Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Whilst arthritis in other affected joints and back pain is known to lead to worse outcomes following total hip replacement surgery, these risk factors have not previously been operationalized as a musculoskeletal morbidity profile. The aim of this study was to measure the influence of other joints and spine (in four musculoskeletal morbidity grades) on the 1-year outcome of primary hip replacement.
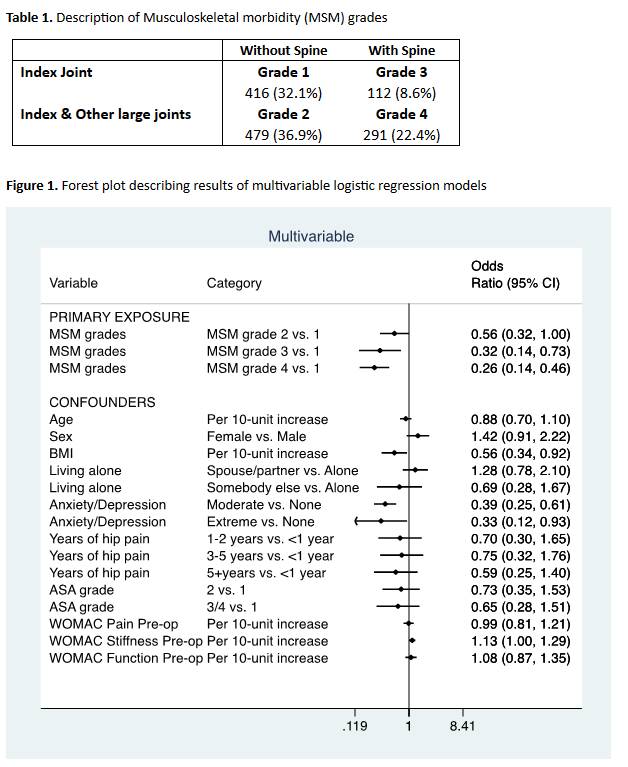
Methods: The European Collaborative Database of Cost and Practice Patterns of Total Hip Replacement study (EUROHIP) consists of 1,327 patients receiving primary THR for osteoarthritis (OA) across 20 European orthopedic centers. The primary outcome was whether or not a patient responded to THR at 12-months as measured by the relative effect per patient (REPP score), calculated for each patient using the total WOMAC score. The primary predictor of interest was the grade of musculoskeletal morbidity (MSM). The cohort was grouped into four combinations of arthritis based on the index joint, other large joints and spine respectively: MSM grade 1 (single-joint), 2 (multi-joints), 3 (single-joint and spine), 4 (multi-joints and spine) (Table 1). Confounders adjusted for were: age, sex, body mass index, living alone, years of hip pain, ASA grade, anxiety/depression, pre-operative WOMAC subscales.
Results: 845 patients were included for this analysis with complete 12-month follow-up WOMAC scores. The mean age was 65.7 years and 55.2% were female. Increasing MSM grade was associated with worse outcomes of surgery, where the responder rates for THR were: 254 (92.4%) MSM grade 1, 272 (87.2%) MSM grade 2, 46 (80.7%) MSM grade 3, 142 (74.4%) MSM grade 4. This was confirmed in adjusted logistic regression models: MSM grade 4 vs. 1 odds ratio (OR) 0.26 95% confidence interval (CI) (0.14, 0.46); MSM grade 3 vs. 1 OR 0.32 95%CI (0.14, 0.73); MSM grade 2 vs. 1 OR 0.56 95%CI (0.32, 1.00) (Fig.1).
Conclusion: Other joints and spine measured as musculoskeletal morbidity have a strong influence on the 1-year outcome after THR. The effect size was large in comparison to other risk factors. Even so, the majority of patients in MSM grade 4 can still profit from surgery (>75% responder rate).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huber J, Dieppe P, Dreinhoefer K, Günther KP, Ruflin G, Judge A. Does Arthritis in Other Joints and Spine Influence the 1-Year Outcome of Total Hip Replacement? a Prospective European Multicenter Cohort Study Measuring the Influence of Musculoskeletal Morbidity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-arthritis-in-other-joints-and-spine-influence-the-1-year-outcome-of-total-hip-replacement-a-prospective-european-multicenter-cohort-study-measuring-the-influence-of-musculoskeletal-mo/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-arthritis-in-other-joints-and-spine-influence-the-1-year-outcome-of-total-hip-replacement-a-prospective-european-multicenter-cohort-study-measuring-the-influence-of-musculoskeletal-mo/