Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I (0660–0682)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Two recent analyses of the Global Burden of Disease Study reported on the rising global burden of gout (Safiri A&R 2020, Xia Rheumatology 2020). Addressing obesity, a major modifiable risk factor for gout, may help alleviate this burden. However, it is also recognized that there is a significant genetic contribution to the risk of hyperuricemia and gout according to genome-wide association studies (GWAS) (Tin Nat Genet 2019). It is unknown whether obesity affects gout risk differently among genetically predisposed individuals. Our objective was to prospectively investigate the association between obesity and the risk of incident gout according to genetic predisposition in two large US cohorts over >32 years, stratified by sex.
Methods: We investigated the joint effects of obesity and genetic predisposition on the future risk of incident gout in 18,247 women in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) over 34 years and 10,899 men in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study (HPFS) over 32 years. We derived a genetic risk score (GRS) using 114 serum urate single nucleotide polymorphisms from the latest GWAS (Tin), with higher GRS indicating higher genetic predisposition for hyperuricemia. We determined gene-body mass index (BMI) interactions among men and women separately. We also calculated the population attributable risk (PAR) for excess weight according to GRS stratum.
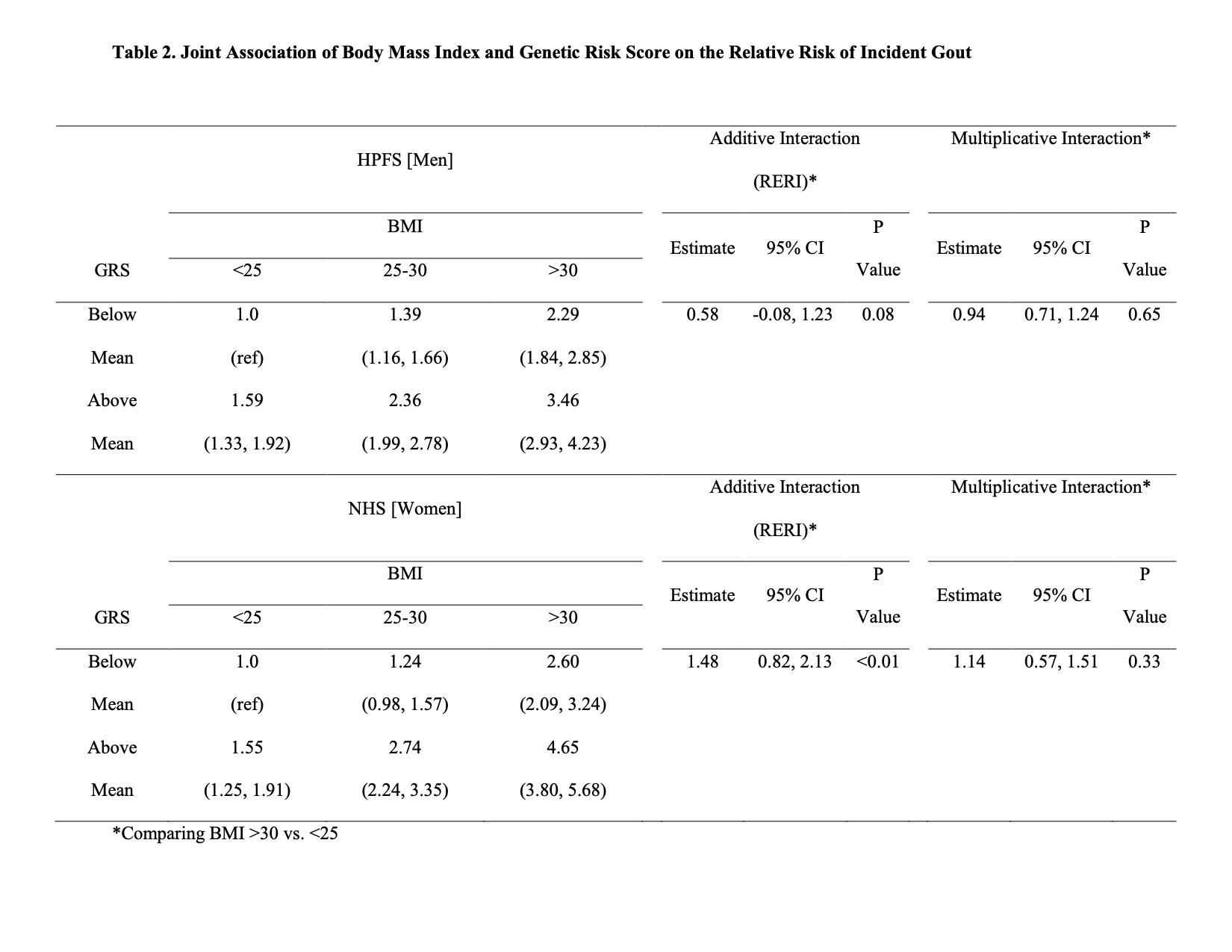
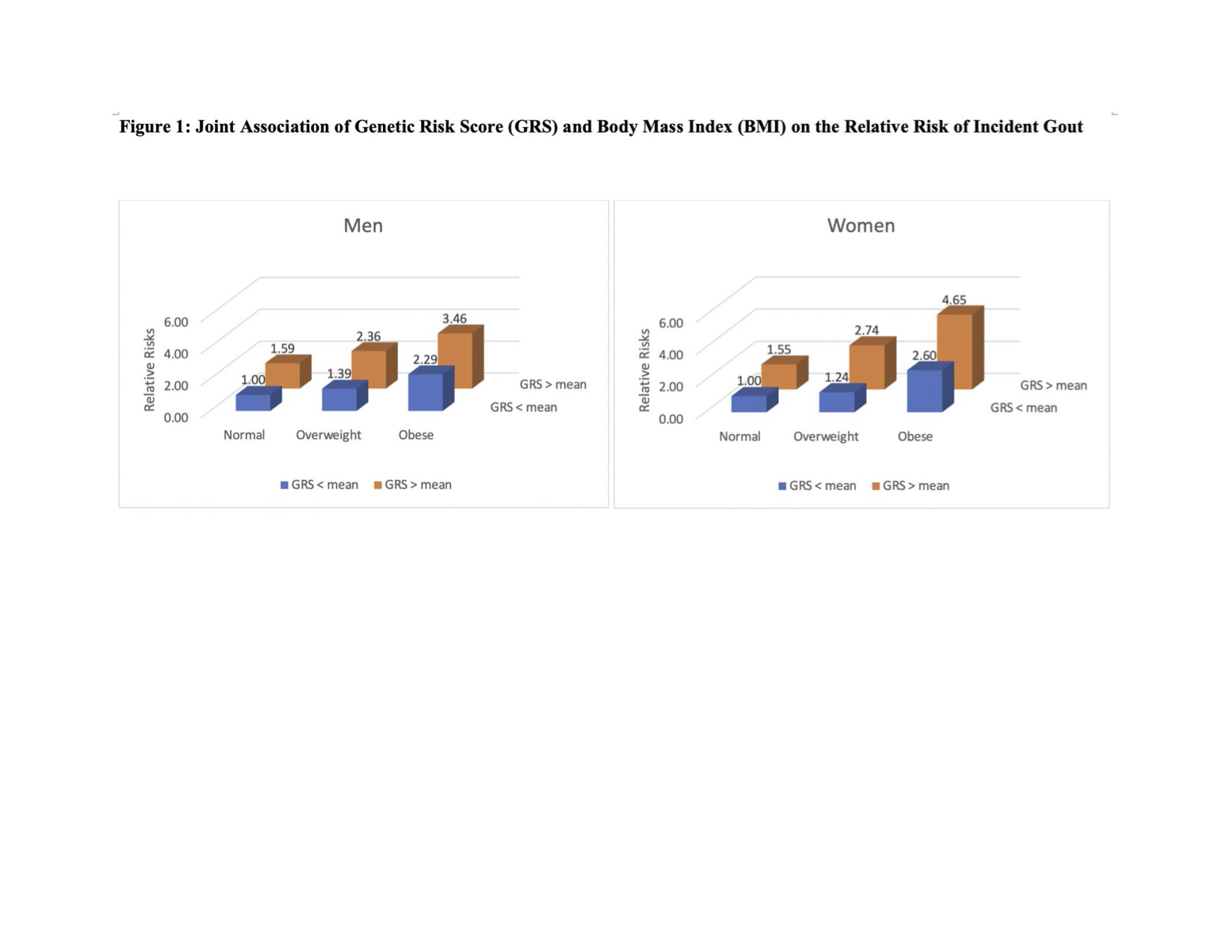
Results: We ascertained 1361 incident cases of self-reported gout in NHS and 1704 in HPFS. The baseline clinical gout risk factors were similar regardless of genetic predisposition within each cohort (Table 1). Among women, the multivariable relative risks (RR) of gout were 1.0, 1.24 (0.98 to 1.57), and 2.60 (2.09 to 3.24) among those with GRS below the mean and 1.55 (1.25 to 1.91), 2.74 (2.24 