Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Nintedanib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has been approved for the treatment of SSc-ILD. As nintedanib may cause fetal harm, patients taking nintedanib should avoid pregnancy. The combination of ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel is a commonly used oral contraceptive. We investigated the pharmacokinetics (PK) of the combination of ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel alone and with nintedanib at steady-state in female patients with SSc-ILD.
Methods: We conducted an open-label, two-period, fixed-sequence, drug–drug interaction study (NCT03675581). Female patients aged ≥18 years, with SSc (based on 2013 ACR/EULAR criteria) and ≥10% extent of fibrotic ILD on a high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scan were eligible to participate. In Period 1, patients received a single tablet containing 30 μg ethinylestradiol and 150 μg levonorgestrel (reference treatment) ≥3 days before the first administration of nintedanib in Period 2. In Period 2, patients received a second tablet containing 30 μg ethinylestradiol and 150 μg levonorgestrel after continuous intake of nintedanib 150 mg bid for ≥10 consecutive days (test treatment). The primary PK endpoints were the areas under the concentration–time curve of ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel in plasma over the time interval from 0 to the last quantifiable data point (AUC0-tz) and the maximum measured concentrations of ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel in plasma (Cmax). The areas under the concentration–time curve of ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel in plasma over the time interval from 0 extrapolated to infinity (AUC0-∞) were secondary PK endpoints. The relative exposure to ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel when administered alone versus in combination with nintedanib was assessed using an ANOVA model.
