Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The health assessment questionnaire (HAQ) and multidimensional HAQ (MDHAQ) were developed initially to assess patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The most feasible method to ensure that each RA patient completes an MDHAQ at each visit is for the receptionist to present an MDHAQ to each patient with any diagnosis when registering for the visit, to complete in the waiting area. Data are then available for patients with all diagnoses, providing an opportunity to compare baseline scores and change over 2 months in patients with any rheumatic disease to patients with RA.
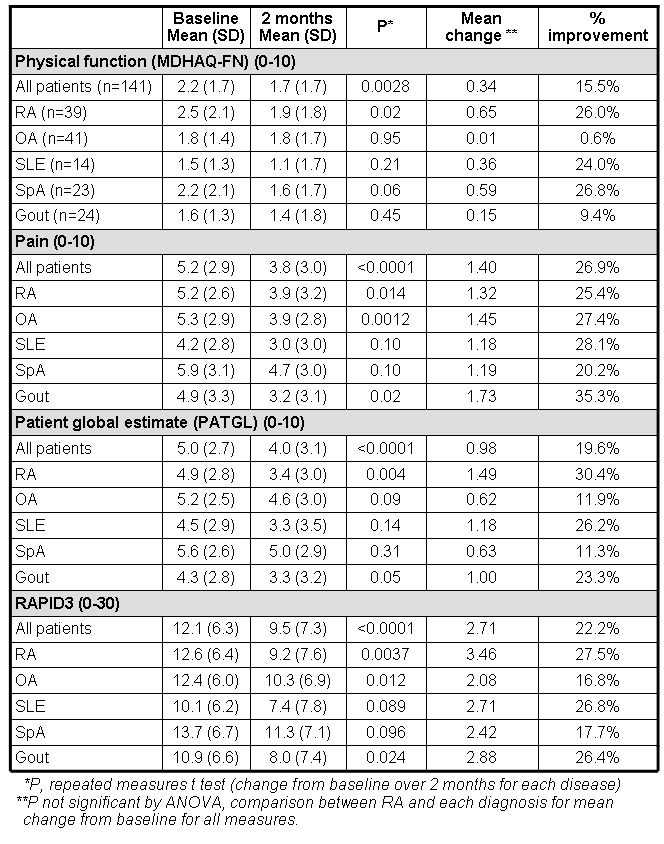
Methods: In the private practice of one rheumatologist, every patient with any diagnosis completes a 2-page MDHAQ at every visit before seeing the doctor. The MDHAQ includes 0-10 scores for physical function (MDHAQ-FN), pain and patient global estimate (PATGL), and a 0-30 score for routine assessment of patient index data (RAPID3), an index of the 3 patient self-report RA Core Data Set measures. Mean scores for individual measures and RAPID3 were compared at first visit and 2 months later for 141 new patients with 5 diagnoses: RA (n=39), osteoarthritis (OA) (n=41), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (n=14), spondyloarthropathy (SpA) (n=23) and gout (n=24). Statistical significance was assessed by t test for change from baseline to 2 months later within each diagnostic group, and by analysis of variance (ANOVA) for change across diagnostic groups.
Results: Mean MDHAQ-FN scores at baseline ranged from 1.5 to 2.5, and from 1.1 to 1.9 two months later, documenting improvement of 9.4–26.8% in all diseases but OA (p <0.05 for all patients and RA). Mean pain scores at baseline ranged from 4.2 to 5.9, and from 3.0 to 4.7 two months later, documenting improvement of 20.2–35.3% in the 5 diagnoses (p <0.05 for all patients, RA, OA and gout). Mean PATGL at baseline ranged from 4.3 to 5.6, and from 3.3 to 5.0 two months later, documenting improvement of 11.2–30.4% (p £0.05 for all patients, RA, OA and gout). RAPID3 scores at baseline ranged from 10.1 to 13.7, and from 7.4 to 11.3 two months later, documenting improvement of 16.8–27.5% (p <0.05 for all patients, RA, OA and gout). No differences for mean change from baseline to 2 months between diagnostic groups were statistically significant.
Conclusion: Disease severity and improvement over 2 months according to MDHAQ-FN, pain, PATGL and RAPID3 scores were similar to RA in OA, SLE, SpA and gout. Physicians appropriately view these 5 diagnoses as distinct, based on differences in their pathophysiology and treatments, emphasizing the need for a knowledgeable physician to establish distinct, accurate diagnoses in individual patients. However, from the patients’ perspective, most rheumatic diseases are viewed more similarly than may be recognized by health professionals, documented by MDHAQ/RAPID3 scores.
Disclosure:
I. Castrejón,
None;
M. J. Bergman,
None;
T. Pincus,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/documentation-of-improvement-over-2-months-in-osteoarthritis-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-spondyloarthropathy-and-gout-similarly-to-rheumatoid-arthritis-according-to-function-pain-patient-global-e/