Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated and Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
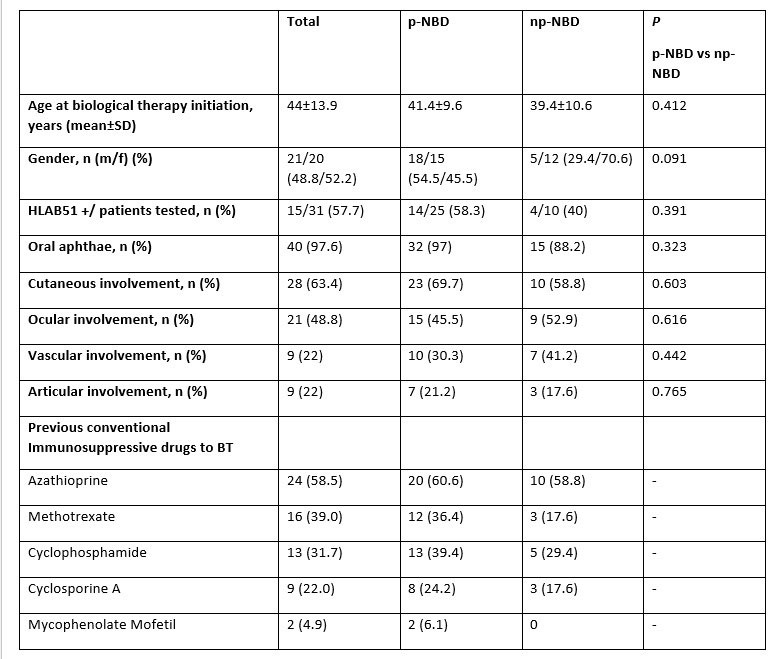
Background/Purpose: Ocular and Neurobehçet’s Disease (NBD) are the most severe manifestations of Behcet’s disease. NBD can be classified as a) primary neural parenchymal lesions, also known as parenchymal NBD (p-NBD) or b) secondary to vascular involvement or non-parenchymal NBD (np-NBD). Response to biologic therapy (BT) in these two refractory subtypes of NBD is unknown. The purpose of the study was to assess efficacy and safety of BT in refractory subtypes of NBD.
Methods: Open-label multicenter study of refractory NBD from 21 different referral National Hospitals. NBD diagnosis was based on the International Consensus Recommendation criteria (4). Efficacy was determined by complete or partial response and no-response. Complete, partial or no response was defined according to the resolution of the neurological syndrome (signs and/or symptoms) after the BT onset.
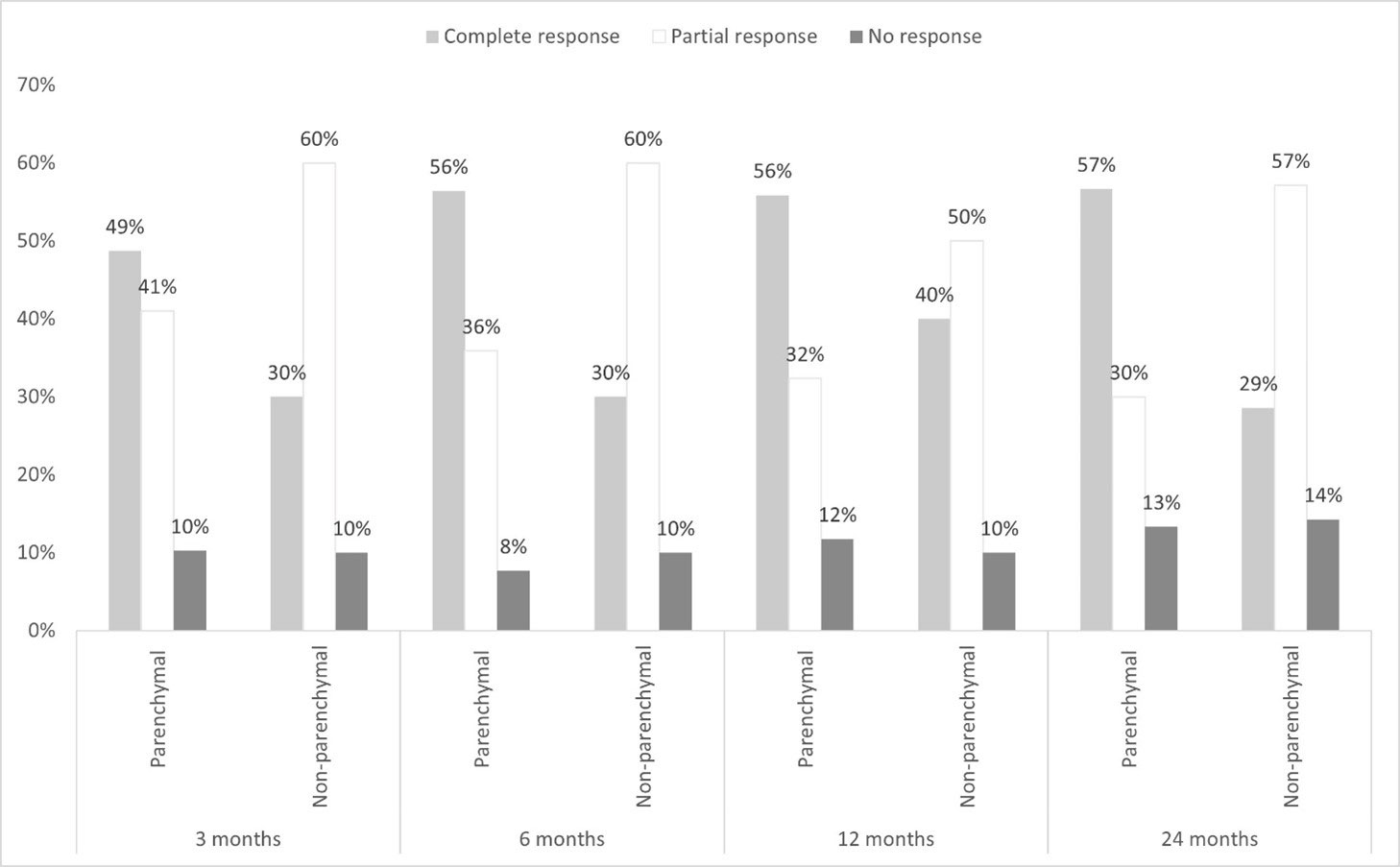
Results: We studied 41 patients (21 women/20 men; mean age: 40.6±10.8 years). NBD was classified as p-NBD (n= 33, 80.5%) and np-NBD (n=17, 41.5%). There were no significant differences in baseline general features and in neurological clinical response in both subgroups (TABLE and FIGURE). The first BT used in p-NBD were Infliximab (IFX) (n=15), Adalimumab (ADA) (n=11), Golimumab (GLM) (n=3), Tocilizumab (TCZ) (n=2) and Etanercept (ETN) (n=2) and in np-NBD were IFX (n=9), ADA (n=6), TCZ (n=1) and ETN (n=1).