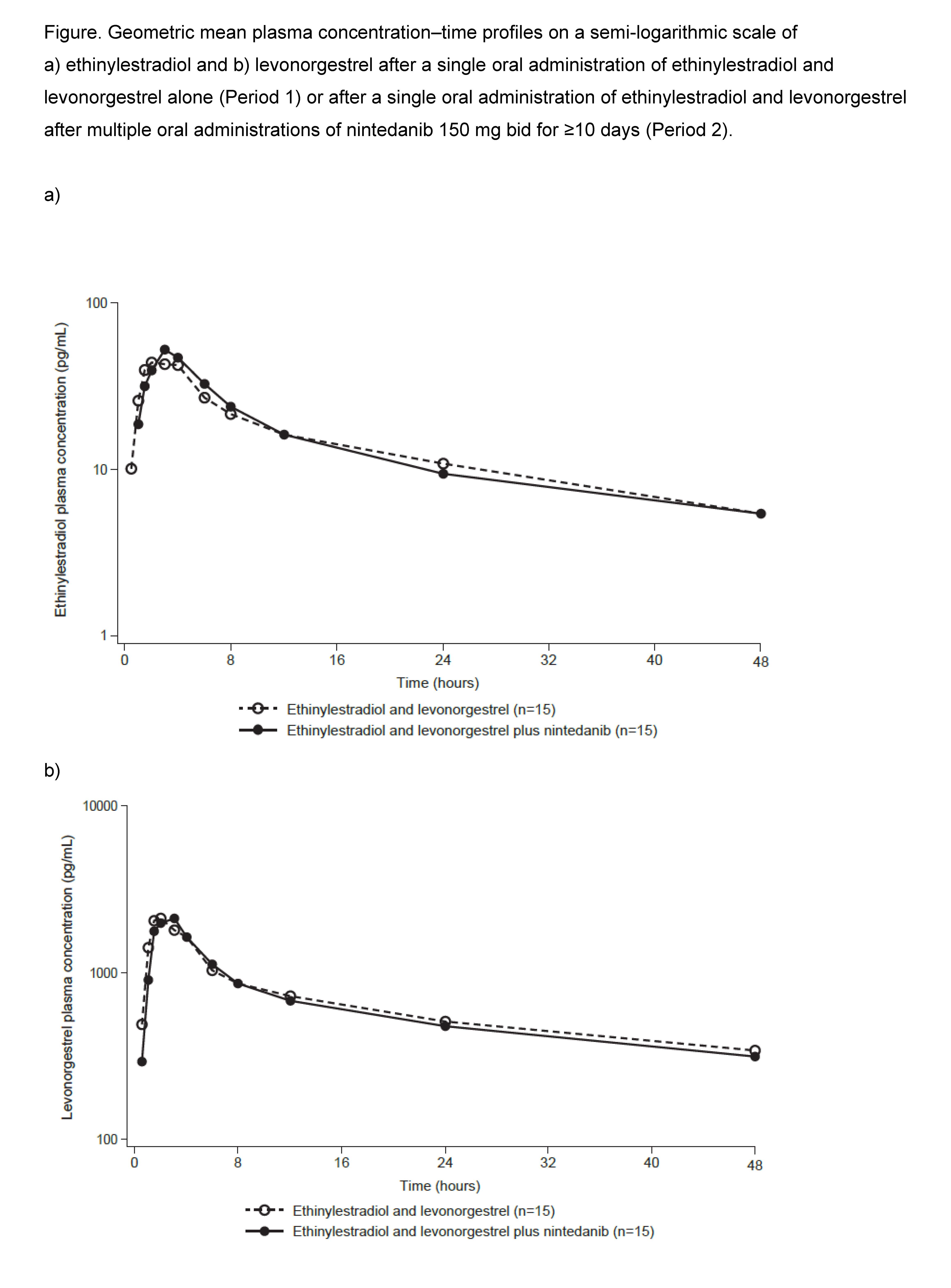
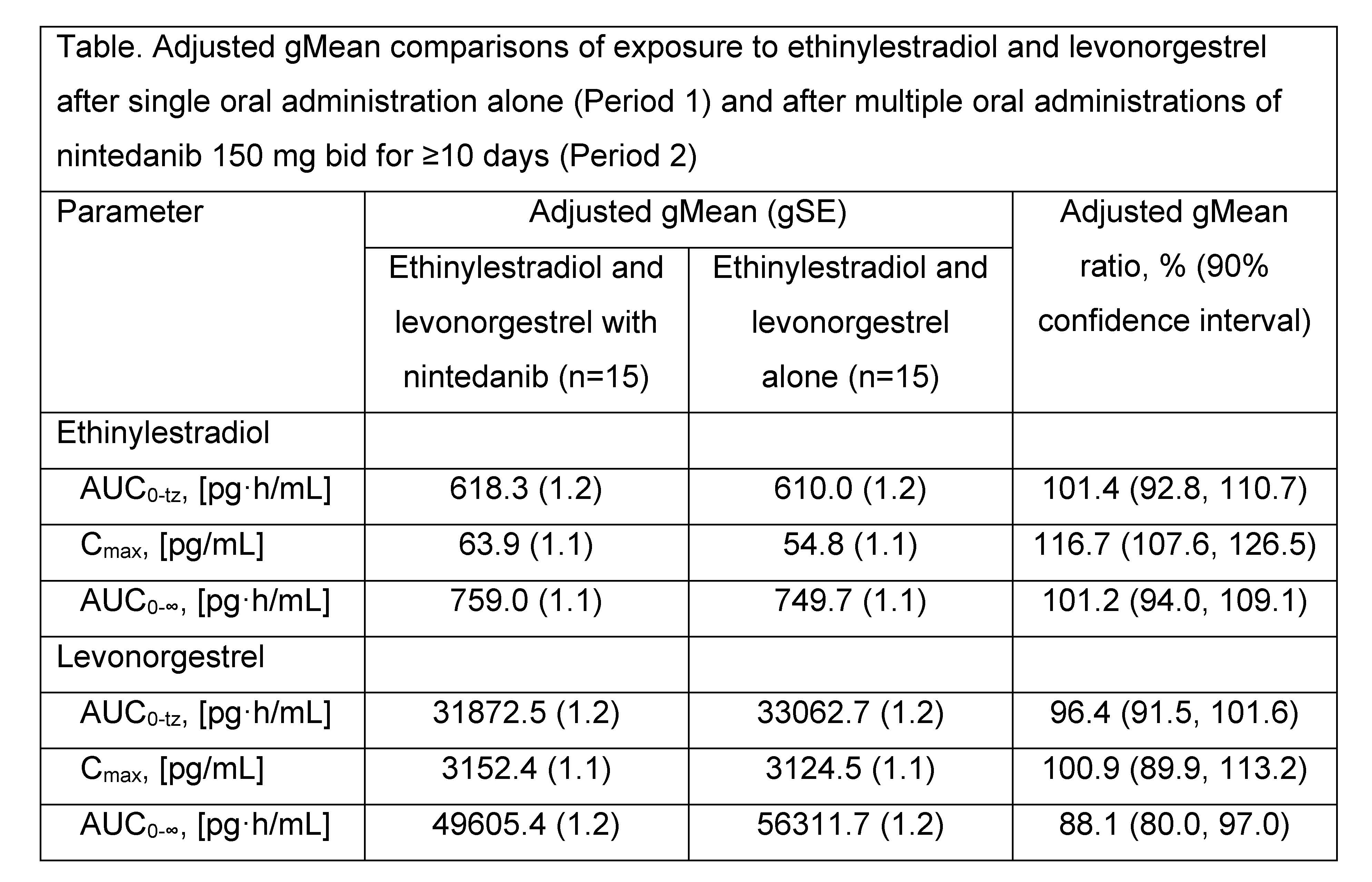
Results: PK data were analyzed from 15 treated patients. Plasma concentration–time profiles of ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel were similar after administration alone or after administration of nintedanib 150 mg bid for ≥10 consecutive days (Figure). Total exposure to ethinylestradiol (AUC0-tz and AUC0-∞) was similar when ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel were administered alone or after multiple administrations of nintedanib and peak exposure to ethinylestradiol (Cmax) slightly increased (by approximately 16%) after multiple administrations of nintedanib (Table). No differences in total or peak exposure to levonorgestrel (AUC0-tz or Cmax) were observed when ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel were administered alone or after multiple administrations of nintedanib (Table).
Conclusion: PK results indicate that there is no relevant effect of nintedanib 150 mg bid on the plasma exposure to ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel in female patients with SSc-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vonk M, Avis M, Marzin K, Mack S, Wind S, Gahlemann M. Drug-Drug Interaction Study of Nintedanib (Ofev®) and the Combination of Ethinylestradiol and Levonorgestrel (Microgynon®) in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-drug-interaction-study-of-nintedanib-ofev-and-the-combination-of-ethinylestradiol-and-levonorgestrel-microgynon-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-di/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-drug-interaction-study-of-nintedanib-ofev-and-the-combination-of-ethinylestradiol-and-levonorgestrel-microgynon-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-di/