Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical III
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Brentuximab vedotin (ADCETRIS®) is a drug antibody conjugate targeting CD30 approved for treatment of Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) and other hematologic malignancies. Association of CD30 with a pro-fibrotic Th2 phenotype and elevated soluble CD30 observed in autoimmune diseases, including SSc, provide rationale for targeting CD30 as a treatment for SSc.
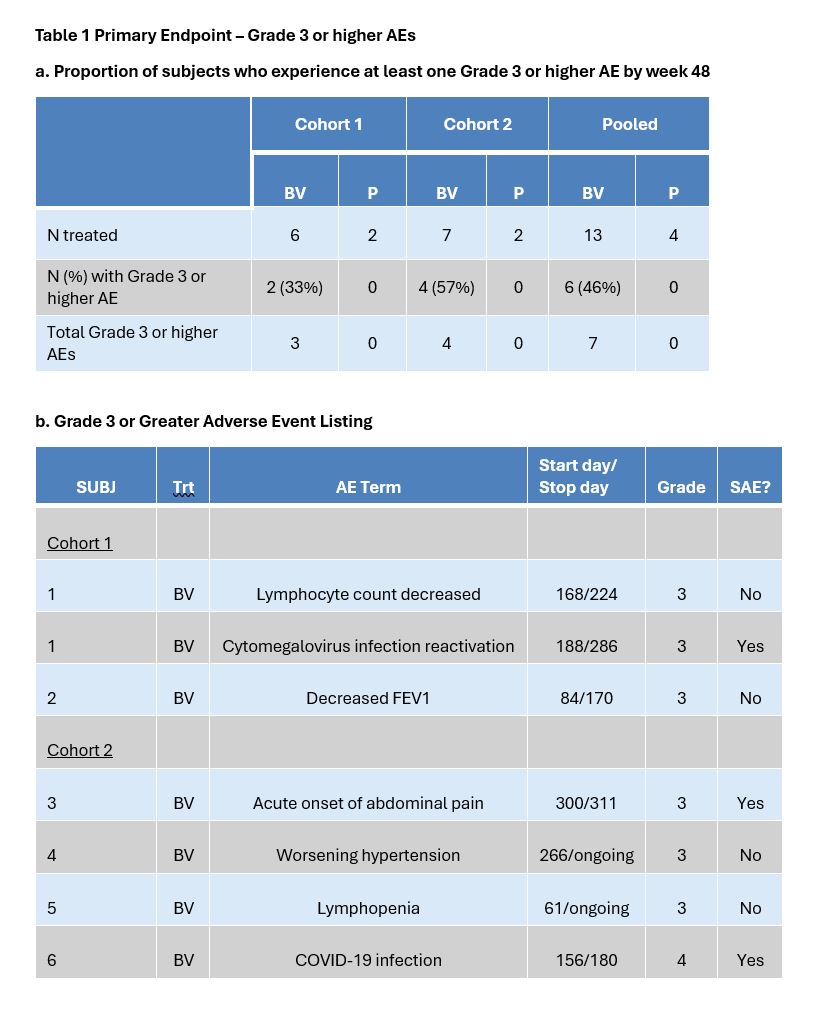
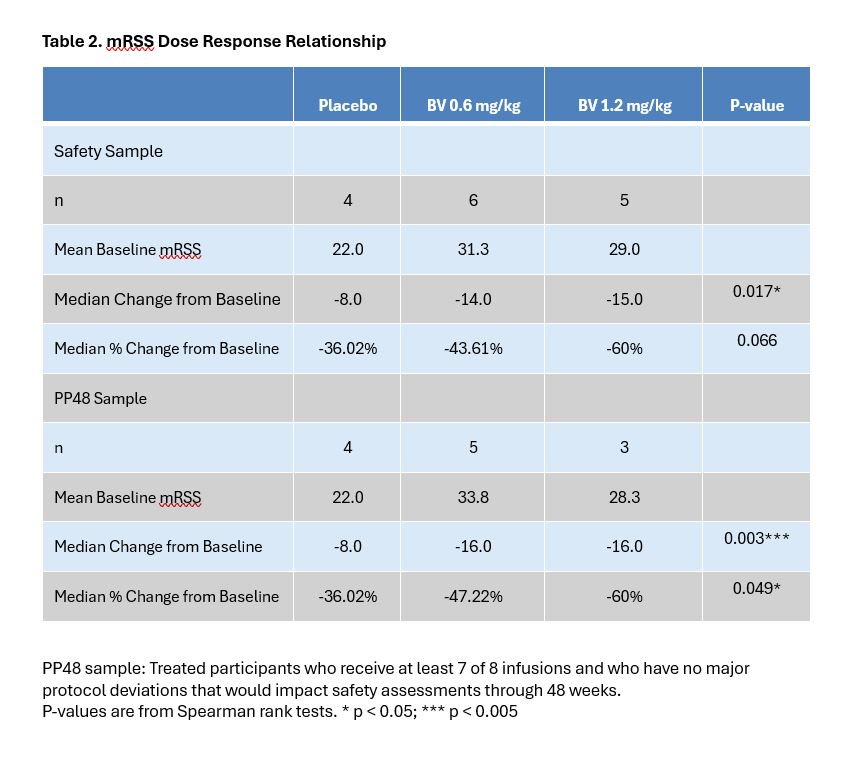
Methods: The BRAVOS trial was a phase 1/2 multicenter randomized double blinded dose escalation safety study of brentuximab vedotin (BV) in diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc). Three ascending dose cohorts of 8 subjects randomized 6:2 BV vs placebo (PBO) were planned, with doses of 0.6 mg/kg, 1.2 mg/kg, and 1.8 mg/kg (FDA approved dose for HL) administered intravenously every three weeks for 8 doses. Subjects were followed for 48 weeks. Approval by a safety committee was required to proceed to the next higher dose. Due to enrollment challenges, enrollment was closed prior to completing cohort 2. Immunophenotyping of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), histological and immunofluorescent staining of skin biopsies, and bulk RNAseq of skin biopsies were conducted. The primary endpoint was proportion of subjects who experienced at least one Grade 3 or higher adverse event (AE) by the CTACE v5.0 by week 48. Exploratory endpoints included the Modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS).
