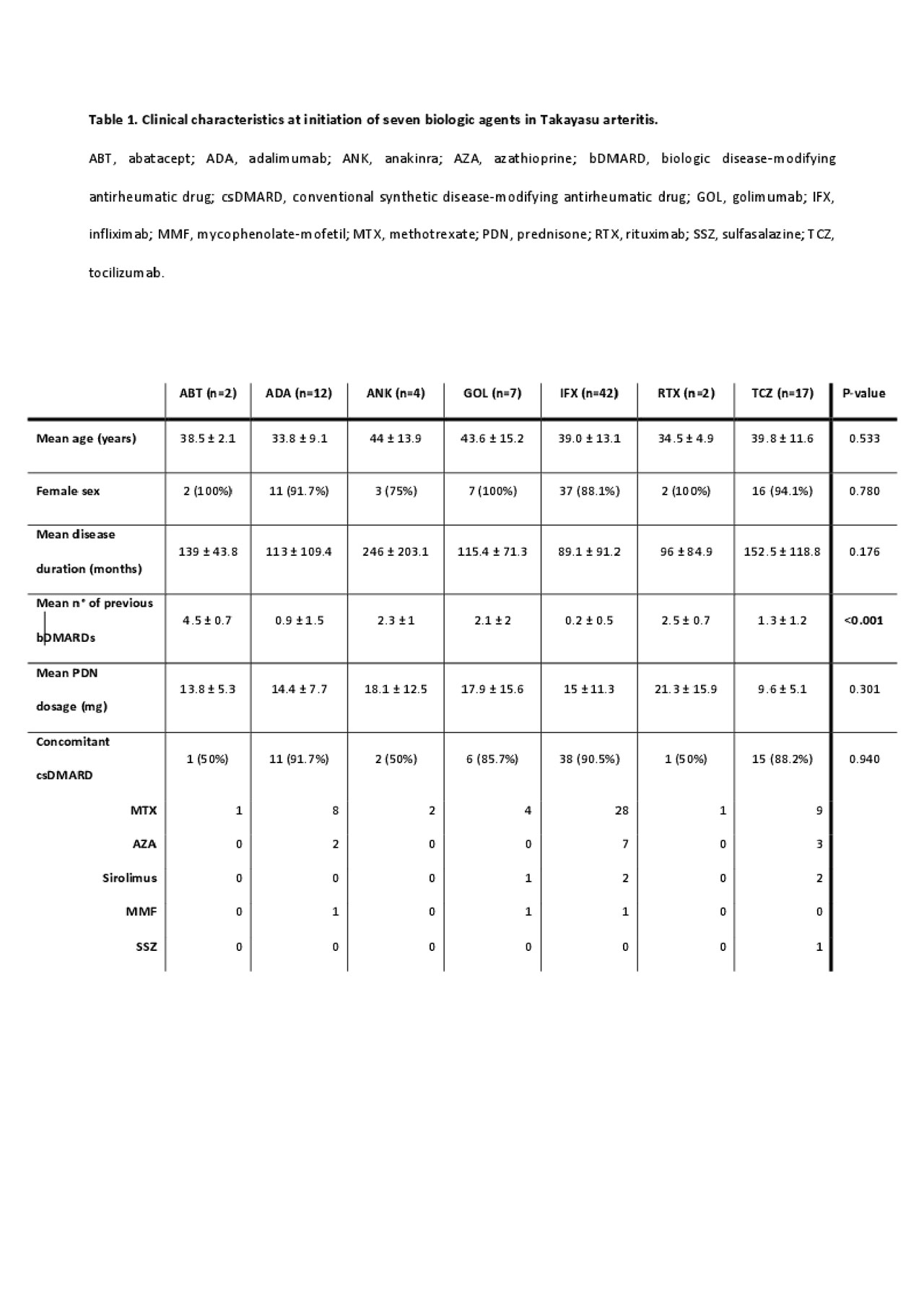
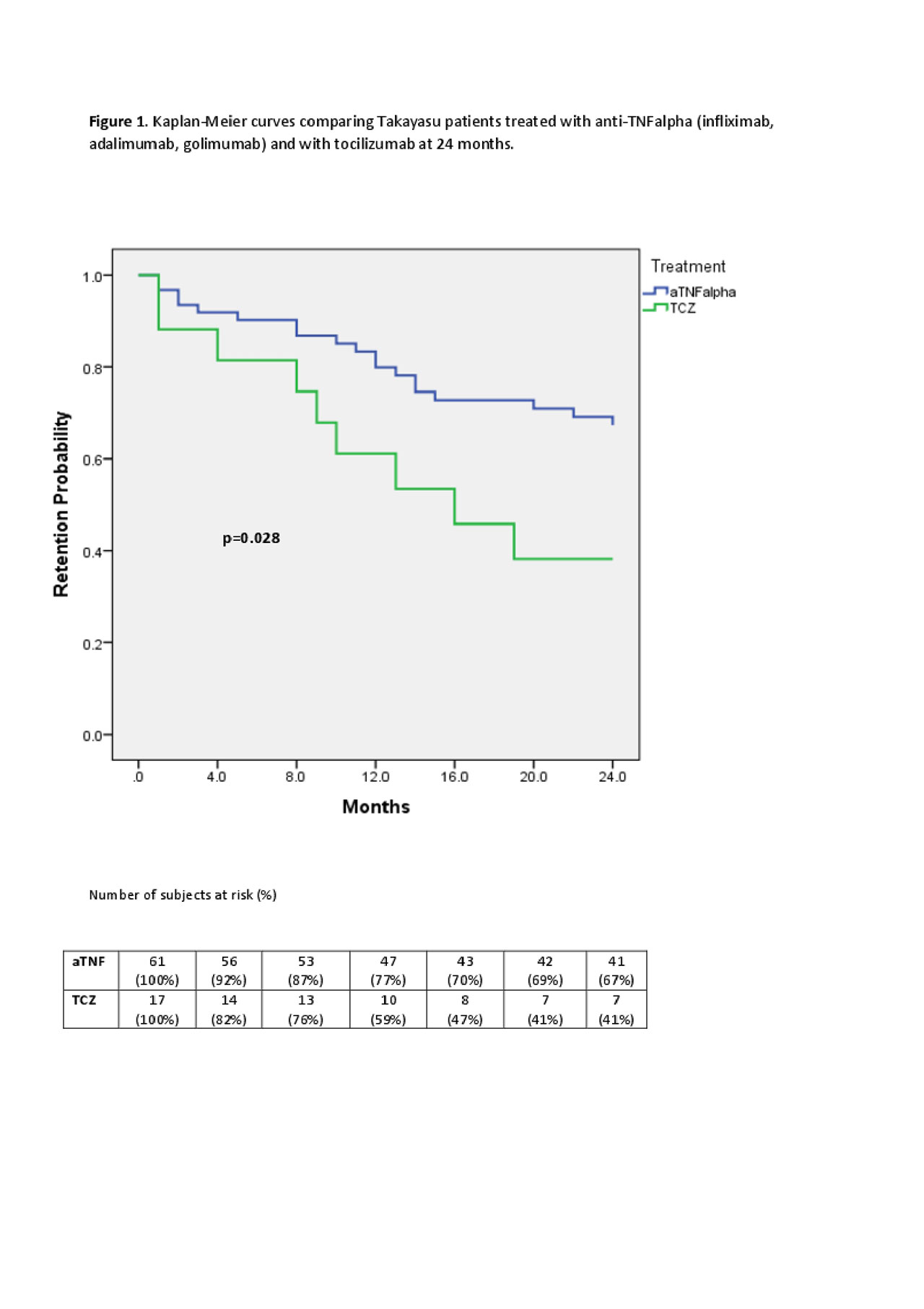
Results: We identified 50 patients and 86 bDMARD-courses. Patients characteristics are summerized in Table 1.No significant differences were observed in age and disease duration between the seven groups (data not shown). Infliximab was the most frequent first-line bDMARD (78.6%). At bDMARDs initiation, all patients were on prednisone (mean dose, 13.5±10.3 mg/day) and 85.2% on concomitant csDMARD therapy. 43% of treatment courses were stopped by 24 months. Golimumab had the highest DRR (71.4%), followed by infliximab (69%), adalimumab (56.3%), abatacept (50%), tocilizumab (41.1%), anakinra (0%) and rituximab (0%), p=0.016. Concomitant csDMARDs therapy showed positive effects on DRR (HR=2.87, 95% CI=1.19-6.92, p=0.019). Anti-TNFα drugs had significantly higher DRR compared to tocilizumab (67.2% vs 41.1%, p=0.028), see Figure 1. Even in these subgroups, csDMARDs showed positive effects on DRR (HR=3.79, 95% CI=1.49-9.6, p=0.005).
Conclusion: Anti-TNFα agents had the highest DRR overall and a higher DRR in a head-to-head comparison with tocilizumab. Concomitant csDMARDs had a significant positive effect on bDMARDs DRR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Campochiaro C, Tomelleri A, Sartorelli S, Cavalli G, Giacomo D, Baldissera E, Dagna L. Drug Retention and Discontinuation Reasons Between Seven Biologics in Patients with Takayasu Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-and-discontinuation-reasons-between-seven-biologics-in-patients-with-takayasu-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-and-discontinuation-reasons-between-seven-biologics-in-patients-with-takayasu-arteritis/