to 3.35), and 4.65 (3.80 to 5.68) among those with GRS above the mean for BMI categories < 25, 25-30, and >30, respectively (Figure 1 and Table 2). There was significant additive interaction with rate difference (RD) between BMI >30 relative to BMI ≤25 being 3.94 and 1.70/1000 person-years (PY) for GRS above and below the mean, respectively, resulting in relative excess risk due to interaction (RERI) of 1.48 (95% CI, 0.82 to 2.13) (p< 0.01). The results for men were similar in that the RR of excess weight appeared larger among men with GRS above the mean than below the mean (Figure 1 and Table 2); there was a similar trend, with a RD of 7.57 and 5.01/1000 PY for GRS above and below the mean, respectively, resulting in RERI of 0.58 (95% CI, -0.08 to 1.23) (p=0.08). Among women, excess weight accounted for a larger proportion of gout cases among those with GRS above the mean (PAR 48.5%, 95% CI, 38.8 to 55.9) compared to those with GRS below the mean (PAR 29.0%, 95% CI, 10.5 to 42.1). The PARs for men were similar within GRS strata (31.6% and 29.7%, respectively).
Conclusion: In these large prospective studies of men and women, we found a significant interaction between obesity and genetic predisposition among women, and a trend towards this in men. Maintaining healthy weight is an important gout prevention strategy, particularly among those with underlying genetic risk.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yokose C, McCormick N, Lu N, Joshi A, Choi H. Does Obesity Affect Gout Risk Differently Among Genetically Predisposed Individuals?: Sex-Specific Prospective Cohort Study Findings over >32 Years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-obesity-affect-gout-risk-differently-among-genetically-predisposed-individuals-sex-specific-prospective-cohort-study-findings-over-32-years/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-obesity-affect-gout-risk-differently-among-genetically-predisposed-individuals-sex-specific-prospective-cohort-study-findings-over-32-years/