Results: Seventeen subjects with dcSSc were recruited at 5 centers; 8 to cohort 1 and 9 to cohort 2. Mean mRSS at baseline was 28.2 (SD 8.9) and mean disease duration after onset of non-Raynaud’s symptoms was 26.6 months (SD 17.35). Background therapy was mycophenolate in 14/17 and methotrexate in 3/17 subjects. In the BV group, 6 Grade 3 and 1 Grade 4 AEs occurred in 6 subjects, compared to no Grade 3 or higher AEs in the PBO group (Table 1). In a dose response analysis, BV was associated with a greater percent change in mRSS compared to PBO at week 48, however the results were confounded by an imbalance in disease severity at baseline (Table 2).
Analysis of PBMCs demonstrated a substantial decline in the frequency of CD30+ T and B lymphocyte subsets in blood following BV treatment, which largely returned to baseline by week 48. At week 24 cumulative depletion of several lymphocyte subsets, particularly activated B cells, exceeded what was expected based on the small percentage of CD30+ cells in these subsets at baseline.
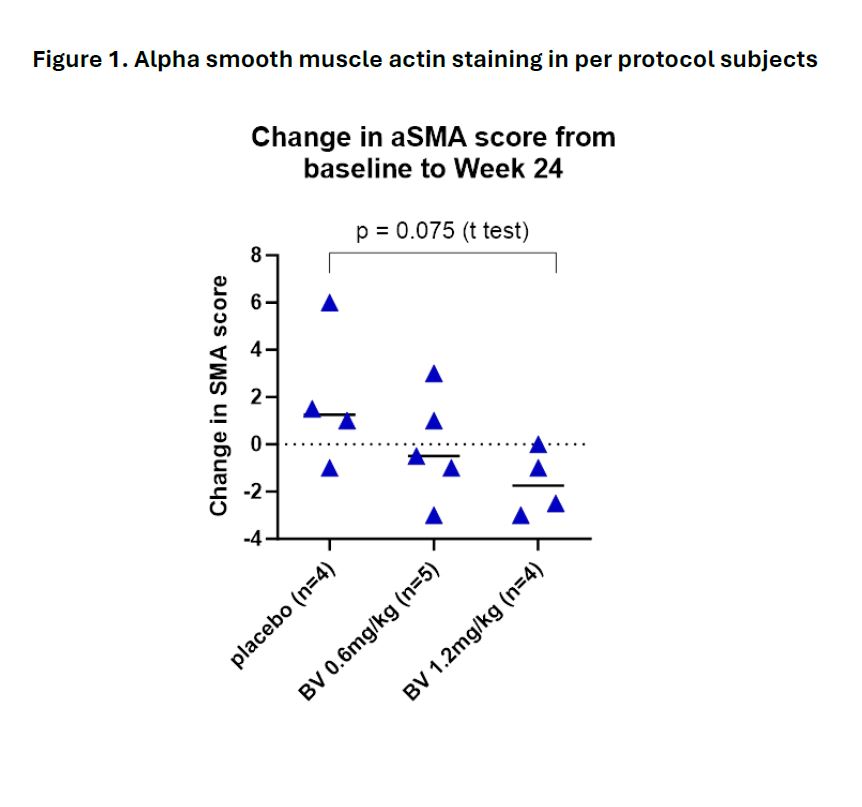
Analyses of skin biopsies demonstrated a trend towards a dose-dependent decline in myofibroblasts, identified by alpha smooth muscle actin staining, in BV versus PBO subjects (Figure 1). Bulk skin RNAseq also showed a decline in gene expression of several disease-relevant pathways in the 1.2mg/kg dosing cohort at week 24, including epidermal cell differentiation, regulation of ERK1/2 cascade, and regulation of inflammatory response.
Conclusion: Grade 3 or higher AEs occurred only in the BV group and were consistent with the known safety profile of BV. Although the results were limited by a small sample size, the data suggest improvement in mRSS with BV and show reduced frequencies of several activated lymphocyte populations in the circulation with a trend towards reduced inflammation and pro-fibrotic signals in skin. The results support conducting a larger study to evaluate efficacy of BV in dcSSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fox D, Cooney L, Stelzig L, Lafyatis R, Gudjonsson J, Tsoi L, Mayes M, Shah A, Kafaja S, Barry W, Goldmuntz E, Smilek D, Khanna D. Dose Escalation Safety Study of Brentuximab Vedotin for Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis:Clinical Results and Mechanistic Analysis of Skin and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dose-escalation-safety-study-of-brentuximab-vedotin-for-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosisclinical-results-and-mechanistic-analysis-of-skin-and-peripheral-blood-mononuclear-cells/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dose-escalation-safety-study-of-brentuximab-vedotin-for-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosisclinical-results-and-mechanistic-analysis-of-skin-and-peripheral-blood-mononuclear-cells/