After an overall mean follow-up of 57.5±50.9 months BT was switched in 22 patients due to inefficacy (n=16) or Adverse Effects (AE) (n=6) and in 4 cases was definitively discontinued because of complete prolonged remission (n=3) or AE (n=1). AE were observed in 7 (17.1%) patients. Severe AE were observed in 2 cases, one due to demyelinating disease and the other due to pulmonary tuberculosis, both in patients undergoing IFX therapy. The other 6 AE were infusion reaction to IFX (n=1), IFX-induced psoriasis (n=1), IFX-induced acneiform eruption (n=1), infusion reaction to TCZ (n=1), intolerance to IFX and recurrent mild infections (n=1) and erosive lichen planus and bullous impetigo (n=1).
Conclusion: In our series, BT seems equally effective and safe in both refractory p-NBD and np-NBD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Herrero-Morant A, Martín-Varillas J, Castañeda S, Maiz O, Sánchez-Martín J, Ortego N, Raya E, Prior-Español Á, Moriano C, Melero R, Graña-Gil G, Urruticoechea A, Ramos A, Loredo-Martínez M, Salgado-Pérez E, Sivera F, Torre I, Narváez F, Andreu J, Martinez O, Gómez-de la Torre R, Fernandez-Aguado S, Romero Yuste S, Gonzalez-Mazon i, Alvarez Reguera C, Martínez-López D, Hernández J, González-Gay M, Blanco R. Distinct Clinical and Therapeutic Features Between Parenchymal and Non-parenchymal Manifestations in Neurobehçet’s Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/distinct-clinical-and-therapeutic-features-between-parenchymal-and-non-parenchymal-manifestations-in-neurobehcets-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/distinct-clinical-and-therapeutic-features-between-parenchymal-and-non-parenchymal-manifestations-in-neurobehcets-disease/