Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Biomarkers are needed which can accurately predict systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) flare, allowing tailoring of immunosuppressive therapy to minimize disease damage and medication toxicity. Urinary hepcidin-25 levels have been shown to decrease 2 months prior to renal SLE flare and show promise as a biomarker of lupus nephritis flare. This study assessed serum hepcidin-25 levels before, during and after renal and non-renal SLE flares.
Methods: As part of the Ohio SLE Study (OSS), serum and urine were obtained in SLE patients prospectively at every 2 month intervals. We identified 34 renal flare cycles in 21 patients and 22 non renal flare cycles in 17 patients. We measured serum 25 hepcidin levels at baseline, at time of flare and at 2 and 4 month intervals prior to flare and after flare. Renal and non-renal flares were defined and adjudicated by OSS protocol. Serum hepcidin-25 was measured in duplicate by enzyme immune assay kits (Bachem). Descriptive statistics were performed.
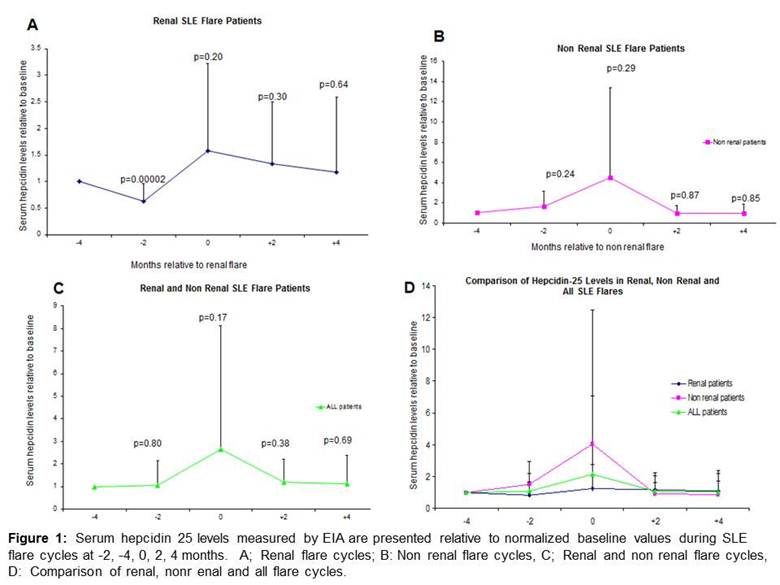
Results: Serum hepcidin-25 levels showed substantial inter-patient variability and were presented relative to normalized baseline levels. As shown in Figure 1, serum hepcidin 25 levels decreased significantly 2 months prior to renal flares but did not decrease prior to non renal flares.
Conclusion: Serum hepcidin-25 levels decrease 2 months prior to renal SLE flare but not prior to non-renal SLE flare. To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that serum hepcidin 25 levels may predict renal SLE flare. These findings need to be confirmed in larger prospective cohorts but support previous evidence that hepcidin 25 may be a biomarker for renal SLE flares.
Disclosure:
A. Friedman,
None;
N. Young,
None;
P. Jensen,
None;
X. Zhang,
None;
W. N. Jarjour,
None;
B. H. Rovin,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
5,
Teva Pharmaceuticals,
2,
Lilly,
5;
D. Birmingham,
None;
L. Hebert,
None;
S. P. Ardoin,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/do-serum-hepcidin-25-levels-predict-sle-renal-or-non-renal-flares/